Fitness, Exercise and Nutrition
- 1. 1 ŌĆ£RESPIRE: Talk on Nutrition and State of Body and MindŌĆØ Fitness, Exercise and Nutrition Jeremy Floyd L. Pedregosa, EdD Associate Professor Far Eastern University, Manila April 10, 2021 10:30-12:00nn
- 2. 2 Fitness is not a permanent condition.
- 3. 3 Sports (athletes) and COViD19 myocarditis - will lead to cardiac arrest
- 4. 4 ┬¦ as ŌĆśŌĆśthe motivation, confidence, physical competence, knowledge and understanding to value and take responsibility for engagement in physical activities for lifeŌĆÖŌĆÖ (Whitehead, 2013). ┬¦ is much wider than physical education and encompasses all participation in physical activity throughout the lifecourse (Whitehead, 2013). ┬¦ foundation for sports and education policies (Mandigo, et al. , 2009) Sources: ┬¦ Edwards, L. C., Bryant, A. S., Keegan, R. J., Morgan, K., & Jones, A. M. (2017). Definitions, foundations and associations of physical literacy: a systematic review. Sports medicine, 47(1), 113-126. ┬¦ Mandigo, J., Francis, N., Lodewyk, K., & Lopez, R. (2009). Physical literacy for educators. Physical and Health Education Journal, 75(3), 27-30. ┬¦ Whitehead, M. (2013). Definition of physical literacy and clarification of related issues. ICSSPE Bulletin, 65(1.2). Physical activity ŌĆó ŌĆśŌĆśany bodily movement produced by skeletal muscles that requires energy expenditureŌĆÖŌĆÖ (WHO, 2015) Other aspects of life (Edwards, et al, 2017)
- 5. 5 FITNESS (physical) EXERCISE (exercise program) Physical activity Proper diet and nutrition Proper rest for recovery Health-related Fitness: 1. Cardio-respiratory Endurance 2. Muscular Strength 3. Muscluar Endurance 4. Body Composition 5. Flexibility Skills-related Fitness: 1. Agility 2. Speed 3. Reaction Time 4. Coordination 5. Balance 6. Power ŌĆó Limbering Exercise (stretching) ŌĆó Muscle-building Exercises ŌĆó Endurance Exercises 1. Warm-up (10-minutes) 2. Program proper 3. Cooldown ┬¦ Goal ┬¦ Type program ┬¦ Muscle group ┬¦ Order of exercise ┬¦ Starting load - Progression
- 6. 6 ŌĆó Is the minimum length of time for a training program to result in improved fitness and energy Duration ŌĆó Refers to the minimum number of training sessions needed per week to ensure improvements in the desired fitness components and energy systems Frequency ŌĆó Is the excretion level at which training is being performed ŌĆó Usually measured according to heart rate Intensity ŌĆó The body responds to stress caused by physical work and therefore your work out needs to change over time to continue to see benefits Progressive Overload ŌĆó Is the process of replicating the characteristics of physical activity during training ŌĆó 4 categories to consider: muscle groups used, the skills performed, the fitness components used, and the energy system used Specificity Basic Training Principles Training units... Min. of 2-3 units for non-athletes 30 minutes? 1 hour? 3 hours 220 - Age = Max HR High/Vigorous (77%-93% of your max HR) Moderate (64%-76% of your max HR) Cardio? Weigh loss? Leg power? Arms? Core? Gradual - Peak
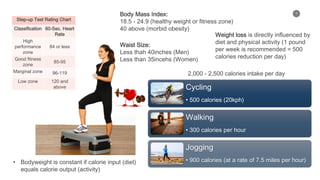
- 7. 7 Step-up Test Rating Chart Classification 60-Sec. Heart Rate High performance zone 84 or less Good fitness zone 85-95 Marginal zone 96-119 Low zone 120 and above Body Mass Index: 18.5 - 24.9 (healthy weight or fitness zone) 40 above (morbid obesity) Waist Size: Less thah 40inches (Men) Less than 35incehs (Women) Weight loss is directly influenced by diet and physical activity (1 pound per week is recommended = 500 calories reduction per day) Cycling ŌĆó 500 calories (20kph) Walking ŌĆó 300 calories per hour Jogging ŌĆó 900 calories (at a rate of 7.5 miles per hour) 2,000 - 2,500 calories intake per day ŌĆó Bodyweight is constant if calorie input (diet) equals calorie output (activity)
- 8. 8 arms, core, back, shoulders
- 9. 9 medicine ball, fitness ball, core exercises, legs exercises
- 10. 10 ladder exercises (footwork & agility), jumping rope (legs), resistance band exercises (muscualr strenght)
- 11. 11 PSYCHOLOGICAL BENEFITS: Physical exercise helps to reduce stress, mental fatique, and anxiety. It provides a sense of pleasure and helps fight against depressions. It improves sleep and increases energy.
- 12. 12 MINERALS ŌĆó contributes towards growth VITAMINS ŌĆó regulates body mechanism PHYTONUTRIENTS ŌĆó support the immune system CARBOHYDRATES ŌĆó provides body with energy LIPIDS/FATS ŌĆó provides stored energy PROTEINS ŌĆó supply matrials for growth and repair of body tissues MACRONUTRIENTS MICRONUTRIENTS WATER ŌĆó 74% the body mass ŌĆó 65-75% of the body volume ŌĆó daily fluid intake of 1.5 liters ŌĆó electrolytes 60-70% carbohydrates 20-25% fats/lipids 10-12% proteins 1,500 calories recommended diet (weight loss) ┬¦ 95 children in the Philippines die from malnutrition (UNICEF). ┬¦ Low immunization and lack of access to clean water and sanitization facilities.
- 13. 13 Challenge: #LSMSiglakas2021 #HealthyHeartMindBodyandSoul #HHMBSChallenge ├śWeight loss challenge (before and after) ├ś 1 pound per week or 4 pounds in a month or; ├ś 2 pounds in a month ŌĆó Biking/Cycling: 120-150 kilometers accummulated distance) ŌĆó Jumping rope (2,021 accumulated counts) ŌĆó Planking (60 seconds, 1 set/straight) ŌĆó Squats & Split Squat - L & R (12 reps, 3 sets in a day) ŌĆó Push-ups (up to 25-30 reps, 1 set/straight)
- 14. 14 THANK YOU! Jeremy Floyd L. Pedregosa jpedregosa@feu.edu.ph References: Family Guide to Health: Visualize, Heal, Prevent (2010). Page One Publishing Dick, Frank W. (2014). Sports Training Principles. 6th Edition. Blomsbury Publishing