Fetal skull
- 1. FETAL SKULL By: Maj Saminder Malik MSc (N) Obs & Gyn
- 2. INTRODUCTION ïContains delicate brain to prevent any pressure as head passes through birth canal ïLarge in comparison to fetal body and maternal pelvis ïRequire adaptation between fetal skull & maternal true pelvis ïMost difficult part to deliver ïSomewhat compressible and made of pliable tubular bones forming vault
- 4. BONES OF SKULL Total 05 bones in skull 1. Occipital bone (1): at the back of head, at the center of it has occipital protuberance 2. Parietal Bones (2):at the either side of head, ossification center of each is Parietal eminence 3. frontal Bones (2): forms the forehead, center of each is known as frontal eminence. Frontal bones fuses into single by 8 yrs. of age
- 6. SUTURES OF THE SKULL 1. LAMBDOID: shape like Greek letter Lambda, separates occipital bone from two Parietal bones 2. SAGITTAL: longitudinal suture, lies between two parietal bones 3. CORONAL: separates frontal bones from parietal bones 4. FRONTAL: lies between two frontal bones
- 8. AREAS OF SKULL 1. VAULT: large dome shaped wall above an imaginary line drawn between the orbital ridges and the nape of neck 2. BASE: comprised of bones which are firmly united to protect the vital centers in the medulla 3. BROW: extends from anterior fontanels and coronal sutures to the orbital ridges 4. FACE: bounded on one side by the root of nose and supraorbital ridges & other side by the junction of the floor of mouth with neck. (composed of 4small bones, firmly united & compressible)
- 9. FONTANELLES 1. ANTERIOR (BREGMA): 2. POSTERIOR( LAMBDA)
- 10. ANTERIOR FONTANEL (BREGMA) ïanteriorly frontal suture, posteriorly sagittal suture and laterally coronal suture ïDiamond shaped ïMeasures 3-4cm long & 1.5 â 2cm wide ïCloses by 18months (1.5yrs) ïPulsations can be felt through it ïHelp in molding of head, assessing position of head during labor, depressed during dehydration, bulging during increased ICP, collection of CSF from lateral angles
- 11. POSTERIOR FONTANEL (LAMBDA) ïFormed by anteriorly sagittal suture and laterally lambdoid suture ïTriangular in shape ïMeasures 1.2 ËĢ 1.2 ïFloor is membranous ïCloses by 6weeks (1.5 months) ïHelps in assessing position and degree of flexion of head of head
- 13. LANDMARKS 1. BREGMA: anterior fontanel 2. LAMBDA: posterior fontanel 3. VERTEX: bounded anteriorly by Bregma, posteriorly by Lambda and laterally by parietal eminence. Quadrangular in area, considered as a presenting part in labor. 4. BROW: bounded superiorly by bregma & coronal sutures and inferiorly by root of nose & supraorbital ridges. 5. GLABELLA: point between two eyebrows 6. FACE: bounded superiorly by root of nose and supraorbital ridges and inferiorly by the junction of floor of mouth with neck 7. SINCIPUT: area in front of bregma, lined by frontal bone 8. OCCIPUT: between foramen magnum & lambda, lined to occipital bone 9. MENTUM: chin
- 14. DIAMETERS OF SKULL 1. ANTEROPOSTERIOR/ LONGITUDINAL 2. TRANSVERSE
- 16. AP /LONGITUDINAL DIAMETERS AP Diameter Extension Clinical Importance SUBOCCIPITOBREGMATIC From below the occipital protuberance to center of bregma, 9.5cm Complete flexion vertex SUBOCCIPIATOFRONTAL From below the occipital protuberance to center of frontal suture, 10cm Partial flexion vertex OCCIPITOFRONTAL From occipital protuberance to the glabella, 11.5cm Deflexion vertex MENTOVERTICAL From midpoint of chin to highest point on vertex, 14cm Partial extension brow SUBMENTOBREGMATIC From junction of floor of mouth & neck to center of bregma, 11.5cm Complete extension, face SUBMENTOVERTICAL From junction of floor of mouth & neck to highest point of vertex, 9.5 cm Partial extension face
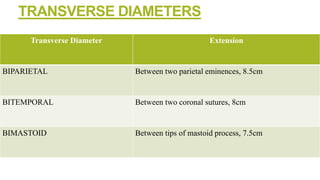
- 18. TRANSVERSE DIAMETERS Transverse Diameter Extension BIPARIETAL Between two parietal eminences, 8.5cm BITEMPORAL Between two coronal sutures, 8cm BIMASTOID Between tips of mastoid process, 7.5cm
- 19. CLINICAL CONDITIONS ïMOLDING OF HEAD ïCAPUT SUCCEDANEUM ïCEPHALHEMATOMA
- 21. MOLDING OF HEAD ïOccurs with descent of fetal head into pelvis to reduce head circumference ïObliteration of sutures ïOverlapping of the bones of vault (frontal bones slip under parietal bones, parietal bones override each other, parietal bones slip under occipital bones) ïReduces the fetal skull diameters by 0.5 -1cm or even more ïDegree: 0 (suture lines separate) +1 (suture lines meet) +2 (suture lines overlap but can be reduced by gentle digital pressure +3 (suture lines overlap irreducible)
- 23. CAPUT SUCCEDANEUM ïDiffuse scalp edema resulting from venous congestion due to prolonged pressure on fetal head by the pelvic bones ïSoft & boggy to touch ïDisappears after birth ïMostly localized in nature ïUsually few mm thick but may be large ïMedico-legal implication: baby was living, difficult labor
- 24. CEPHALHEMATOMA ïSwelling due to bleeding between skull bone & periosteum ïBleeding occurs due to friction between overriding bones and periosteum during molding ïLikely to occur during difficult vaginal labor ïLow prothrombin levels can be contributory ïNot present at birth but appears after 2-3 days ïSwelling is limited by periosteum, so doesn't cross the suture line ïHead appears more red & bruised ïSwelling can increase & may take 6weeks to disappear