First lesson in gst
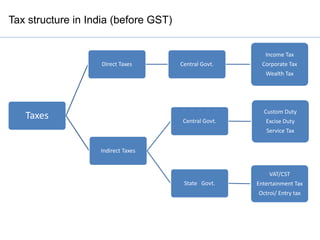
- 2. Tax structure in India (before GST) Taxes Direct Taxes Central Govt. Income Tax Corporate Tax Wealth Tax Indirect Taxes Central Govt. Custom Duty Excise Duty Service Tax State Govt. VAT/CST Entertainment Tax Octroi/ Entry tax
- 3. Share of different taxes collected by GOI in 2015 http://pib.nic.in/newsite/PrintRelease.aspx?relid=136519 These details to understand the different source of income
- 4. Major products on which GST is not applicable ï Petroleum Products ï Alcohol ï Stamp duty ï Custom duty ï Electricity duty ï Natural Gas
- 5. Calculation of duties on imports ï Basic Custom duty - 7.5% and 10% ï Countervailing duty (CVD) - 12.5% ï Education Cess on Custom duty - 2% ï Secondary and Higher Education Cess â 1% ï Special additional duty (SAD) - 4% This gives an understanding how import duties are calculated. Assessable value mean value of goods + freight + insurance + landing cost
- 6. An illustration on cascading effect Total tax loaded on the final product of Rs. 275/- is Rs. 70/- (ie. 10 by A +15 by B +20 by C +25 by D. This due to no input credit at every stage).
- 7. Tax credit system to remove cascading effect
- 8. Goods and Services Tax (GST) What is GST? | Wonderfully Explained by Pallavi Joshi https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yzk5Hsw_SWs Is the GST is one more tax on existing taxes ?
- 9. One nation , One Tax: One nation, one tax means GST in place of CE, Vat, CST, Octroi. We cannot have one rate, because, if you make one rate many goods write now is at zero rated or 5% rated will be charged at higher rate say 10%. Which GOI donât want to do to protect the interest of low income people.
- 10. Goods and Services Tax (GST) means ï It is a tax on supply of Goods or Services or both. ï âSupplyâ includes stock transfer, free samples etc. ï Services means anything other than goods. ï Dual GST- i.e. State GST (SGST) and Central GST (CGST), both will be on supply of goods and services within the state.
- 11. Goods and Services Tax (GST) includes GST â includes â SGST, CGST, IGST and UGST
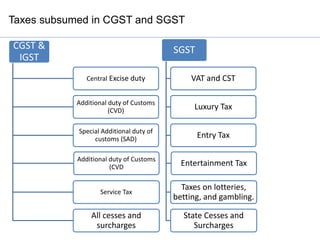
- 12. Taxes subsumed in CGST and SGST CGST & IGST Central Excise duty Additional duty of Customs (CVD) Special Additional duty of customs (SAD) Additional duty of Customs (CVD Service Tax All cesses and surcharges SGST VAT and CST Luxury Tax Entry Tax Entertainment Tax Taxes on lotteries, betting, and gambling. State Cesses and Surcharges
- 13. GST payable on supply ïCGST â Intra â State supply of âgoodsâ / âservicesâ ïSGST (State âAâ) â Intra â State supply of âgoodsâ / âservicesâ ïIGST â Import of âgoodsâ and âservicesâ and Inter-State supply of âgoodsâ/âservicesâ.
- 14. Where the GST is now 3. 01st July 2017 GST came in effect. 2. All States approved 1. 12th April 2017
- 15. GST registration number -15 digits code Assess has to take registration in every state wherever they have place of business.
- 16. Input tax credit under GST Eligible input tax credit under GST ï CGST/IGST/SGST/UGST charged on any supply of goods and services and includes: ï IGST paid on imported goods. ï CGST/IGST/SGST/UGST paid under reverse charge on Goods and Services. ï CGST/IGST/SGST/UGST paid under reverse charge on supply of Goods and Services from un-registered person.
- 17. Input tax credit under GST Input tax credit not eligible under GST ï Motor vehicles and conveyances (only in specified cases eligible). ï Food and beverages, outdoor catering ï Rent a cab, life insurance, health insurance ï Eligible if obligatory for an employer under any law for the time being in force. ï Travel benefits extended to employees on vacation such as leave ï Works contract services for construction of immovable property Other than plant and machinery. ï Goods / services used for construction of immovable property ï Tax paid on composite Scheme. ï Goods and services used for personal consumption. ï Goods lost, stolen, destroyed, written off or disposed by way of free gifts and samples. ï Credit after the expiry of one year from the date of issue of tax invoice.
- 18. D. SRIRANGANADHAM Cost Accountant E-mail: dsriranganadham@gmail.com