Fibre optic
- 1. C B KORE POLYTECHNIC CHIKODI Topic :OPTIC FIBRE COMMUNICATIONS BY: VANDANA DESAI V sem EC SHARVANI MUSANDI V sem EC
- 2. Brief Flow of the Presentation. 1. Introduction 2. What are Optical Fibers? 3. Construction of optical fiber 4. Working principle 5. Fiber optic configuration 6. Working of optical fiber 7. Fiber optics in uses 8. Advantages of Optical fiber 9. Future of fiber optics
- 3. Optical fiber ï§ INTRODUCTION ï§ Fiber optics (optical fibers) are long, thin strands of very pure glass about the diameter of a human hair. They are arranged in bundles called optical cables and used to transmit light signals over long distances. ï§ CAUSES FOR THE CREATION OF THE OPTICAL FIBER----- Manâs HUNGER ï§ Lastly optical fiberâs were invented to satisfy the Manâs hunger for communication
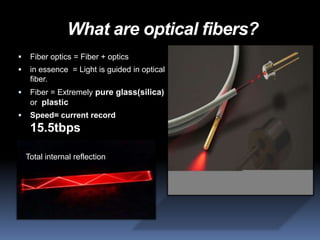
- 4. What are optical fibers? ï§ Fiber optics = Fiber + optics ï§ in essence = Light is guided in optical fiber. ï§ Fiber = Extremely pure glass(silica) or plastic ï§ Speed= current record 15.5tbps Total internal reflection
- 5. Construction of optical fiber ï§ Core-thin glass center of fiber where light travels. ï§ Cladding-outer optical material surrounding the core. ï§ Buffer coating-plastic coating that protects the fiber.
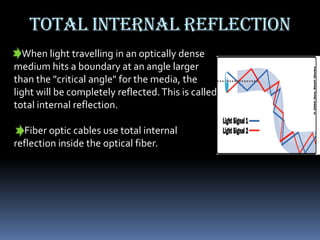
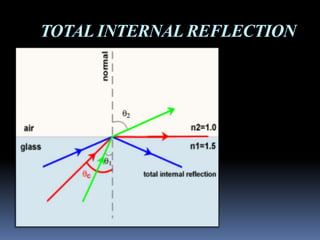
- 6. TOTAL INTERNAL REFLECTION When light travelling in an optically dense medium hits a boundary at an angle larger than the "critical angle" for the media, the light will be completely reflected. This is called total internal reflection. Fiber optic cables use total internal reflection inside the optical fiber.
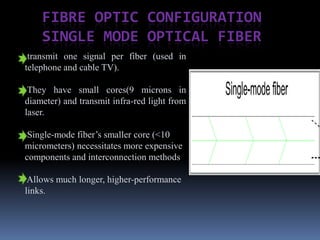
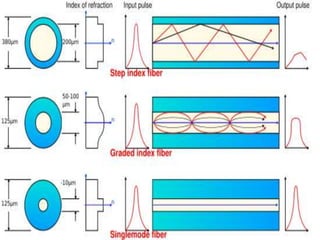
- 8. FIBRE OPTIC CONFIGURATION SINGLE MODE OPTICAL FIBER transmit one signal per fiber (used in telephone and cable TV). They have small cores(9 microns in diameter) and transmit infra-red light from laser. Single-mode fiberâs smaller core (<10 micrometers) necessitates more expensive components and interconnection methods Allows much longer, higher-performance links.
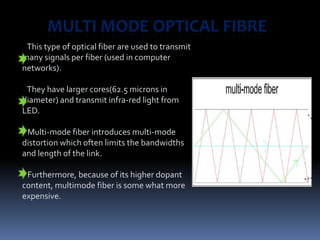
- 9. MULTI MODE OPTICAL FIBRE This type of optical fiber are used to transmit many signals per fiber (used in computer networks). They have larger cores(62.5 microns in diameter) and transmit infra-red light from LED. Multi-mode fiber introduces multi-mode distortion which often limits the bandwidths and length of the link. Furthermore, because of its higher dopant content, multimode fiber is some what more expensive.
- 10. Step Index fibre ï§ The refractive index of core is constant ï§ The refractive index of cladding is constant ï§ The refractive index of cladding is slightly lower than that of core
- 11. Graded index fibre ï§ Refractive index of core decreases smoothly from the centre to the outer edge ï§ Refractive index of cladding is constant
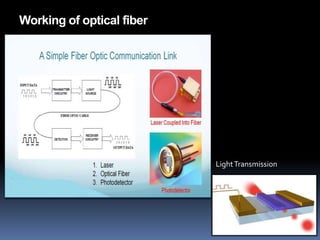
- 13. Working of optical fiber Light Transmission
- 14. Fiber Optics in uses ï§ Communication Systems ï§ Cable Television ï§ Imaging ï§ Additional Uses
- 15. Communication Systems ï§ Networking and telecommunication are two areas where fiber-optic cables are ideal signal conductors. ï§ well-matched for both long-distance and short-distance communication ï§ Individual glass fibers can transmit independent light pulses on multiple wavelengths, which allows each strand to carry simultaneous streams of data on various channels.
- 16. Cable Television ï§ Usage of fiber-optic cables in the cable- television industry began.. ï§ Advantages of using fiber optic in cable television ï§ Fiber-optic cable allows cable providers to offer more customized service
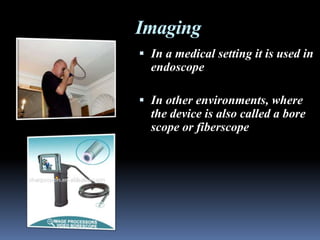
- 17. Imaging ï§ In a medical setting it is used in endoscope ï§ In other environments, where the device is also called a bore scope or fiberscope
- 18. Additional Uses ï§ Computer and Internet technology has improved due to optical fibers' enhanced transmission of digital signals. ï§ fiber-optic signals stay strong longer, requiring less power over time to transmit signals than copper-wire systems.
- 19. ADVANTAGES ïķ Much higher bandwidth ïķ Thousands of channels can be multiplexed together over one strand of fiber ïķ Immunity to noise ïķ Safety ïķ Security ïķ Attenuation ïķ Reliability ïķ Size
- 20. Advantages of optical fiber The optical fiber has following advantages over twisted -pair and coaxial cable. âĒ Resistance to noise âĒ Huge bandwidth âĒ Higher signal carrying capacity
- 21. The Future of Fiber Optic ï§ As with all technology current fiber optics does have a theoretical limit. The idea that transferring data through light was at one time thought to be limitless, however laboratory tests are showing that we are quickly reaching the ceiling that fiber optics offer us. ï§ Small improvements are on the horizon modifying the way signals are encoded, which would carry us a few extra years. ï§ The next big breakthrough is still deep in development though, and little is known what the future holds.
- 22. âĒ Conclusion: This is the greatest discovery that man have done in the field of communication. Modern communication will not be possible without the invention of fiber optics. These small cables touch every facet of our lives, mostly without us even noticing. REFERENCE: Wikipedia â Internet. Freud enrich Craig. How Fiber Optics Work. n.d. Date Retrieved 30 Nov. 2010. http://communication.howstuffworks.com/fiber-optic- communications/fiber-optic2.htm Maddox Nathanial. What Is Fiber Optic Cable Used for? n.d. Date Retrieved 14 Nov. 2010 http://www.ehow.com/about_4895491_what-fiber- optic-cable-used.html Murphy D. 40Gbps internet connection installed in Swede's home. 13 July 2007. Date Retrieved 25 Nov. 2010. http://www.engadget.com/2007/07/13/40gbps-internet-connection-installed- in-swedes-home/ TELUS' Network Technology. n.d. Date Retrieved 25 Nov. 2010. http://about.telus.com/networktechnology/index.html THANK YOU