File io
- 2. Opening a File ŌĆó To read from a file, must use a file handle. ŌĆō by convention, all caps ŌĆó open a file (for reading): ŌĆō open FILE, ŌĆ£myfile.txtŌĆØ; ŌĆó open file for writing: ŌĆō open OUTFILE, ŌĆ£>output.txtŌĆØ; ŌĆó open file for appending: ŌĆō open APPFILE, ŌĆ£>>append.txtŌĆØ;
- 3. Reading from a file ŌĆó open FILE, ŌĆ£myfile.txtŌĆØ; ŌĆó $one_line = <FILE>; ŌĆó @all_lines = <FILE>; ŌĆō @all_lines get all remaining lines from myfile.txt ŌĆō puts each line of file into one member of array ŌĆó remember chomp!
- 4. printing to a file ŌĆó open OUTFILE, ŌĆ£>output.txtŌĆØ; ŌĆó print OUTFILE, ŌĆ£Hello World!nŌĆØ; ŌĆó this can be tedious if all outputs are to same output file. ŌĆó select OUTFILE; ŌĆō make OUTFILE the default file handle for all print statements.
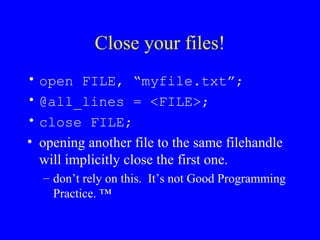
- 5. Close your files! ŌĆó open FILE, ŌĆ£myfile.txtŌĆØ; ŌĆó @all_lines = <FILE>; ŌĆó close FILE; ŌĆó opening another file to the same filehandle will implicitly close the first one. ŌĆō donŌĆÖt rely on this. ItŌĆÖs not Good Programming Practice. Ōäó
- 6. File Test Operators ŌĆó Test to see if something is true about a file ŌĆó full list on page 98 of Prog. Perl. if (-e ŌĆ£myfile.txtŌĆØ){ print ŌĆ£file exists, now openingnŌĆØ; open FILE, myfile.txt; } ŌĆó can operate on filename or already existing filehandle
- 7. Directory manipulation ŌĆó directories can be opened, read, created, deleted, much like files. ŌĆó take care when doing these operations: youŌĆÖre affecting your directory structure ŌĆó many of the functionsŌĆÖ success will depend on what permissions you have on the specified directories.
- 8. open, read, close opendir DIR ŌĆ£public_htmlŌĆØ; $nextfile = readdir DIR; @remaining_files = readdir DIR; closedir DIR;
- 9. Rewind opendir DIR ŌĆ£.ŌĆØ; $firstfile = readdir DIR; $secondfile = readdir DIR; rewinddir DIR; @allfiles = readdir DIR;
- 10. Change, Create, and Delete ŌĆó chdir ’ā© change working directory. ŌĆó mkdir ’ā© create directory (like unix call) ŌĆó rmdir ’ā© remove directory (like unix call) ŌĆō works if and only if directory is empty chdir ŌĆ£public_htmlŌĆØ; mkdir ŌĆ£imagesŌĆØ rmdir ŌĆ£tempŌĆØ;