fertilizer definitions components classify.pptx
- 1. Fertilizer ŌĆō Definition- Components and its classification
- 2. Soil fertility and soil productivity ŌĆ£Soil fertility is the ability of the soil to supply essential plant nutrients during growth period of the plants, without toxic concentration of any nutrientsŌĆØ. ŌĆ£the capacity of the soil to supply nutrient in available form to cropŌĆØ.
- 3. Soil fertility and soil productivity ŌĆ£Soil productivity is the ability of the soil to produce a particular crop or sequence of crops under specified management systemŌĆØ All productive soils are fertile but all fertile soils need not be productiveŌĆØ
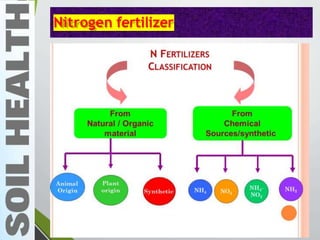
- 4. Fertilizer ŌĆó Fertilizer is any material of natural or synthetic origin added to the soil to supply one or more plant nutrients ŌĆó Usually fertilizers are inorganic in nature and most of them are products of different industries. (exceptions are urea and CaCN2 ŌĆō organic fertilizers)
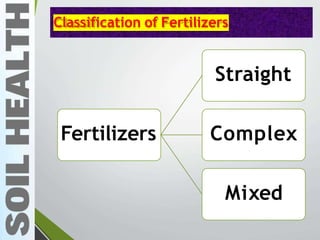
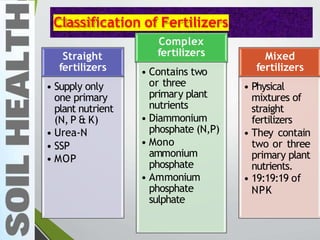
- 6. Classification of Fertilizers Straight fertilizers ŌĆó Supply only one primary plant nutrient (N, P & K) ŌĆó Urea-N ŌĆó SSP ŌĆó MOP Complex fertilizers ŌĆó Contains two or three primary plant nutrients ŌĆó Diammonium phosphate (N,P) ŌĆó Mono ammonium phosphate ŌĆó Ammonium phosphate sulphate Mixed fertilizers ŌĆó Physical mixtures of straight fertilizers ŌĆó They contain two or three primary plant nutrients. ŌĆó 19:19:19 of NPK
- 7. Fertilizer Complete fertilizer ŌĆó Which contains all three major nutrients (N, P & K) Incomplete fertilizer ŌĆó Which lacks any one of the three major nutrients Acid ,Base and Neutral fertilizers Fertilizer Grade ŌĆó Refer to minimum guarantee of the available plant nutrients expressed as a percentage by weight in a fertilizer in terms of total N, P2O5 ,K2O (Complex / Mixed) 12:32:16 grade of NPK complex fertilizer
- 10. Fertilizer
- 11. Phosphatic fertilizers ŌĆó Phosphorus present in the phosphatic fertilizer is usually expressed as phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5) ŌĆó Phosphorus moves very slowly from the point of placement Water soluble Mono- calcium phosphate Citric acid soluble Di-calcium phosphate Citric acid (or) water insoluble Tri-calcium phosphate
- 12. Classification of phosphatic fertilizers Water soluble SingleSuper Phosphate-16-18%- Ca(H2PO4)2.H2O Doublesuper phosphate-32% 2Ca(H2PO4)2.H2O T ripleSuper Phosphate-46- 48% 3Ca(H2PO4)2.H2O Citricacid soluble Dicalcium phosphate- 40% CaHPO4 Basicslag- 13-18% (CaO)3P2O5SiO2 Citric acid insoluble Rock phosphate- 20-40% Bonemeal- 20-25% *Rhenania phosphate- 26-28%
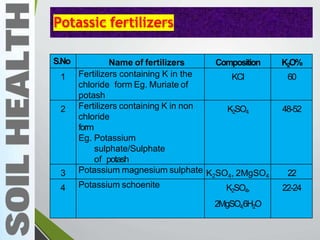
- 13. Potassic fertilizers S.No Name of fertilizers Composition K2O% 1 Fertilizers containing K in the chloride form Eg. Muriate of potash KCl 60 2 Fertilizers containing K in non chloride form Eg. Potassium sulphate/Sulphate of potash K2SO4 48-52 3 Potassium magnesium sulphate K2SO4, 2MgSO4 22 4 Potassium schoenite K2SO4, 2MgSO4.6H2O 22-24