Fermentation Notes aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
- 1. 4.6 Fermentation KEY CONCEPT Fermentation allows the production of a small amount of ATP without oxygen.
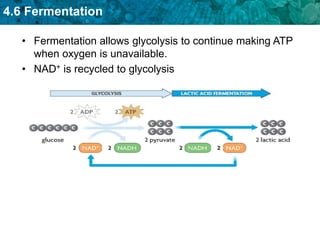
- 2. 4.6 Fermentation Fermentation allows glycolysis to continue. • Fermentation is an anaerobic process. – occurs when oxygen is not available for cellular respiration – does not produce ATP • Fermentation allows glycolysis to continue making ATP when oxygen is unavailable.
- 3. 4.6 Fermentation • Fermentation allows glycolysis to continue making ATP when oxygen is unavailable. • NAD+ is recycled to glycolysis
- 4. 4.6 Fermentation There are 2 types of fermentation • Named for the products produced – Lactic acid fermentation – Alcoholic fermentation
- 5. 4.6 Fermentation • Lactic acid fermentation occurs in muscle cells. – glycolysis splits glucose into two pyruvate molecules – pyruvate and NADH enter fermentation – energy from NADH converts pyruvate into lactic acid – NADH is changed back into NAD+
- 6. 4.6 Fermentation Energy and Exercise Quick Energy 1. Cells contain only enough ATP for a few seconds of intense activity 2. Then cells rely on lactic acid fermentation (can supply for about 90 seconds) 3. Lactic acid build-up causes burning in muscles. Only way to get rid of lactic acid is chemical pathway that requires oxygen (why you breathe heavy after heavy excercise.)
- 7. 4.6 Fermentation Build up of lactic acid in muscles cause burning sensation
- 8. 4.6 Fermentation Fermentation and its products are important in several ways. • Alcoholic fermentation is similar to lactic acid fermentation. – glycolysis splits glucose and the products enter fermentation – energy from NADH is used to split pyruvate into an alcohol and carbon dioxide – NADH is changed back into NAD+ – NAD+ is recycled to glycolysis
- 10. 4.6 Fermentation • Yeast do alcoholic fermentation • Fermentation is used in food production. – yogurt – cheese – bread
- 11. 4.6 Fermentation In cheese making, fungi or bacteria are added to large vats of milk. The microorganisms carry out lactic acid fermentation, converting some of the sugar in the milk to lactic acid.