Fat soluble vitamins
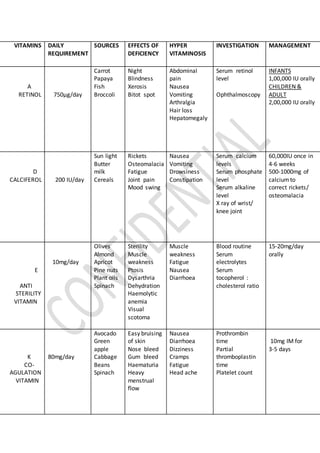
- 1. VITAMINS DAILY REQUIREMENT SOURCES EFFECTS OF DEFICIENCY HYPER VITAMINOSIS INVESTIGATION MANAGEMENT A RETINOL 750µg/day Carrot Papaya Fish Broccoli Night Blindness Xerosis Bitot spot Abdominal pain Nausea Vomiting Arthralgia Hair loss Hepatomegaly Serum retinol level Ophthalmoscopy INFANTS 1,00,000 IU orally CHILDREN & ADULT 2,00,000 IU orally D CALCIFEROL 200 IU/day Sun light Butter milk Cereals Rickets Osteomalacia Fatigue Joint pain Mood swing Nausea Vomiting Drowsiness Constipation Serum calcium levels Serum phosphate level Serum alkaline level X ray of wrist/ knee joint 60,000IU once in 4-6 weeks 500-1000mg of calciumto correct rickets/ osteomalacia E ANTI STERILITY VITAMIN 10mg/day Olives Almond Apricot Pine nuts Plant oils Spinach Sterility Muscle weakness Ptosis Dysarthria Dehydration Haemolytic anemia Visual scotoma Muscle weakness Fatigue Nausea Diarrhoea Blood routine Serum electrolytes Serum tocopherol : cholesterol ratio 15-20mg/day orally K CO- AGULATION VITAMIN 80mg/day Avocado Green apple Cabbage Beans Spinach Easy bruising of skin Nose bleed Gum bleed Haematuria Heavy menstrual flow Nausea Diarrhoea Dizziness Cramps Fatigue Head ache Prothrombin time Partial thromboplastin time Platelet count 10mg IM for 3-5 days