Field Teaching Concepts
- 1. Teaching Concepts Tim Field
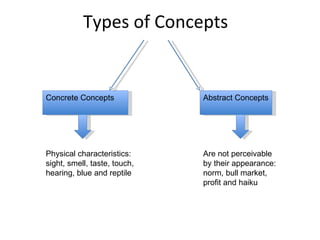
- 2. Types of Concepts Concrete Concepts Abstract Concepts Physical characteristics: sight, smell, taste, touch, hearing, blue and reptile Are not perceivable by their appearance: norm, bull market, profit and haiku
- 3. Generalize Concepts First exposed to a concept must generalize beyond the single instance of the concept. Overgeneralization tends to happen to people after they first learn that concept. People learn how to discriminate between examples of the concepts and non-examples. Learners can undergeneralize concepts. Example of the the °∞child who thinks only black-and-white animals with cow features are °∞cows°±.(pg174)
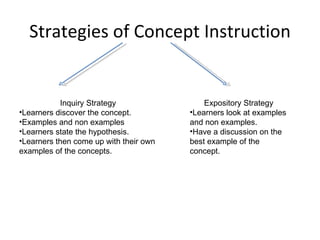
- 4. Strategies of Concept Instruction Inquiry Strategy Learners discover the concept. Examples and non examples Learners state the hypothesis. Learners then come up with their own examples of the concepts. Expository Strategy Learners look at examples and non examples. Have a discussion on the best example of the concept.
- 5. Attribute Isolation Pointing out criterial attributes Low aptitude, few learning strategies, younger students and anxious learners might do better if they are provided visual cues to the attributes.
- 6. Feedback Feedback should be given with an explanation why something is classifies as an example or non-example.
- 7. Strategies Analogies: Helps learners understand and remember concepts, particularly concepts for which the learners have little related prior knowledge. Mnemonics: Used to remember verbal information than in concept learning but there are verbal information components to learning a concept. Imagery: Creating a mental images may be easier with concrete concepts objectives, some learners may find that developing a visual that concretely represents an abstract concept is helpful
- 8. Reference Information was taken from Strategies for Instruction Leading to Concept Learning Chapter 9 Smith and Ragan 2005
- 9. Concepts in Social Studies The concept is Causes and Effects of the Revolutionary War. Students use concept of cause and effect. Understand why groups of people rebel against their government. Students will use cause and effect for many different concepts. How would I teach the Causes and Effects of the Revolutionary War. Preview activity that would be an analogy Students then would make a PowerPoint presentation that would use metaphors to what really happened in history. Students then be given historical figure and re-create a 1776 colonial town meeting which they would debate where to declare independence form Britain. Loyalists and Patriots would try to persuade Neutralists to join their cause. Each side will do research and then create a presentation to persuade the Neutralists. Students would have a threaded discussion/town meeting online. Students would do a share presentation about their side (Patriot/loyalists). Students will be able to make choices and have discussions about the choices they made.