Experiential learning
- 1. START
- 2. ŌĆó What is Experiential Learning? ŌĆó Who is the Proponent of this ABOUT theory? ŌĆó The Stages of its cycle CYCLE ŌĆó Possible Methods to be used in METHODS Experiential Learning Strategy
- 3. ’ü▒Process of making meaning out of a direct experience ’ü▒LEARNING BY DOING CRTITICAL FACTORS ’ü▒ Personalized reflection about an experience ’ü▒ formulation of plans to apply learning to other contexts
- 4. The process of learning and not on the product.
- 5. ’ü▒ ŌĆ£Experiential learning is equivalent to personal change and growthŌĆØ ’ü▒ feels that all human beings have a natural propensity to learn; the role of the teacher is to facilitate such learning.
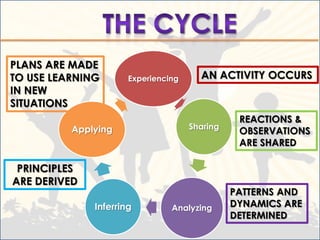
- 6. PLANS ARE MADE TO USE LEARNING Experiencing AN ACTIVITY OCCURS IN NEW SITUATIONS REACTIONS & Applying Sharing OBSERVATIONS ARE SHARED PRINCIPLES ARE DERIVED PATTERNS AND Inferring Analyzing DYNAMICS ARE DETERMINED
- 7. Fieldtrips Narratives Conducting Experiments Simulations Games Storytelling Focused Imaging Field Observations Role Playing Model Building Surveys
- 8. ŌĆó structured activity that occurs outside the classroom. ŌĆó can be a brief observational activity or a longer more sustained investigation or project.
- 9. ŌĆó offer an opportunity for students to get exposure to "real" people and events ŌĆóopportunity to make connections with others. ŌĆóvisit people and places that they are not normally exposed to during the school day.
- 10. Be clear about what Prepare students for the field trip will the learning accomplish Have a debriefing session for students to share their learning when they return to the classroom LIST
- 11. ŌĆóNarrative essays are told from a defined point of view, often the author's, so there is feeling ŌĆó Specific and often sensory details provided to get the reader involved in the elements and sequence of the story.
- 12. relies on personal experiences often in the form of a story Includes all convention of story telling: plot, character, setting, climax, and ending usually filled with details that are carefully selected to explain, support, or enhance the story All of the details relate to the main point the writer is attempting to make.
- 13. ŌĆó The writing in your essay should be lively. 5 LIST
- 14. ŌĆó methodical trial and error procedure carried out with the goal of verifying, falsifying, or establishing the validity of a hypothesis. ŌĆó Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a particular factor is manipulated LIST
- 15. ŌĆó The teacher controls the parameters of this "world" ŌĆó instructional scenarios and uses it to achieve the where the learner is desired instructional results. placed in a "world" defined by the teacher
- 16. Enjoyable, motivating activity Element of reality is compatible with principles of constructivism Enhances appreciation of the more subtle aspects of a concept/principle Promotes critical thinking
- 17. Preparation Time Cost can be an issue Assessment is more complex than some traditional teaching methods
- 18. ŌĆó promote concept attainment through experiential practice ŌĆó effective at helping students understand the nuances of a concept or circumstance ŌĆó Students are often more deeply involved in simulations than other activities
- 19. ŌĆó Ensure that students ŌĆó Try to anticipate understand the questions before procedures before they are asked. beginning ŌĆó Know what you wish to accomplish.
- 20. TIME CONTENT EXPECTATIONS LIST
- 21. ŌĆó Play helps children learn about the world in which they live. ŌĆó It provides the opportunity for children to work out their feelings. ŌĆó Play builds social skills LIST
- 22. ŌĆó conveying of events in words, images and One reason for storytelling sounds, often by is to capture a moment or improvisation or event and immortalize it embellishment Storytelling should have the ability to transport the listener to another time or place LIST
- 23. Imaging enables students to: ŌĆó imaging exercises ŌĆó relax and allow their imaginations nurture and develop to take them on journeys students' creative ŌĆó "experience" situations first hand ŌĆó respond with their senses to the potentials mental images formed. ŌĆó Imaging provides a focus and an opportunity for open- minded exploration of new concepts in all areas of study LIST
- 24. LIST
- 25. In role playing, students act out characters in a predefined "situation". ŌĆó allows students to take risk-free positions by acting out characters in hypothetical situations. ŌĆó can help them understand the range of concerns, values, and positions held by other people. LIST
- 26. ŌĆó involves the creation of models either from kits or from materials and components acquired by the builder. LIST
- 27. ŌĆó The purpose of a survey depends what the survey is used for. ŌĆó It is a method of gathering information from a selection of individuals. LIST
- 28. http://olc.spsd.sk.ca/de/pd/instr/index.html http://www.instructionaldesign.org/theories/experiental- learning.html http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Experiment http://sueatkins1.wordpress.com/2010/10/05/the- importance-of-play/ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Storytelling http://www.enotes.com/lit/discuss/what-purpose- storytelling-119639 http://www.blurtit.com/q392146.html