Example Projectile Motion
- 1. Few Guidelines Please sit with your pen and paper as you go through this power point show. Follow the instructions provided in the slides for maximum learning of the concepts. Lets Start !!!
- 2. Problem Statement A ball is thrown at a certain angle α from base of a incline with an inclination β . The initial speed of the ball is u. The ball hits the inclined surface perpendicularly as it lands back on the incline. Find : The time for which the ball was in air. The distance traversed by the ball along the incline.
- 3. Instructions Try to visualize the problem as the picture in the problem is not provided. Correct visualization of the problem is half the job done. Don’t click on the next slide before you finish the pictorial representation of the problem statement. Click for next to see the picture drawn by you matches with the given picture in the slides.
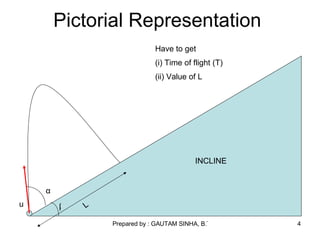
- 4. Pictorial Representation u β α INCLINE L Have to get (i) Time of flight (T) (ii) Value of L
- 5. Instructions Those students who got their pictures right have 25% done with the problem as they know what to do. The main concern is how to do !!! Those students who did not got their pictures right , please go back and read the question again for two-three times and try to visualize it and draw it again.
- 6. Solution The first step to solve a problem of this kind must involve a co-ordinate axis selection. A lot of students I have seen select the co- ordinates as shown on the picture on the next slide.
- 7. Axis Selection u β α INCLINE Y X
- 8. This is not a smart selection The selection of such co ordinates is not a smart selection as the solution will consume a lot of tedious calculations. Why don’t we think something out of the box !!! What if a new type of co-ordinate axis is selected as shown in the picture on the next slide.
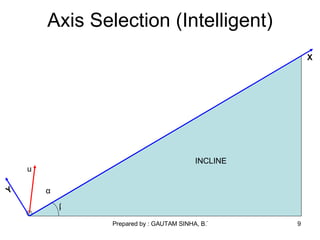
- 9. Axis Selection (Intelligent) u β α INCLINE Y X
- 10. How this is smart !!! Now we will have a look on how this subjective looking question can be solved in few lines like an objective multiple choice question. For Step 2 we will decide the accelerations along the X axis and Y axis.
- 11. Acceleration along the axes u β α INCLINE Y X g β g Cos β g Sin β
- 12. Instruction Always indicate accelerations in the diagram using dotted lines. (Many students never draw it ending up with unclear diagrams) You will never confuse the other lines with the acceleration lines in the picture drawn by you. This will minimize the chance of mistake by you.
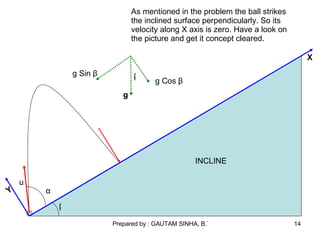
- 13. Data Collected till now As it is very much clear by the picture that Acceleration along X axis = -g Sin β . Acceleration along Y axis = -g Cos β . Initial Velocity along X axis = u Cos α . Initial Velocity along Y axis = u Sin α . Final Velocity along X axis = 0.(How !!!) Please think how the final velocity along Y axis is zero before going on next slide.
- 14. u β α INCLINE Y X g β g Cos β g Sin β As mentioned in the problem the ball strikes the inclined surface perpendicularly. So its velocity along X axis is zero. Have a look on the picture and get it concept cleared.
- 15. Formula to be used !!! v = u + at v 2 – u 2 = 2as Now applying the first formula along the X axis to get the time of flight !!!
- 16. v x = u x + a x t Substituting the values we have, 0 = u Cos α - g Sin β × t or, time of flight (t) = u Cos α / g Sin β Answer for first sub question : Time of Flight = u Cos α / g Sin β Solution Steps
- 17. Instruction Solve this question using the Axis selection as shown on slide number 7. Match the answer as calculated in the previous slide. After solving the question by the above mentioned axis selection , you will realize the value for this smart axis selection. You got your answer in a single line by this method.
- 18. Solution Steps Continued : Now to calculate the value of L we use the second formula along the X axis. v 2 x – u 2 x = 2a x L or, 0 – ( u Cos α ) 2 = 2 (-g Sin β ) L or, L = u 2 Cos 2 α / 2g Sin β . The distance traversed by the ball along the incline = u 2 Cos 2 α / 2g Sin β
- 19. Instructions You can choose the Axis smartly from now onwards for questions on similar lines. Be cautious if you are adopting a new style of problem solving as your concepts must be crystal clear before applying it on some problems Short-Cut helps only if your concepts are clear !!!
- 20. For Future Correspondence For any assistance, feel free to contact me on 9920685139. You can always contact me at www.vidyacenter.com You can write me at [email_address]
- 21. Thank You
















![For Future Correspondence For any assistance, feel free to contact me on 9920685139. You can always contact me at www.vidyacenter.com You can write me at [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/example-projectile-motion-1210059560187500-8/85/Example-Projectile-Motion-20-320.jpg)
