Fluroquinolones 2
- 1. DR.VIJAY NAGDEV H.O. MEDICAL UNIT-I CHANDKA MEDICAL COLLEGE LARKANA
- 2. Background In 1962 nalidixic acid was discovered by George lesher during synthesis of chloroquine and was named as quinolone Fluoroquinolones were derived by adding flourine atom in nalidixic acid.
- 3. Earlier quinolones were useful only for treatment of UTI. Fluorinated derivatives achieve bactericidal levels in blood and tissues so they have improved antibacterial spectrum.
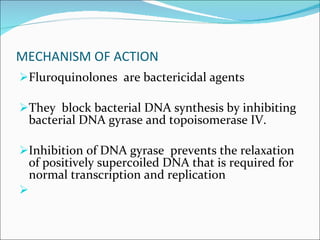
- 4. MECHANISM OF ACTION Fluroquinolones are bactericidal agents They block bacterial DNA synthesis by inhibiting bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. Inhibition of DNA gyrase prevents the relaxation of positively supercoiled DNA that is required for normal transcription and replication
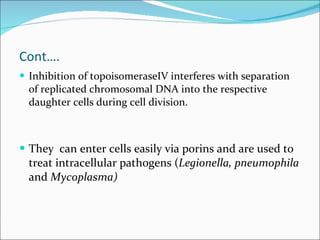
- 5. Cont…. Inhibition of topoisomeraseIV interferes with separation of replicated chromosomal DNA into the respective daughter cells during cell division. They can enter cells easily via porins and are used to treat intracellular pathogens ( Legionella, pneumophila and Mycoplasma)
- 6. RESISTANCE Resistance is due to one or more point mutations in the quinolone binding region of the target enzyme OR to a change in the permeability of the organism Resistance to one FQL confers cross resistance to all members of the class.
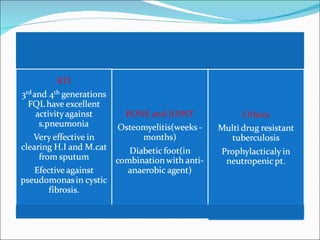
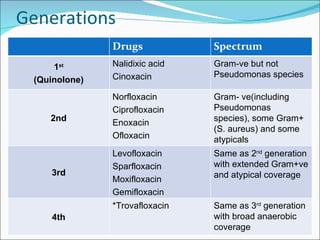
- 8. Generations Drugs Spectrum 1 st (Quinolone) Nalidixic acid Cinoxacin Gram-ve but not Pseudomonas species 2nd Norfloxacin Ciprofloxacin Enoxacin Ofloxacin Gram- ve(including Pseudomonas species), some Gram+ (S. aureus) and some atypicals 3rd Levofloxacin Sparfloxacin Moxifloxacin Gemifloxacin Same as 2 nd generation with extended Gram+ve and atypical coverage 4th *Trovafloxacin Same as 3 rd generation with broad anaerobic coverage
- 9. Pharmacokinectics Well absorbed orally with bioavailability 80-95% almost equal to i.v. Half life 3-10 hours Oral absorption impaired by divalent cations(Antacids containg Mg, Ca,or AL ). Most of fluoroquinolones eleminated by renal mechanism so adjustment required in patients with creatinine clearance <50 ml/min. Limited CSF penetration.
- 10. Distribution [Conc] > serum: Prostate tissue Stool Bile Lung Kidneys Neutrophils Macrophages [Conc] < serum: Prostatic fluid Bone CSF
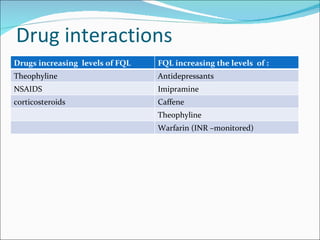
- 11. Drug interactions Drugs increasing levels of FQL FQL increasing the levels of : Theophyline Antidepressants NSAIDS Imipramine corticosteroids Caffene Theophyline Warfarin (INR –monitored)
- 12. Ěý
- 13. Ěý
- 14. Adverse effects. Generally safe antibiotics G.I.T -nausea,vomiting,diarrhea and antibiotic associated colitis have been reported. CNS -confusion,insomnia,dizziness,anxiety,and seizures(displacement of GABA from its receptors). CVS -torsade de pointes,prolonged QTc interval. May damage growing cartilage resulting in arthropathy(but that’s reversible so may b used in psudomonal infections in C.F where benefit outweighs the risk.)
- 15. Cont. Tendonitis and tendon rupture is rare but very serious. Phototoxicity-avoid excesive sun exposure. Leukopenia,eosinophilia (rare) Mild elevation in transaminases (rare)
- 16. Contraindication Childrens (not absolute) Pregnancy Lactation Epilepsy QTc prolongation
- 18. Ciprofloxacin 2 nd generation fluoroquinolone Mainly effective against G –ve bacteria : Enterobacteriacae H. influenzae M. catarrhalis Campylobacter Pseudomonas N. gonorrheae Intracellular pathogens M. Tuberculosis Mycoplasma Chlamydia Legionella Brucella Not effective against G+ and anaerobes
- 19. Clinical uses 1.Urinary tract infections (G- bacteria) 2. Osteomyelitis due to P. aeruginosa 3. Gonorrhea 4. Travellers’ diarrhea- ciprofloxacin commonly used 5. Tuberculosis 6. Prostatitis 7. Community- acquired pneumoniae 8. Diabetic foot infections ( P. aeruginosa ) 9.Anthrax
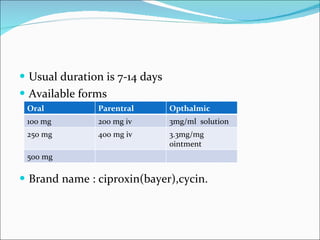
- 20. Usual duration is 7-14 days Available forms Brand name : ciproxin(bayer),cycin. Oral Parentral Opthalmic 100 mg 200 mg iv 3mg/ml solution 250 mg 400 mg iv 3.3mg/mg ointment 500 mg
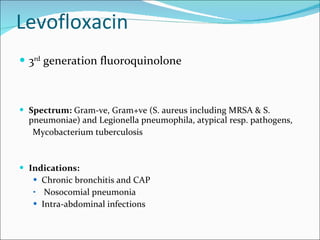
- 21. Levofloxacin 3 rd generation fluoroquinolone Spectrum: Gram-ve, Gram+ve (S. aureus including MRSA & S. pneumoniae) and Legionella pneumophila, atypical resp. pathogens, Mycobacterium tuberculosis Indications: Chronic bronchitis and CAP Nosocomial pneumonia Intra-abdominal infections
- 22. Cont. Adverse reaction. Blood glucose disturbances in DM patients QTC prolongation, torsades de pointes, arrhythmias Nausea, GI upset Interstitial nephritis
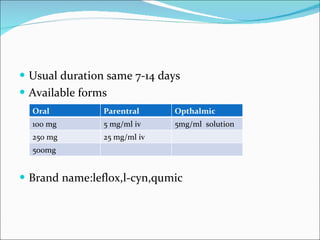
- 23. Usual duration same 7-14 days Available forms Brand name:leflox,l-cyn,qumic Oral Parentral Opthalmic 100 mg 5 mg/ml iv 5mg/ml solution 250 mg 25 mg/ml iv 500mg
- 24. Ěý







![Distribution [Conc] > serum: Prostate tissue Stool Bile Lung Kidneys Neutrophils Macrophages [Conc] < serum: Prostatic fluid Bone CSF](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fluroquinolones2-110307004430-phpapp01/85/Fluroquinolones-2-10-320.jpg)