Field work 1 (1)
- 2. Definition of terms used in levelling: A bench mark (B.M) : - It is fixed reference point of known elevation. The line of collimation: - It is the line joining the intersection of cross hairs of the optical centre of the object glass. It is also called the line of sight. An axis of the telescope: - It is a line joining the optical center of the object glass to the center of the eye piece. Foresight: - (Also called a foresight reading) It is a staff (or rod) reading on a point whose elevation is to be determined or on a change point. It is also termed as minus sight. It is the last staff reading denoting the shifting of the instrument. An Intermediate sight (I.S): - It is any other staff reading taken on appoint of unknown elevation from the same set up of the level. All sights taken between the back sight and the fore sight and the foresight are intermediate sights. A Station: - It is a point whose elevation is to be determined. It may be noted that it is a point where the staff is held not the point where they leveled is set up.
- 3. Objective To determine the relative heights of different objects on or below the surface of the earth and to determine the undulation of the ground surface. To prepare a contour map for fixing sites for reservoirs dams, barrages etcâĶ and to fix the alignment of roads, railways, irrigation canals, and so on. To determine the altitudes of different important points on a hill or to know the reduce levels of different points on or below the surface of the earth. To prepare a longitudinal section and cross-section of a project (roads, railways, irrigation cannel, etc) in order to determine the volume of the earth work To prepare a layout map for the water supply, sanitary, or drainage schemes.
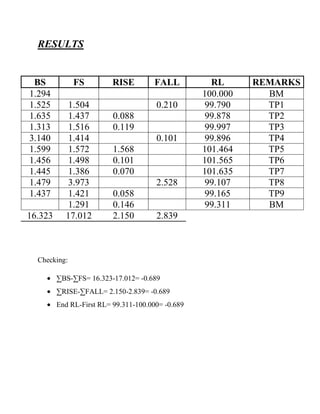
- 4. RESULTS BS 1.294 1.525 1.635 1.313 3.140 1.599 1.456 1.445 1.479 1.437 16.323 FS 1.504 1.437 1.516 1.414 1.572 1.498 1.386 3.973 1.421 1.291 17.012 RISE FALL 0.210 0.088 0.119 0.101 1.568 0.101 0.070 2.528 0.058 0.146 2.150 2.839 Checking: âBS-âFS= 16.323-17.012= -0.689 âRISE-âFALL= 2.150-2.839= -0.689 End RL-First RL= 99.311-100.000= -0.689 RL 100.000 99.790 99.878 99.997 99.896 101.464 101.565 101.635 99.107 99.165 99.311 REMARKS BM TP1 TP2 TP3 TP4 TP5 TP6 TP7 TP8 TP9 BM
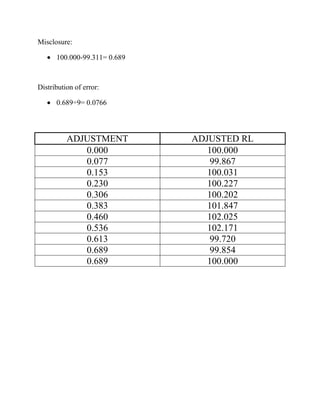
- 5. Misclosure: 100.000-99.311= 0.689 Distribution of error: 0.689÷9= 0.0766 ADJUSTMENT 0.000 0.077 0.153 0.230 0.306 0.383 0.460 0.536 0.613 0.689 0.689 ADJUSTED RL 100.000 99.867 100.031 100.227 100.202 101.847 102.025 102.171 99.720 99.854 100.000
- 6. Discussion 1. At first there was a slight difference between the final RL and the initial RL, this is due to some errors like parallax error or the uneven ground which the equipment is set up on. 2. After that, in order to right the wrong, first we had to do the checkings by finding the difference between the total value of backsight and the total value of foresight, difference between the total value of rise and fall and the difference between the final RL and the initial RL. 3. If the checkings are all the same, then we had to find the misclosure by deducting the actual RL and the measured RL. 4. The next step is to distribute the error by the number of set ups. In this case, there were 9 set ups. For instance, -the first set up: (0.689÷9)x 1 -second set up :(0.689÷9)x2 -third set up :(0.689÷9)x3 5. Since the checkings are negative, the adjustment should be added in to the RL.
- 7. Conclusion Leveling is to determine the difference in height between two points in an area. The main purpose of leveling is to design the highways, railroad, sewers, watersupply system and provides grade lines on the existing topography. Besides that, leveling can also lay out the construction projects according to the planned elevations and enables to calculate the volume of earthworks. Leveling requires equipment such as leveling staff, tripod, auto level meter, staff bubble and measuring tape. Leveling method is now widely used in construction sites. Leveling is an inexpensive, simple and accurate method for measuring height. Besides construction site, leveling are also used for measurements of rivers or lake.
- 8. References 1. McCormack, AJ. "Setting out Auto-levels & Lasers." Pavingexpert.N.p., 1997. Web. 28 Nov. 2013. <http://www.pavingexpert.com/setout04.html>. 2. Wong, KhaiJee. "Levelling."Site Surveying.Taylor's Lakeside University, Subang Jaya. 11 Sept. 2013. Lecture. 3. Nosek, Aaron. "Long Tape." Make Your Mark. Keson, 1968.Web. 28 Nov. 2013. <http://www.keson.com/products/Measuring/Long-Tapes.aspx>. 4. Retrieved from http://www.agriinfo.in/?page=topic&superid=8&topicid=54 5. Retrieved from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Levelling