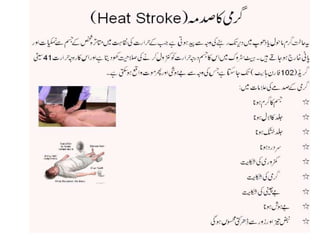
First aid-heat-stroke in Urdu
Download as pptx, pdf5 likes8,063 views
In Urdu first time first aid for heat stroke and care
1 of 6
Downloaded 246 times





Ad
Recommended
Work place safety
Work place safetyKashaan Iftikhar
╠²
The document consists of 20 pages that repeatedly provide instructions to click on a link to download a free green floral PowerPoint template. It also provides a link for more PowerPoint template presentations. The document promotes the download of a single PowerPoint template design over multiple pages.Needle stick injury
Needle stick injuryTheRoyAshish
╠²
This document discusses needle stick injuries, which are percutaneous wounds caused by sharp medical instruments like needles. It aims to educate healthcare workers about needle stick risks, prevention, and management. The document outlines who is most at risk, where injuries typically occur, common devices involved, and best practices like proper disposal and post-exposure procedures. The overall message is that needle stick injuries represent an occupational hazard for healthcare workers, but establishments can significantly reduce risks through proper safety protocols and staff training.First Aid In Urdu for Freacture
First Aid In Urdu for FreactureSyed Shakil Ahmed
╠²
The document is a compilation by Syed Shakil Ahmed of 10 job completion notices (JCNs) for various jobs signed off by Mr. Zafar Iqbal at the JMCH. Each JCN provides information about the job number and is signed by the compiler, Syed Shakil Ahmed.Psychology of Emotions
Psychology of Emotions Dr Shaini Suraj
╠²
The document discusses emotions from a psychological perspective. It defines emotions, describes their components including subjective feelings, physiological changes, and expressions. It explains major theories of emotions and how they relate to emotional adjustment and health. The objectives are to help students and professionals better understand emotions, their nature, dynamics and control to help improve emotional well-being.Man and machine interface
Man and machine interfaceDwarika Bhushan Sharma
╠²
The document outlines essential safety protocols for working around heavy equipment, emphasizing the importance of proper training, equipment maintenance, and accessible certification records. It details specific precautionary measures to prevent accidents and ensure operator awareness, including alerts for movements and the necessity of machine guarding. Supervision consultants are responsible for verifying compliance with operator and equipment certification before operations can proceed.First Aid in Urdu for Burns
First Aid in Urdu for BurnsSyed Shakil Ahmed
╠²
This document contains 6 entries compiled by Syed Shakil Ahmed for different Job Creation Numbers (JCN) at the Jinnah Medical and Dental College Hospital (JMCH). Each entry lists the JCN followed by the compiler's name and the hospital name.Personal hygiene for kids.pptx
Personal hygiene for kids.pptxBushraMahmah
╠²
The document outlines the importance of personal hygiene, defining it as the practice of keeping the body clean to prevent illness. It includes an engaging science experiment illustrating how germs spread and emphasizes key hygiene practices such as handwashing and tooth brushing. Additionally, it provides tips on when and how to maintain personal hygiene, especially before and after certain activities.First aid and_respiration
First aid and_respiration Adnan Masood
╠²
The document is a guide on first aid and respiration, detailing various topics such as shock, skin burns, eye injuries, artificial respiration methods, and recovery positions. It includes stages of artificial respiration and instructions for specific emergencies like drowning and fractures. The publication was authored by Adnan Masood and released in July 2012.Site induction uks 2007 2011
Site induction uks 2007 2011Clive Burgess
╠²
The UK Security site induction programme outlines essential safety procedures and rules for personnel on assignment, including required personal protective equipment (PPE) and reporting protocols for accidents. It emphasizes the importance of adhering to site regulations, safety instructions, and maintaining a tidy workspace to prevent accidents and emergencies. Participants are informed about the health and safety responsibilities of both the management and the workers, aiming for a safe working environment with no disabling accidents.Near miss presentation
Near miss presentationKyawKoKo13
╠²
This presentation defines hazards, near misses, and accidents. It explains that a near miss is an undesired event that could have caused harm under different circumstances, while an accident actually causes injury or damage. Reporting and investigating near misses is important to identify causes and remove hazards before an accident occurs. Reducing near misses can predictably reduce accidents. The presentation encourages attendees to report any near misses to their company's health and safety department.How to Increase Near Miss Reporting
How to Increase Near Miss ReportingSteve Wise
╠²
Near miss reporting is low, with less than 20% of incidents typically reported. Reasons for low reporting include fear of punishment, lack of follow up, and belief that near misses are normal. Improving near miss reporting can benefit safety by revealing unsafe conditions and helping prevent injuries. Actions to improve reporting include establishing a reporting system, investigating incidents and taking corrective actions, and ensuring no penalty for reporting. Senior management must also support near miss reporting for it to be successful.Safety Posters
Safety Posters Adnan Masood
╠²
Safety posters provide important safety information and reminders for employees. The manager of QHSE at The Chishtian Logistic, Adnan Masood, oversees safety posters. Contact information is provided should any questions arise regarding safety posters and their messages.A Part 1 Safety Induction
A Part 1 Safety InductionJames McCann
╠²
Three key points from the document:
1. Safety is important to prevent accidents in the workplace caused by negligence, poor training, unsafe equipment or behaviors. Most accidents follow a pattern of lack of management controls, unsafe acts or conditions, and result in losses.
2. Employers and employees have legal duties under health and safety laws to protect workers and others from risks. This includes conducting risk assessments, implementing controls, providing training, and following safe systems of work.
3. Ignoring safety risks and procedures is against the law and can lead to prosecution, fines, injuries or even death for those involved and affected. All workers are responsible for keeping themselves and others safe by raising concerns and following safety rules.Defensive Driving Safety Training
Defensive Driving Safety TrainingGaurav Singh Rajput
╠²
This document provides information on defensive driving techniques to help prevent vehicle accidents. It discusses key defensive driving strategies like planning ahead, being observant of others, anticipating errors, and showing consideration for other road users. Statistics on road accidents worldwide are presented. Common causes of accidents like speeding, tailgating, and driving under the influence are examined. The document also outlines driver responsibilities, vehicle safety checks, traffic rules, and steps to take in the event of an accident. The overall goal is to promote safe driving habits and help readers drive defensively to avoid collisions and injuries.Health and safety powerpoint complete (1)
Health and safety powerpoint complete (1)brownjamesa
╠²
This presentation provides an overview of environmental health and safety topics for employees. It begins by explaining the importance of safety training and responsibilities of both employers and employees. It then covers a range of safety issues including vehicle safety, driving hazards, office ergonomics, fire safety, hazardous materials, and more. The document emphasizes that safety is a shared responsibility and provides contact information for the environmental health and safety committee.Behaviour based safety
Behaviour based safetyPrudhvi raj
╠²
This document provides an overview of behavior-based safety. It defines key concepts like activators, behaviors, and consequences using the ABC model of behavior change. Unsafe behaviors, not incidents or injuries, are identified as the root cause of 96% of injuries. The power of consequences on behaviors is emphasized, with positive reinforcement being the most effective at increasing safe behaviors. A behavior-based safety program involves pinpointing critical behaviors, communicating expectations, conducting observations to provide feedback, and using data to reinforce safe behaviors and correct unsafe ones. The goal is to measure and modify behaviors to drive cultural and accident rate improvements over time.General Safety Presentationupdated 04842993 1
General Safety Presentationupdated 04842993 1debandleigh
╠²
The document outlines various workplace safety guidelines and procedures. It discusses the importance of working safely, proper personal protective equipment, emergency evacuation plans, safe operation of equipment like forklifts, identifying and avoiding death zones, lockout/tagout procedures, hazard communication, and medical emergencies. Disciplinary action may result from disregarding safety rules.Letter of recommendation HSE
Letter of recommendation HSELuis Mota
╠²
Brendan O'Neill writes a letter of recommendation for Luis Manuel de Almeida Nunes da Mota for a job opening. O'Neill worked with Mota for over 6 months on the Camster windfarm project in Scotland, where Mota successfully served as an erection supervisor. Mota is a dedicated employee who strives for the highest safety and quality standards with great attention to detail. He is also great at fault finding and resolving erection and installation issues. O'Neill found Mota to be very easy to work with as he is enthusiastic about new challenges and maintains a high level of professionalism. O'Neill highly recommends Mota as an asset to any company.-- Heat Stress -- Training PPT
-- Heat Stress -- Training PPTalutarep1
╠²
The document outlines the dangers and management of heat stress, emphasizing the critical need for prevention and treatment in warm work environments. It details symptoms associated with heat-related illnesses such as heat rash, cramps, exhaustion, and heat stroke, along with their respective treatments. Additionally, it provides guidelines for hydration, clothing, and monitoring coworkers to prevent severe health outcomes.Work At Height
Work At HeightJames McCann
╠²
The document discusses the Work at Height Regulations in the UK. It notes that falls from height are a major cause of workplace fatalities and injuries. The regulations were introduced to improve safety by establishing a clear and consistent framework to manage risks associated with working at height. The regulations require hazards to be identified and risks to be properly assessed, controlled, and mitigated through measures such as proper planning, supervision, safe work equipment selection, inspection, and worker training.Risk assessment
Risk assessmentSahil Sheikh
╠²
This document contains 26 pages of information from a QHSE (Quality, Health, Safety and Environment) department. It identifies various hazards associated with substructure water proofing work, including dust particles, slips/trips, manual handling, chemical spills, short circuits, sharp edges, falls, gas cylinder storage, fires, inhalation of fumes, extreme weather, and provides guidance on dos and don'ts to mitigate the risks from each hazard.Health And Safety Induction
Health And Safety Inductionpauljanicki
╠²
The document outlines employers' and employees' health and safety duties and responsibilities under UK law. It explains that employers must protect employees' health and safety through measures like risk assessments, safety policies, training, and personal protective equipment if needed. Employees must follow safety instructions and report any hazards. Accidents must be reported, and some are legally required to be recorded. The Health and Safety Executive enforces these regulations through inspections and potential penalties.Staff safety hand book
Staff safety hand bookMumtaz A. Khan CMIOSH, IDipNEBOSH
╠²
This document provides an introduction and contents for a health and safety training. The introduction discusses how accidents can cause suffering and how all hazardous situations must be identified and corrected. It emphasizes employees' responsibility to comply with health and safety requirements.
The contents section lists 28 topics that will be covered in the training, including health and safety policies, duties and responsibilities, personal protective equipment, permits to work, first aid, and fire prevention. The training aims to help employees fulfill their obligation to work safely.Construction site safety
Construction site safetyDebajit Roy
╠²
Construction site safety is important to prevent common accidents like falls, collisions, and injuries. Common risks include falling objects, excavation collapses, electrocutions, and falls from ladders or roofs. Proper protective equipment like hard hats, high-visibility vests, safety boots, and harnesses can help prevent injuries when working at heights or with heavy machinery. All workers must follow safety protocols to ensure their own protection and that of others on the jobsite.Heat stress
Heat stressMike Slater
╠²
The document discusses the effects of heat stress on the human body, including various heat-related conditions such as heat stroke, heat exhaustion, and heat cramps, along with their symptoms and physiological responses. It emphasizes the importance of monitoring environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and work rates to prevent adverse health effects. Additionally, it outlines recommendations for controlling heat exposure through acclimatization, engineering controls, and personal protective equipment.Working at-height
Working at-height Reliance
╠²
The document defines work at height as any work performed 1.8 meters or more above ground level, including below ground. Work above 1.8 meters requires a permit and safety checklist. Fall distances increase rapidly with time, emphasizing the need for fall protection like railings, safety harnesses attached to lifelines, and safety nets. Proper planning, equipment, and rescue procedures are required for working at heights.Safety orientation urdu
Safety orientation urduRana Irfan Ali
╠²
This document provides an overview of safety orientation topics, including:
- Defining HSE (health, safety, environment)
- Emphasizing the importance of safety and possible consequences of not following safety protocols
- Discussing personal protective equipment like helmets, shoes, glasses
- Defining near misses and promoting safe work conditions and compliance with relevant acts
- Guidance on specific safety hazards and protocols for excavation work, working at heights, use of chemicals, electricity, tools, cranes, lifting and more
- Promoting clean housekeeping, driving safety, and avoiding horseplay or fighting on site
- Stressing that safety is everyone's responsibility to protect lives and health5S Urdu Training
5S Urdu TrainingFarid Ud Din
╠²
This document outlines a 6 step process for organizing a workspace: 1) Red tag unnecessary items, 2) Restore available space, 3) Reduce inventory, 4) Ensure easy accessibility, 5) Create a feeling of comfort, and 6) Achieve a healthy change in outlook through sorting, setting locations, shining and sweeping, standardizing, and sustaining the new organization system. The overall aim is for teams to work together to organize and maintain their workspace.House keeping in urdu
House keeping in urduFire Protection Association of Pakistan
╠²
Housekeeping and fire safety procedures should be followed to minimize risks. Regular cleaning and waste disposal is important. Flammable materials must be properly stored away from heat sources and ignition points. Smoking restrictions and fire equipment maintenance helps prevent fires.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Site induction uks 2007 2011
Site induction uks 2007 2011Clive Burgess
╠²
The UK Security site induction programme outlines essential safety procedures and rules for personnel on assignment, including required personal protective equipment (PPE) and reporting protocols for accidents. It emphasizes the importance of adhering to site regulations, safety instructions, and maintaining a tidy workspace to prevent accidents and emergencies. Participants are informed about the health and safety responsibilities of both the management and the workers, aiming for a safe working environment with no disabling accidents.Near miss presentation
Near miss presentationKyawKoKo13
╠²
This presentation defines hazards, near misses, and accidents. It explains that a near miss is an undesired event that could have caused harm under different circumstances, while an accident actually causes injury or damage. Reporting and investigating near misses is important to identify causes and remove hazards before an accident occurs. Reducing near misses can predictably reduce accidents. The presentation encourages attendees to report any near misses to their company's health and safety department.How to Increase Near Miss Reporting
How to Increase Near Miss ReportingSteve Wise
╠²
Near miss reporting is low, with less than 20% of incidents typically reported. Reasons for low reporting include fear of punishment, lack of follow up, and belief that near misses are normal. Improving near miss reporting can benefit safety by revealing unsafe conditions and helping prevent injuries. Actions to improve reporting include establishing a reporting system, investigating incidents and taking corrective actions, and ensuring no penalty for reporting. Senior management must also support near miss reporting for it to be successful.Safety Posters
Safety Posters Adnan Masood
╠²
Safety posters provide important safety information and reminders for employees. The manager of QHSE at The Chishtian Logistic, Adnan Masood, oversees safety posters. Contact information is provided should any questions arise regarding safety posters and their messages.A Part 1 Safety Induction
A Part 1 Safety InductionJames McCann
╠²
Three key points from the document:
1. Safety is important to prevent accidents in the workplace caused by negligence, poor training, unsafe equipment or behaviors. Most accidents follow a pattern of lack of management controls, unsafe acts or conditions, and result in losses.
2. Employers and employees have legal duties under health and safety laws to protect workers and others from risks. This includes conducting risk assessments, implementing controls, providing training, and following safe systems of work.
3. Ignoring safety risks and procedures is against the law and can lead to prosecution, fines, injuries or even death for those involved and affected. All workers are responsible for keeping themselves and others safe by raising concerns and following safety rules.Defensive Driving Safety Training
Defensive Driving Safety TrainingGaurav Singh Rajput
╠²
This document provides information on defensive driving techniques to help prevent vehicle accidents. It discusses key defensive driving strategies like planning ahead, being observant of others, anticipating errors, and showing consideration for other road users. Statistics on road accidents worldwide are presented. Common causes of accidents like speeding, tailgating, and driving under the influence are examined. The document also outlines driver responsibilities, vehicle safety checks, traffic rules, and steps to take in the event of an accident. The overall goal is to promote safe driving habits and help readers drive defensively to avoid collisions and injuries.Health and safety powerpoint complete (1)
Health and safety powerpoint complete (1)brownjamesa
╠²
This presentation provides an overview of environmental health and safety topics for employees. It begins by explaining the importance of safety training and responsibilities of both employers and employees. It then covers a range of safety issues including vehicle safety, driving hazards, office ergonomics, fire safety, hazardous materials, and more. The document emphasizes that safety is a shared responsibility and provides contact information for the environmental health and safety committee.Behaviour based safety
Behaviour based safetyPrudhvi raj
╠²
This document provides an overview of behavior-based safety. It defines key concepts like activators, behaviors, and consequences using the ABC model of behavior change. Unsafe behaviors, not incidents or injuries, are identified as the root cause of 96% of injuries. The power of consequences on behaviors is emphasized, with positive reinforcement being the most effective at increasing safe behaviors. A behavior-based safety program involves pinpointing critical behaviors, communicating expectations, conducting observations to provide feedback, and using data to reinforce safe behaviors and correct unsafe ones. The goal is to measure and modify behaviors to drive cultural and accident rate improvements over time.General Safety Presentationupdated 04842993 1
General Safety Presentationupdated 04842993 1debandleigh
╠²
The document outlines various workplace safety guidelines and procedures. It discusses the importance of working safely, proper personal protective equipment, emergency evacuation plans, safe operation of equipment like forklifts, identifying and avoiding death zones, lockout/tagout procedures, hazard communication, and medical emergencies. Disciplinary action may result from disregarding safety rules.Letter of recommendation HSE
Letter of recommendation HSELuis Mota
╠²
Brendan O'Neill writes a letter of recommendation for Luis Manuel de Almeida Nunes da Mota for a job opening. O'Neill worked with Mota for over 6 months on the Camster windfarm project in Scotland, where Mota successfully served as an erection supervisor. Mota is a dedicated employee who strives for the highest safety and quality standards with great attention to detail. He is also great at fault finding and resolving erection and installation issues. O'Neill found Mota to be very easy to work with as he is enthusiastic about new challenges and maintains a high level of professionalism. O'Neill highly recommends Mota as an asset to any company.-- Heat Stress -- Training PPT
-- Heat Stress -- Training PPTalutarep1
╠²
The document outlines the dangers and management of heat stress, emphasizing the critical need for prevention and treatment in warm work environments. It details symptoms associated with heat-related illnesses such as heat rash, cramps, exhaustion, and heat stroke, along with their respective treatments. Additionally, it provides guidelines for hydration, clothing, and monitoring coworkers to prevent severe health outcomes.Work At Height
Work At HeightJames McCann
╠²
The document discusses the Work at Height Regulations in the UK. It notes that falls from height are a major cause of workplace fatalities and injuries. The regulations were introduced to improve safety by establishing a clear and consistent framework to manage risks associated with working at height. The regulations require hazards to be identified and risks to be properly assessed, controlled, and mitigated through measures such as proper planning, supervision, safe work equipment selection, inspection, and worker training.Risk assessment
Risk assessmentSahil Sheikh
╠²
This document contains 26 pages of information from a QHSE (Quality, Health, Safety and Environment) department. It identifies various hazards associated with substructure water proofing work, including dust particles, slips/trips, manual handling, chemical spills, short circuits, sharp edges, falls, gas cylinder storage, fires, inhalation of fumes, extreme weather, and provides guidance on dos and don'ts to mitigate the risks from each hazard.Health And Safety Induction
Health And Safety Inductionpauljanicki
╠²
The document outlines employers' and employees' health and safety duties and responsibilities under UK law. It explains that employers must protect employees' health and safety through measures like risk assessments, safety policies, training, and personal protective equipment if needed. Employees must follow safety instructions and report any hazards. Accidents must be reported, and some are legally required to be recorded. The Health and Safety Executive enforces these regulations through inspections and potential penalties.Staff safety hand book
Staff safety hand bookMumtaz A. Khan CMIOSH, IDipNEBOSH
╠²
This document provides an introduction and contents for a health and safety training. The introduction discusses how accidents can cause suffering and how all hazardous situations must be identified and corrected. It emphasizes employees' responsibility to comply with health and safety requirements.
The contents section lists 28 topics that will be covered in the training, including health and safety policies, duties and responsibilities, personal protective equipment, permits to work, first aid, and fire prevention. The training aims to help employees fulfill their obligation to work safely.Construction site safety
Construction site safetyDebajit Roy
╠²
Construction site safety is important to prevent common accidents like falls, collisions, and injuries. Common risks include falling objects, excavation collapses, electrocutions, and falls from ladders or roofs. Proper protective equipment like hard hats, high-visibility vests, safety boots, and harnesses can help prevent injuries when working at heights or with heavy machinery. All workers must follow safety protocols to ensure their own protection and that of others on the jobsite.Heat stress
Heat stressMike Slater
╠²
The document discusses the effects of heat stress on the human body, including various heat-related conditions such as heat stroke, heat exhaustion, and heat cramps, along with their symptoms and physiological responses. It emphasizes the importance of monitoring environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and work rates to prevent adverse health effects. Additionally, it outlines recommendations for controlling heat exposure through acclimatization, engineering controls, and personal protective equipment.Working at-height
Working at-height Reliance
╠²
The document defines work at height as any work performed 1.8 meters or more above ground level, including below ground. Work above 1.8 meters requires a permit and safety checklist. Fall distances increase rapidly with time, emphasizing the need for fall protection like railings, safety harnesses attached to lifelines, and safety nets. Proper planning, equipment, and rescue procedures are required for working at heights.Safety orientation urdu
Safety orientation urduRana Irfan Ali
╠²
This document provides an overview of safety orientation topics, including:
- Defining HSE (health, safety, environment)
- Emphasizing the importance of safety and possible consequences of not following safety protocols
- Discussing personal protective equipment like helmets, shoes, glasses
- Defining near misses and promoting safe work conditions and compliance with relevant acts
- Guidance on specific safety hazards and protocols for excavation work, working at heights, use of chemicals, electricity, tools, cranes, lifting and more
- Promoting clean housekeeping, driving safety, and avoiding horseplay or fighting on site
- Stressing that safety is everyone's responsibility to protect lives and healthViewers also liked (13)
5S Urdu Training
5S Urdu TrainingFarid Ud Din
╠²
This document outlines a 6 step process for organizing a workspace: 1) Red tag unnecessary items, 2) Restore available space, 3) Reduce inventory, 4) Ensure easy accessibility, 5) Create a feeling of comfort, and 6) Achieve a healthy change in outlook through sorting, setting locations, shining and sweeping, standardizing, and sustaining the new organization system. The overall aim is for teams to work together to organize and maintain their workspace.House keeping in urdu
House keeping in urduFire Protection Association of Pakistan
╠²
Housekeeping and fire safety procedures should be followed to minimize risks. Regular cleaning and waste disposal is important. Flammable materials must be properly stored away from heat sources and ignition points. Smoking restrictions and fire equipment maintenance helps prevent fires.Heat stroke
Heat strokeMahmoud Ahmad
╠²
Heat stroke occurs when the body's temperature regulation system fails and body temperature rises to dangerous levels. It represents a failure of the body's ability to maintain thermoregulatory homeostasis. Symptoms include headache, nausea, confusion and loss of consciousness. Treatment involves rapid cooling of the body, typically using evaporative cooling techniques, to lower the core temperature and prevent irreversible organ damage. Aggressive rehydration and treatment of complications such as seizures, arrhythmias or hypotension are also important for management. Rapid cooling is crucial to improving outcomes in heat stroke patients.Heat Stroke
Heat Stroke Muhammad Asim Rana
╠²
The document discusses heat-related illnesses, specifically heat stroke, which occurs when the body's core temperature exceeds 40┬░C, leading to central nervous system dysfunction. It highlights the classification of heat stroke into classic and exertional types, the populations at risk, clinical features, diagnosis, emergency management strategies including cooling methods, and potential complications. Prevention tips emphasize proper hydration, clothing choices, and cooling measures during physical activity in high temperatures.Blunt traumatic injury of the innominate artery resulting in a stroke ŌĆō A rar...
Blunt traumatic injury of the innominate artery resulting in a stroke ŌĆō A rar...Apollo Hospitals
╠²
This document reports a rare case of blunt traumatic injury of the innominate artery resulting in an ischemic stroke in a 20-year-old man involved in a serious traffic accident. Despite initially stable vital signs, the patient developed left hemiparesis, and imaging revealed a pseudoaneurysm and intimal transection of the artery requiring surgical intervention. It emphasizes the need for high suspicion of major vascular injuries in patients with severe upper torso trauma and neurological deficits.Heat stroke by dr nida
Heat stroke by dr nidaWest Medicine Ward
╠²
Din Muhammad, a 65-year old laborer, presented with altered sensorium, fever, and a body temperature of 106 degrees for 1 day. He has a history of hypertension and diabetes. Initial examinations revealed an unconscious patient with abnormal vital signs. Laboratory investigations showed metabolic acidosis and elevated liver enzymes. Imaging showed diffuse brain edema. He was diagnosed with exertional heat stroke due to his profession involving sun exposure.Heat stroke
Heat strokeJamiLa Khan
╠²
This document discusses heat stroke, including its definition, recent statistics in Pakistan, causes, symptoms, vulnerable groups, preventive measures, basic treatment, and the roles of individuals and the government. It aims to educate learners about heat stroke by having them define it, review statistics, list causes, recognize symptoms, identify at-risk groups, discuss prevention, and explain treatment. Key points covered include staying hydrated, avoiding strenuous activity in heat, recognizing symptoms like high fever and seizures, and quickly cooling the body if heat stroke is suspected.Autonomous Maintenance Urdu
Autonomous Maintenance UrduFarid Ud Din
╠²
CLIT is an acronym for Cleaning, Lubrication, Inspection, and Tightening, which are important maintenance procedures. The document outlines each part of the CLIT process, explaining why they are important and describing appropriate methods and tools for cleaning parts, applying lubrication, inspecting for issues, and ensuring proper tightening. It emphasizes the importance of regular CLIT maintenance to keep equipment functioning properly and provides resources like stickers and cards to track maintenance.Planning: Islamic perspective
Planning: Islamic perspectiveazeez luthfullah
╠²
The document discusses the importance of planning (mansooba bandhi) in shaping the future and emphasizes the need for awareness of one's actions and their outcomes based on Islamic principles. It highlights key concepts such as foresight, proper communication, the significance of individual roles within a plan, and setting clear objectives to achieve desired results. The text also underscores the need for continuous questioning and evaluations to ensure that efforts align with the overarching goals defined by faith and societal needs.Guidelines for Managers and Leaders!
Guidelines for Managers and Leaders!MuQeet
╠²
This document is a translated Urdu book titled 'Guidelines for Managers', which consists of historical advice and wills aimed at helping individuals achieve personal progression and success in life. It emphasizes self-assessment, the importance of prioritizing actions, and fostering a connection with God for guidance. The text includes directives for using these guidelines effectively in personal and organizational settings, promoting ethical behavior and mindfulness of one's actions in both the present and the afterlife.LEARN URDU
LEARN URDUiiafl
╠²
The Indian Institute of Arabic and Foreign Languages (IIAFL) focuses on promoting language richness and facilitating cultural exchange through language education, particularly Urdu. Urdu, spoken by around 65 million people globally, is an official language in Pakistan and several Indian states, with a rich literary tradition that emphasizes politeness and delicacy. IIAFL offers a structured curriculum designed to effectively teach modern standard Urdu through three tailored modules, accommodating learners from diverse backgrounds.Heat Stroke
Heat StrokeCrisbert Cualteros
╠²
Heat stroke occurs when the body is unable to regulate its temperature, leading to high core temperatures that can cause direct tissue damage and acute renal failure. There are two main types - classic heat stroke which occurs after prolonged heat exposure in vulnerable individuals like the elderly or chronically ill, and exertional heat stroke which occurs rapidly in unacclimated people exercising in hot environments. Symptoms include a core temperature over 40┬░C and changes in mental status. Treatment involves rapid cooling through ice application and cold water gastric lavage to reduce the core temperature to 39┬░C within 30 minutes, followed by monitoring for complications like rhabdomyolysis or organ damage.Dyslexia & PUFA
Dyslexia & PUFADina m.
╠²
This document discusses dyslexia, including its characteristics, signs, potential causes, and treatments. It summarizes two studies that found fatty acid supplementation, particularly omega-3, improved reading speed, motor skills, and behavior in children with dyslexia or developmental coordination disorder. The document also notes famous historical figures who achieved success despite having dyslexia.Blunt traumatic injury of the innominate artery resulting in a stroke ŌĆō A rar...
Blunt traumatic injury of the innominate artery resulting in a stroke ŌĆō A rar...Apollo Hospitals
╠²
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding and its Management
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding and its ManagementChandrika Kulkarni
╠²
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding and its ManagementCoarse Dispersion, Physical Pharmaceutics
Coarse Dispersion, Physical Pharmaceuticsnishiprakashj
╠²
Its a compilation of unit 3 as per PCI syllabus of B.Pharm IV sem, Subject Physical Pharmaceutics.CEREBRAL PALSY - classification, types and Management
CEREBRAL PALSY - classification, types and ManagementSSIMS & RC
╠²
competency based classes for MBBS students.. Tuberculosis burden , case finding tools and management .pptx
Tuberculosis burden , case finding tools and management .pptxDr. Anu Marhatta
╠²
This presentation is for educational purposes only. Day care surgery anaesthesia and management of complications in postoperative...
Day care surgery anaesthesia and management of complications in postoperative...deepika582423
╠²
Day care From Wheals to Wellness: Transforming Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria Care With...
From Wheals to Wellness: Transforming Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria Care With...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Chair, Michael E. Manning, MD, FAAAAI, FACAAI, discusses chronic spontaneous urticaria in this CME activity titled ŌĆ£From Wheals to Wellness: Transforming Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria Care With Emerging Solutions.ŌĆØ For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at . CME credit will be available until June 11, 2026.whooping cough community health nursing.
whooping cough community health nursing.ASWIN S
╠²
Whooping cough for BSC 5th sem community health nursing..
This includes
Introduction
Definition
Incidence
Incubation period
Causes
Clinical manifestations
Diagnostic evaluation
Treatment
Prevention
Complications
Of whooping cough....Tuberculosis Nepal 2025 National Plan.pptx
Tuberculosis Nepal 2025 National Plan.pptxDr. Anu Marhatta
╠²
The presentation contains preventive therapy, the DOTS program, and the national program of Nepal. This material is intended for educational purposes only.Ratricharya according to ayurveda along with day and night pattern in various...
Ratricharya according to ayurveda along with day and night pattern in various...DR DHARMENDRA BINJHWAR
╠²
This slide are more importents for ayurveda students and teachers because i have mentioned in this slide night time routine in ayurveda the ancient science of India along with day and night pattern in various counteries within in one ppt. thanks for watching i will be greatful for your suggestion and feedback... please like share and suppourtIrradiation to prevent TA-GvHD by Dr. Abrar Kabir Shishir.pptx
Irradiation to prevent TA-GvHD by Dr. Abrar Kabir Shishir.pptxAbrarKabir3
╠²
This presentation discusses the role of irradiation in preventing transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease (TA-GvHD). Covers pathophysiology, risk factors, investigation, prevention strategies, and irradiation procedures. Includes visuals and real-life context from Dhaka Medical College.Navigating the Open Enrollment Period for Medicare Supplement Insurance in Sa...
Navigating the Open Enrollment Period for Medicare Supplement Insurance in Sa...dfwdirectinsurance
╠²
Understanding Medicare options can feel like navigating a maze, especially during the open enrollment period. For residents of Sarasota approaching age 65 or already enrolled in Medicare, this window offers a vital opportunity to secure additional health coverage that helps reduce out-of-pocket costs. If you're planning to enhance your Medicare plan, it's essential to understand the rules, deadlines, and options that apply to Medicare supplement insurance in Sarasota.An interesting case of facial Swelling in an autoimmune rheumatic disease Ahm...
An interesting case of facial Swelling in an autoimmune rheumatic disease Ahm...Internal medicine department, faculty of Medicine Beni-Suef University Egypt
╠²
An interesting case of facial Swelling in an autoimmune rheumatic disease Ahmed Yehia EGYSIR Conference Update on Anesthesia for Pediatric Ophthalmic Surgery.pptx
Update on Anesthesia for Pediatric Ophthalmic Surgery.pptxDr.Umang Sharma
╠²
Based on practices on my hospital and 2021 bja articleDrug use in Peptic Ulcer_A complete review.pptx
Drug use in Peptic Ulcer_A complete review.pptxBaasir Umair Khattak
╠²
Open PPT for detail description: Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
Peptic ulcer disease refers to mucosal erosions equal to or greater than 5 mm in the stomach or proximal duodenum, caused primarily by an imbalance between gastric acid/pepsin secretion and mucosal defense mechanisms. The most common etiologies include Helicobacter pylori infection, chronic use of NSAIDs, and physiological stress.
Classification of Peptic Ulcers
¤ö╣ Based on Location
Gastric Ulcers ŌĆō Occur in the stomach lining.
Duodenal Ulcers ŌĆō Occur in the first part of the small intestine (duodenum).
¤ö╣ Based on Etiology
H. pyloriŌĆōAssociated Ulcers
NSAID-Induced Ulcers
Stress-Related Mucosal Disease (SRMD)
ZollingerŌĆōEllison Syndrome (gastrinoma-related)
CushingŌĆÖs Ulcer (due to intracranial injury)
CurlingŌĆÖs Ulcer (seen in burn patients)
Pharmacological Management
¤ö╣ 1. Acid Suppression Therapy
Class Examples Mechanism
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) Omeprazole, Pantoprazole Irreversibly inhibit H+/K+ ATPase pump
H2-Receptor Antagonists Ranitidine, Famotidine Block histamine-mediated gastric acid secretion
¤ö╣ 2. Mucosal Protective Agents
Class Examples Mechanism
Prostaglandin Analogues Misoprostol Increases mucus & bicarbonate; decreases acid; protects mucosa
Mucosal Coating Agents Sucralfate Forms protective barrier over ulcer site
Bismuth Compounds Bismuth subsalicylate Antimicrobial, mucosal protective, and anti-inflammatory
¤ö╣ 3. Eradication Therapy (for H. pylori)
Combination of:
PPI + Two Antibiotics (e.g., amoxicillin + clarithromycin OR metronidazole + tetracycline)
Duration: 7ŌĆō14 days depending on local guidelines
See BNF regimens above for detailed protocols
¤ö╣ 4. Cytoprotective/Adjunctive Agents
Class Examples Role in PUD
Somatostatin Analogues Octreotide Used in bleeding ulcers; reduces splanchnic blood flow and gastric secretions
Antacids Magnesium hydroxide, Aluminium hydroxide Neutralize gastric acid; provide symptomatic relief
Non-Pharmacologic Measures
Avoid NSAIDs, smoking, alcohol, and spicy foods
Small, frequent meals in symptomatic patients
Stress reduction
Endoscopic therapy in case of bleeding or perforation
Surgical Indications (rarely needed)
Perforated ulcer
Gastric outlet obstruction
Refractory ulcers not responding to medical therapy
Severe bleeding unresponsive to endoscopic management
Ō£ģ Summary
Peptic ulcer disease is primarily driven by H. pylori infection and NSAID use, with duodenal ulcers more common than gastric. Treatment is tailored based on etiology and includes acid suppression, H. pylori eradication, and mucosal protection. Advanced cases may require somatostatin analogues for hemorrhage control or surgery for complications. Prostaglandin analogues like misoprostol are especially valuable in preventing NSAID-induced ulcers.INTERPRETATION OF LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS.pptx
INTERPRETATION OF LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS.pptxEliLawluvi
╠²
THE DOCUMENT SUMMARIZES THE KEY COMPONENTS OF INTERPRETING FULL BLOOD CUNTComprehensive Guide on Adsorption and Partition Chromatography Techniques
Comprehensive Guide on Adsorption and Partition Chromatography TechniquesSajini
╠²
This presentation provides an in-depth overview of chromatography, focusing on adsorption and partition chromatography. It covers the principles, methodologies, types, classification, column preparation, detection methods, advantages, disadvantages, and pharmaceutical applications. A useful resource for pharmacy students and professionals in pharmaceutical chemistry.
COUGH AND THIER DRUGS AND MODE OF ACTION.pptx
COUGH AND THIER DRUGS AND MODE OF ACTION.pptxPackialakshmiP
╠²
COUGH AND THIER DRUGS AND MODE OF ACTIONinferential statistics Part - 1 i.e Parametric tests
inferential statistics Part - 1 i.e Parametric testsBabitha Devu
╠²
This part deals with the Inferential Statistics.
Basic Terminologies.
Parametric Test.
T-test
paired & unpaired T -test
Z testFrom Wheals to Wellness: Transforming Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria Care With...
From Wheals to Wellness: Transforming Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria Care With...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
╠²
Ratricharya according to ayurveda along with day and night pattern in various...
Ratricharya according to ayurveda along with day and night pattern in various...DR DHARMENDRA BINJHWAR
╠²
Navigating the Open Enrollment Period for Medicare Supplement Insurance in Sa...
Navigating the Open Enrollment Period for Medicare Supplement Insurance in Sa...dfwdirectinsurance
╠²
An interesting case of facial Swelling in an autoimmune rheumatic disease Ahm...
An interesting case of facial Swelling in an autoimmune rheumatic disease Ahm...Internal medicine department, faculty of Medicine Beni-Suef University Egypt
╠²
Ad
First aid-heat-stroke in Urdu
- 1. Compile by: Syed Shakil Ahmed: JCN 1 By: Mr. Zafar Iqbal (N.S) JMCH
