File Upload
- 1. CSC 2720 Building Web Applications PHP File Upload
- 2. Handling File Uploads in PHP PHP must run with the right settings. You may need to change the PHP configuration file php.ini . A temporary storage directory must exists with the correct permissions. Uploaded files are stored here temporarily; the files may be removed from here when your PHP script finishes processing the HTTP request. The final storage directory must exists with the correct permissions. You have to write codes to move the uploaded files from the temporary directory to another directory.
- 3. Configuring php.ini file_uploads Enable/disable PHP support for file uploads max_input_time Indicates how long, in seconds, a PHP script is allowed to receive input post_max_size Size, in bytes, of the total allowed POST data upload_tmp_dir Indicates where uploaded files should be temporarily stored upload_max_filesize Size, in bytes, of the largest possible file upload allowed
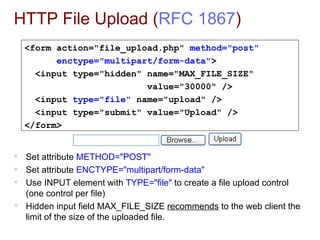
- 4. HTTP File Upload ( RFC 1867 ) Set attribute METHOD="POST" Set attribute ENCTYPE="multipart/form-data" Use INPUT element with TYPE="file" to create a file upload control (one control per file) Hidden input field MAX_FILE_SIZE recommends to the web client the limit of the size of the uploaded file. <form action="file_upload.php" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data" > <input type="hidden" name="MAX_FILE_SIZE" value="30000" /> <input type="file" name="upload" /> <input type="submit" value="Upload" /> </form>
- 5. POST register.jsp HTTP/1.1 Host: hi/iq User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; en-US; rv:1.2) Gecko/20021126 Accept: text/xml,application/xml,application/xhtml+xml,text/html;q=0.9,text/plain;q=0.8, video/x-mng,image/png,image/jpeg,image/gif;q=0.2,text/css,*/*;q=0.1 Accept-Language: en-us, en;q=0.50 Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, compress;q=0.9 Accept-Charset: ISO-8859-1, utf-8;q=0.66, *;q=0.66 Keep-Alive: 300 Connection: keep-alive Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=---------------------------29772313742745 Content-Length: 452 -----------------------------29772313742745 Content-Disposition: form-data; name="name" J.Doe -----------------------------29772313742745 Content-Disposition: form-data; name="email" [email_address] -----------------------------29772313742745 Content-Disposition: form-data; name="file-upload"; filename="test.txt" Content-Type: text/plain test data with some high ascii: ÃÂŋComo estÃÂĄs? -----------------------------29772313742745-- An example of data sent via POST method with enctype="multipart/form-data" (Copied from http://www.devx.com/Java/Article/17679/0/page/2 )
- 6. The $_FILES Array The error code associated with any problem. error The temporary filename of the uploaded file as it was stored on the server. tmp_name The size of the uploaded file in bytes. size The MIME type of the file, as provided by the browser. type The original name of the file (as it was on the user's computer). name Meaning Index
- 7. Processing the uploaded items // "upload" is the name assigned to the input element, as in // <input type="file" name="upload" /> if (isset( $_FILES['upload'] )) { if ( $_FILES['upload']['error'] > 0)) { // File upload fails. See next slide for detailed info about the // meaning of the error code. } else { // e.g., only allows JPEG image files to be uploaded // Note: This is not a complete list of MIME types for JPEG images $allowed = array('image/jpeg', 'image/jpg'); // Continue next page âĶ
- 8. Processing the uploaded items ( âĶ continue) if (in_array( $_FILES['upload']['type'] , $allowed)) { $tmp = $_FILES['upload']['tmp_name'] ; $dst = "C:/uploads/{ $_FILES['upload']['name'] }"; if ( move_upload_file ($tmp, $dst)) { // Success ! } } } // End of else // Manually delete the temporary uploaded file if // it still exists $tmp = $_FILES['upload']['tmp_name'] ; if (file_exists($tmp) && is_file($tmp)) unlink($tmp); } Note: move_uploaded_file() will overwrite an existing file without warning.
- 9. File Upload Error Messages Explained UPLOAD_ERR_OK Value: 0; There is no error, the file uploaded with success. UPLOAD_ERR_INI_SIZE Value: 1; The uploaded file exceeds the upload_max_filesize directive in php.ini . UPLOAD_ERR_FORM_SIZE Value: 2; The uploaded file exceeds the MAX_FILE_SIZE directive that was specified in the HTML form. UPLOAD_ERR_PARTIAL Value: 3; The uploaded file was only partially uploaded. UPLOAD_ERR_NO_FILE Value: 4; No file was uploaded. UPLOAD_ERR_NO_TMP_DIR Value: 6; Missing a temporary folder. Introduced in PHP 4.3.10 and PHP 5.0.3. UPLOAD_ERR_CANT_WRITE Value: 7; Failed to write file to disk. Introduced in PHP 5.1.0. UPLOAD_ERR_EXTENSION Value: 8; File upload stopped by extension. Introduced in PHP 5.2.0. Source: http://www.php.net/manual/en/features.file-upload.errors.php
- 10. References and Related Resources PHP: Filesystem Functions e.g., mkdir() â Create a directory filesie() â Get the size of a file copy() â Copy a file rename() â Rename a file or folder filemtime() â Get file modification time http://www.php.net/manual/en/ref.filesystem.php PHP: Handling File Uploads http://www.php.net/manual/en/features.file-upload.php PHP 6 and MySQL 5 for Dynamic Web Sites: Visual QuickPro Guide (3rd Edition) , by Larry Ullman. Peachpit Press, 2007 (pp 302-15)



![POST register.jsp HTTP/1.1 Host: hi/iq User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; en-US; rv:1.2) Gecko/20021126 Accept: text/xml,application/xml,application/xhtml+xml,text/html;q=0.9,text/plain;q=0.8, video/x-mng,image/png,image/jpeg,image/gif;q=0.2,text/css,*/*;q=0.1 Accept-Language: en-us, en;q=0.50 Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, compress;q=0.9 Accept-Charset: ISO-8859-1, utf-8;q=0.66, *;q=0.66 Keep-Alive: 300 Connection: keep-alive Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=---------------------------29772313742745 Content-Length: 452 -----------------------------29772313742745 Content-Disposition: form-data; name="name" J.Doe -----------------------------29772313742745 Content-Disposition: form-data; name="email" [email_address] -----------------------------29772313742745 Content-Disposition: form-data; name="file-upload"; filename="test.txt" Content-Type: text/plain test data with some high ascii: ÃÂŋComo estÃÂĄs? -----------------------------29772313742745-- An example of data sent via POST method with enctype="multipart/form-data" (Copied from http://www.devx.com/Java/Article/17679/0/page/2 )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/file-upload2580/85/File-Upload-5-320.jpg)

![Processing the uploaded items // "upload" is the name assigned to the input element, as in // <input type="file" name="upload" /> if (isset( $_FILES['upload'] )) { if ( $_FILES['upload']['error'] > 0)) { // File upload fails. See next slide for detailed info about the // meaning of the error code. } else { // e.g., only allows JPEG image files to be uploaded // Note: This is not a complete list of MIME types for JPEG images $allowed = array('image/jpeg', 'image/jpg'); // Continue next page âĶ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/file-upload2580/85/File-Upload-7-320.jpg)
![Processing the uploaded items ( âĶ continue) if (in_array( $_FILES['upload']['type'] , $allowed)) { $tmp = $_FILES['upload']['tmp_name'] ; $dst = "C:/uploads/{ $_FILES['upload']['name'] }"; if ( move_upload_file ($tmp, $dst)) { // Success ! } } } // End of else // Manually delete the temporary uploaded file if // it still exists $tmp = $_FILES['upload']['tmp_name'] ; if (file_exists($tmp) && is_file($tmp)) unlink($tmp); } Note: move_uploaded_file() will overwrite an existing file without warning.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/file-upload2580/85/File-Upload-8-320.jpg)

