Field control of compaction and compaction Equipment
- 1. Field control of compaction and compaction Equipment Guided By Prof. Dr. A.K. Chaudhary Sir NIT, Jamshedpur Submitted By Aishwarya Gupta Roll No.- 2020PGCEGE03 Mtech -2nd Semester GeotechnicalEngineering Department of Civil Engineering
- 2. Field Comapaction Control It is very important to undersatand the factor affecting compaction in field and to estimate the co-relation between laboratory and field test Field Compaction Control Depends on a) Placement water content b) Type of Equipment for compation c) Type of compaction based on soil type & degree of compaction desired
- 3. (a) Placement Water Content: ?The water content to be used for compacting the soil in the field is known as placement water content. ?Usually, a placement water content of ¡À2% of OMC obtained from relevant laboratory compaction test is adopted.
- 4. ? For highway embankments of cohesive soils to achieve higher shear strength and lower compressibility we compact it Dry Of Optimum. ? outer shells of earth dams are compacted at 1 to 2.5% less then OMC (dry of optimum) to reduce pore water pressure developement ? the core of an earth dam is compacted at more than the OMC (wet of optimum) to reduce the permeability and achieve safty against cracking
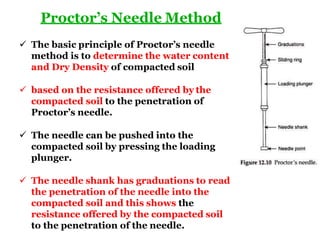
- 5. ? The basic principle of Proctor¡¯s needle method is to determine the water content and Dry Density of compacted soil ? based on the resistance offered by the compacted soil to the penetration of Proctor¡¯s needle. ? The needle can be pushed into the compacted soil by pressing the loading plunger. ? The needle shank has graduations to read the penetration of the needle into the compacted soil and this shows the resistance offered by the compacted soil to the penetration of the needle. Proctor¡¯s Needle Method
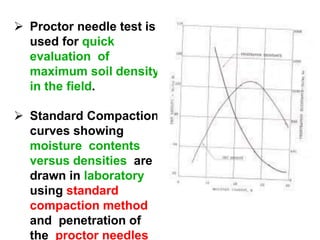
- 6. ? Proctor needle test is used for quick evaluation of maximum soil density in the field. ? Standard Compaction curves showing moisture contents versus densities are drawn in laboratory using standard compaction method and penetration of the proctor needles
- 7. Relative Compaction (R.C.) ?100% R.C.? Typical required R.C. = 90% ~ 95% ? MDD obtained from laboratory IS light or heavy compaction Test ? By deciding relative compaction and maximum dry density in laboratory we can calculate the In situ dry density of the fill. In situ dry density of compacted fill Max. Dry density from lab.comapaction test
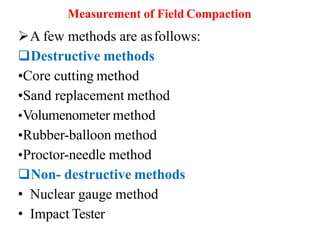
- 8. 8 Measurement of Field Compaction ?A few methods are asfollows: ?Destructive methods ?Core cutting method ?Sand replacement method ?Volumenometer method ?Rubber-balloon method ?Proctor-needle method ?Non- destructive methods ? Nuclear gauge method ? Impact Tester
- 9. 9 Equipment For Field Compaction ?Ordinary compaction in the field is done by rollers. Of the several types of roller used, the most common are ?Smooth-wheelrollers(or smoothdrum rollers) ?pneumatic rubber-tiredrollers ?Sheepfootrollers ?Vibratoryrollers
- 10. Smooth-wheelrollers(or smooth drumrollers) ? This type of roller incorporates a large steel drum at the front and one at the rear. ? It can be used for compaction of both type of soil; cohesive and cohesion less soil. ?It produce contact pressure of 400 ¨C 500 kN/m2 . ? They do not uniform unit produce a weight of compaction when used on thick layers. Fig. Smooth WheelRoller
- 11. Pneumatic rubber-tired rollers ? Pneumatic rubber-tired rollers consist of a heavily loaded wagon with several rows of tires, produce a combination of and kneading pressure action during compaction. ? Pneumatic rollers, which can be used for sandy and clayey soil compaction. ? The contact pressure under the tires may range up to 600- 700 kN/m2. ? They provide 70¨C80% coverage under the wheels. Fig.Pneumaticrubber-tired rollers
- 12. Sheep foot rollers ? Sheepsfoot rollers also known as a tamping roller. Steel drum of sheepsfoot roller consist of many rectangular shaped boots of equal sizes fixed in hexagonal pattern. ? These rollers are most effective in compacting cohesivesoils. ? The contact pressure under the projections may range from 1500 to 7500 kN/m2. ? During compaction in the field, the initial passes compact the lower portion of a lift. Later, the middle andtopof thelift are compacted. Fig.Sheep footrollers 12
- 13. Vibratory rollers ? In vibratory rollers vibration is produced by weights placed eccentrically on a rotating shaft in such a manner that the forces produced by the weights are in a vertical rotating essentially direction. ? Vibratory efficient in rollers are compacting granular soils. ? The weights of vibratory rollers range from 120 to 300 kN. Fig.Vibratoryrollers