Fisheries and Aquaculture Activities in Kurdistan Region
- 1. Fisheries and Aquaculture Activities in Kurdistan Region Firas Abdul Malik
- 2. Introduction: The total population of Kurdistan Region is about 4.9 million. The Kurdistan Region consist of Erbil, Duhok and Sulaimania Governorates with Garmian Administration (KFC, 2014). Fish Activity in Kurdistan region begins in 1960 when entered common carp fish to Dokan dam and Darbandikhan, did not come after that any economically an important experience until 1999, where the Food and Agriculture organization the establishment of two projects for fish one in Erbil and the other in Sulaimania, projects contain a hatchery for artificial reproduction of the species (common carp, silver carp and grass carp ), (Srhnk, 2012) the project contain the number of model fish pond the purpose of these model ponds is for demonstration and training, as well as the Food and Agriculture Organization establishment of 6 model fish pond in the Agriculture College in Duhok governorate purpose of these model ponds is for demonstration and training, as well as the organization2
- 3. Has distributed hand size fish to farmers who are found in has farm small ponds its establishment for the purpose of storing water as well as irrigation ,which is the first step to teach farmers in the Kurdistan region , profession raising fish, which is a new profession on the region (MAWR,2014). Some estimates state that the total quantities of fish production (fisheries and river fishing) reached about 4.300 ton. The production, however, was affected by a number of factors, like fishermen’s non-compliance with fishing prohibitions during breeding season, in addition to fodder shortages, and insufficient monitoring. Available statistics indicate that there are 930 fisheries in the Region, most of which are fish farms. (MA, 2014; FAO,2009; FAO,2012). 3 Introduction:
- 4. Table (1): Kurdistan Population (MP, 2013). Kurdistan Population 2007 Erbil Sulaimania Duhok Total 2019688 1917936 973118 4.910.742 Sources of Water: The Sources of water in Kurdistan include: A. Rainfall and Snow 300 up to 1000 mm / year. B. Surface Water (Rivers, Streams & Springs). (30 BCM) Billion cubic meters…..(12 BCM) %40 outside of Kurdistan…(18 BCM) 60% inside of Kurdistan (Khabur , Greater Zab, Lesser Zab, Sirwan & Awa Spi (Uthaim)) C. Ground water and subsurface water (Deep wells & shallow wells) - around 19000 deep wells. 4
- 5. Figure (1): Average total annual precipitation (MAWR,20153).
- 6. Table (2): Kurdistan Tributaries Production (Annual Flow) (FAO,2012). 6 Rivers Length (KM) Annual flow M3 % outside of Kurdistan % inside of Kurdistan Khabour 160 2.2 58 42 Greater Zab 392 14.3 42 58 Lesser Zab 400 7.07 36 64 Awa Spi 230 0.7 0 100 Sirwan 384 5.86 59 41 Total Amount of Water 30.15 40.2 59.8
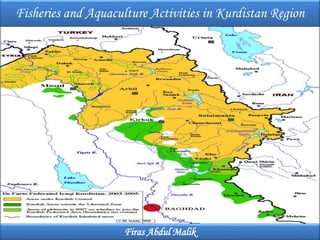
- 7. Duhok Dam Dokan Dam DarbandiKhan Dam Figure (2): Kurdistan Major Dams. (MAWR,2014). 7
- 8. 8 Table (3): Different Fish breeding methods in Duhok Governorate-Northern Kurdistan (KFC,2014) No. Project Type Project Number 1 Ground Ponds 301 2 Concrete Ponds 7 3 Floating Cages Projects 5 4 Floating Cage Number 48 5 Fish Breeders Number 12
- 9. Figure (3): Kurdistan Major Rivers. (FAO,2012). 9
- 10. 1- Cyprinus carpio (common carp) 2- Silurus triostegus (Asian Djirri) 10 Fish Catch: Species caught in Kurdistan:
- 11. 3- Barbus grypus (Shabbout) 4- Barbus esocinus (Bizz) 11 Fish Catch: Species caught in Kurdistan:
- 12. 5- Liza abu (Khishni) 6- Aspias vorax (Shilik) 12 Fish Catch: Species caught in Kurdistan:
- 13. 7- Barbus sharpeyi (Bunni) 8- Cyprinion macrostomus (Bunni Kaper) 13 Fish Catch: Species caught in Kurdistan:
- 14. 9- Barbus luteus (Himri) 10- Mastacembelus mastacembelus (Marmaritc) (Salbouh Abu Sian) 14 Fish Catch: Species caught in Kurdistan:
- 15. 11- Carassius carassius (Shokhatt) 12- Barbus xanthopterus (Gattan) 15 Fish Catch: Species caught in Kurdistan:
- 16. 13- Condrostoma regium (Baloot Muluki) 14- Barbus belayewi (Toueni,Birtein) 16 Fish Catch: Species caught in Kurdistan:
- 17. Kurdistan Region Government fiats /Ministry of Agriculture & Water Resources to support & improve the fisheries resources 1. Distributing (1262) ton of diets for fish breeding projects which contain about (50%) from diet coast-about (753 million Iraqi Dinars). 2. Producing about (654470) fingerlings from Erbil & Sulaimania hatcheries with supported price (25 ID/fingerling). 3. Distributing (48) fish floating cages for (12) fishermen in Duhok governorate in supported coats in (75%) which reached about (186 million Iraqi Dinars) . 4. Release (100.000) fingerlings to Dams. (KFC, 2014). 17
- 18. Gear used in Kurdistan: Fishing gears. (FAO,2012). 1. Gillnets. 2. Hand grenades. 3. Dynamite. 4. Electro fishing. 18 Fish species farmed in Kurdistan 1- Cyprinus carpio 2- Ctenopharyngodon idellus 3- Hypophthalmichthys molitrix 4- Salmon 18
- 19. Fishing vessels: Erbil, Duhok and Sulaimania Governorates with Garmian Administration Gillnets. Table (4): Fishing vessels in Kurdistan Region # Governorate Fishing vessels Total Kind of motors 19 Motorboat Non-Motorized used boat 1 Erbil 150 60 210 Johnson - Yamaha - Mercur - horsepower range from 8 hp to 55 hp 2 Sulaimania 235 78 313 3 Duhok 70 23 93 4 Garmian Administration 165 80 245 Grand total 2855 2285 861 (FAO,2012).
- 20. Locations: Fishing locations in Kurdistan region mostly spread in the dam locations Table (5): Fishing locations (FAO,2012). 20 Aquatic body Governorate and Location Water area / donam Dokan dam Lake Sulaimania 76000 Donam Darbandikhan dam Lake Garmian Administration 36000 Donam Mosul dam Lake Duhok 135000 Donam Khabour Duhok 160 Km length Greater Zab Erbil 392 Km length Lesser Zab Erbil 400 Km length Awa Spi Garmian Administration 230 Km length Sirwan Garmian Administration 384 Km length
- 21. People involved: Most of the fishermen in Kurdistan do not have official licenses and aged between 15-20 years, as well as fishing is not considered important profession in Kurdistan region because of the nature and style of this region where fish is not of the main meals in the region, women do not work in the profession of fishing, most fishermen are illiterate, number of fishermen in Kurdistan governorates (930) fishermen. 21 # Governorate No. of fishermen 1 Erbil 220 2 Sulaimania 335 3 Duhok 104 4 Garmian Administration 271 total 930 Table (6): Number of fishermen in Kurdistan. (FAO,2012).
- 22. Trading/Marketing: There are no private markets in the Kurdistan region to fish sell as it exists in the central and southern governorates, fish sold in small shops within the vegetables & meat markets, There are no minutes statistics on the quantities marketed to the absence of a Statistics, but according to estimates by the Ministry of Agriculture in Kurdistan of inland production of 1500 tons of fish annually (MAWR,2014). Law regulating the exploitation and protection of aquatic life (Law No. 48 of 1976). (FAO,2012). Closed seasons have been implemented for inland fishing in various areas in Kurdistan Region These periods extend from: April 1 to June 15. 22 Policies/legislation affecting activities
- 23. Management initiatives, enforcement, implementing body: There are no private associations and cooperatives of fishermen, the responsible on the implementation and application of these laws and conventions and instructions are the General Directorate of animal resources and Veterinary belonging to the Ministry of Agriculture in cooperation with the Ministry of the Interior in Kurdistan region. (FAO,2012). 23
- 24. Table (6): Number of fish project and water area in Erbil. (FAO,2012). 24
- 25. Table (7): Number of fish project and water area in Sulaimania. (FAO,2012). 25
- 26. Table (8): Number of fish project and water area in Duhok. (FAO,2012). 26
- 27. Table (9): Number of fish project and water area in Garmian. (FAO,2012). 27
- 28. 1.Most fish projects unfortunately depend on well water to be high establishment cost as well as the production cost, because the filling ponds require energy which redoubles the production cost that 50% of these projects only work. 2. The high cost of production because of the mountainous nature. 3. The adoption of the projects on groundwater which may be few nutrients and dissolved oxygen which causes the limited of production and the spread of diseases that are difficult to treatment. 28 Conclusions:
- 29. Recommendations: 1. Better management and utilization of natural resources and the employment of manpower and financial resources for development of aquaculture in the region. 2. Further diversification of the species cultured. 3. Further research on techniques to increase the productivity of a given volume of water. 4. Additional improvement of the balanced fish feeds produced in the region. 5. Developing the fish breeders skills by opening workshops. 6. Establishment of specialized syndicates or associations for fish & fishing. 29
- 30. References: Al-Doori, I. E. (1979). Fundamentals and principles of agricultural policy in Iraq Government Advertising and Printing Corporation, Baghdad. Cooley, J. K. (1992). Middle East water: Power for peace. Middle East Policy 1, no. 2 1-15. FAO, (1998). The state of the world’s plant genetic resources for food and agriculture. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome, Italy. Pp. 510. FAO/Regional Commission for Fisheries. (2009). Report of the Regional Technical Workshop on Aquatic Animal Health. Jeddah, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, 6–10 April 2008. FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Report. No. 876. Rome, FAO. 2009. 119 pp. FAO.(2012) . Aquaculture topics and activities. Aquaculture. In: FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Department [online]. Rome. FAO. Cited www.fao.org/fishery/aquaculture/en. FAO. Fisheries and Aquaculture Department, National Aquaculture Sector Overview - Iraq. 30
- 31. References: (KFS).http://www.kurdistanfoodsecurity.com/.(2014). Kurdistan: Food Security, Food Safety,Agriculture,Water, Livestock. Mhalhal, A. (1967). Agriculture extension, Ministry of Agriculture, Baghdad. Pp. 89. MA.(2014). Ministry of Agriculture General Directorate of Fisheries in Iraq. MP.(2013) Ministry of Planning General Directorate of Statistics in Iraq. MAWR.(2013) Ministry of Agriculture & Water Resources. Opportunities for Investment in Agriculture Sector in Kurdistan Region – Iraq Projects For Investors. Kurdistan Region Government.pdf 19-40pp. MAWR.(2014).Ministry of Agriculture and Water Resources. General Directorate of animal resources and Veterinary in Kurdistan Region. Srhnk ,Nawzad Tawfiq .(2012). Regional Development Strategy for Kurdistan Region 2012-2016. Kurdistan Regional Government. Consultant Engineer .D. G of Strategic Planning.pdf.215pp. 31
- 32. Thanks Firas Abdul Malik Department of Animal Production





























![References:
Al-Doori, I. E. (1979). Fundamentals and principles of agricultural policy in
Iraq Government Advertising and Printing Corporation, Baghdad.
Cooley, J. K. (1992). Middle East water: Power for peace. Middle East Policy
1, no. 2 1-15.
FAO, (1998). The state of the world’s plant genetic resources for food and
agriculture. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United
Nations, Rome, Italy. Pp. 510.
FAO/Regional Commission for Fisheries. (2009). Report of the Regional
Technical Workshop on Aquatic Animal Health. Jeddah, Kingdom of
Saudi Arabia, 6–10 April 2008. FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture
Report. No. 876. Rome, FAO. 2009. 119 pp.
FAO.(2012) . Aquaculture topics and activities. Aquaculture. In: FAO
Fisheries and Aquaculture Department [online]. Rome. FAO. Cited
www.fao.org/fishery/aquaculture/en. FAO. Fisheries and
Aquaculture Department, National Aquaculture Sector Overview -
Iraq. 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/myseminar7-5-2014-140924041359-phpapp01/85/Fisheries-and-Aquaculture-Activities-in-Kurdistan-Region-30-320.jpg)

