FMEA - What is FMEA. Everything about FMEA.
- 1. WHAT IS FMEA? It is a structured approach to ’āś recognize & evaluate the potential failure & its effects. ’āś Identify actions to eliminate or reduce the chance of potential failure occurring. ’āś Document the process.
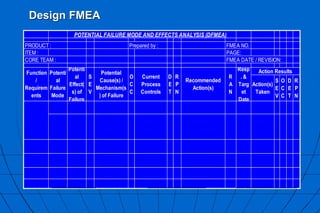
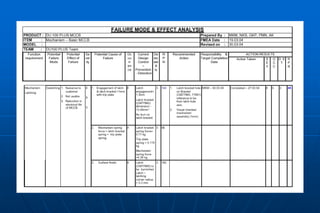
- 2. POTENTIAL FAILURE MODE AND EFFECTS ANALYSIS (DFMEA) PRODUCT : Prepared by : FMEA NO. ITEM : PAGE: CORE TEAM : FMEA DATE / REVISION: Action(s) Taken S E V O C C D E T R P N Function / Requirem ents Potenti al Failure Mode Potenti al Effect( s) of Failure S E V Action Results Potential Cause(s) / Mechanism(s ) of Failure R P N Recommended Action(s) R A N Resp . & Targ et Date O C C Current Process Controls D E T Design FMEA
- 4. ROLE OF FMEA IN QS
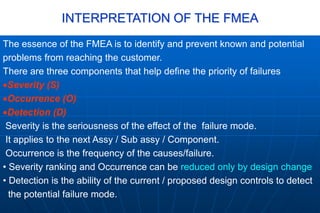
- 5. INTERPRETATION OF THE FMEA The essence of the FMEA is to identify and prevent known and potential problems from reaching the customer. There are three components that help define the priority of failures ’éĘSeverity (S) ’éĘOccurrence (O) ’éĘDetection (D) Severity is the seriousness of the effect of the failure mode. It applies to the next Assy / Sub assy / Component. Occurrence is the frequency of the causes/failure. ŌĆó Severity ranking and Occurrence can be reduced only by design change ŌĆó Detection is the ability of the current / proposed design controls to detect the potential failure mode.
- 6. RPN = Severity (S) X Occurrence (O) X Detection (D) RPN is a measure of ŌĆ£design riskŌĆØ & is used to prioritize failures. It can have a value of 1 to 1000, higher RPM means higher risk. How to reduce RPN ? Design verification, Design Validation. Design change. Change of material. RISK PRIORITY NUMBER ( RPN )
- 7. ’ü¼ Design FMEA (DFMEA) ’āśIt addresses the design intent;assumes the design will be manufactured/assembled to this intent & no mfg failure. ’āśThe causes are design limitations, constraints. ’āśRecommended actions are design changes, design verifications. ’ü¼ Process FMEA (PFMEA) ’āśIt looks for manufacturing failure. ’āśThe causes are manufacturing problems. ’āśRecommended actions are process/product control plans. TYPES OF FMEA
- 8. ’éź Design of new products/processes. ’éź Changes in existing products/processes. ’éź New applications for existing products/processes. ’éź Upgrading existing products/processes. WHEN TO START FMEA?
- 9. APPLICATION OF FMEA The FMEA can be applied in all stages of product life cycle. It is a living document, first level FMEA shall begin at the conceptual design & be completed before the design release. Who conducts FMEA? It is a team function and can not be done on an individual basis.
- 10. ’éź Function/Requirement: The task that the system / subsystem / item performs to meet the design intent. It has to be concise, exact & easy to understand. List all functions & include environment conditions if any. Examples : Lubricate, Position, Retain, Support. VOCABULARY OF THE FMEA
- 11. POTENTIAL FAILURE MODE ’éźIt is the manner in which a component / sub Assy / Assy could potentially fail to meet the design intent. It has to be described in ŌĆ£physicalŌĆØ or ŌĆ£technicalŌĆØ terms and not as a symptom noticed by the customer. ’éźIt may also be the cause of a P.F. mode in a higher level assy or be the effect of one in lower level component. ’éźPF modes under certain operating & usage conditions shall also to be considered. ’éźAssumption: PF could occur ,but may not necessary occur. ’éźEx. Cracked, Deformed, Leaking, Oxidised.
- 12. It is the effect of the failure mode on the function, as perceived by the customer. The customer can be external or external. State clearly the impact on safety, non compliance to regulations or deterioration of the function. Examples: Noise, Erratic operation, Poor appearance, Unstable POTENTIAL EFFECTS OF FAILURE
- 13. EFFECT CRITERIA : SEVERITY OF EFFECT RANKING ’āś Hazardous- Without warning Many endanger machine or assembly operator. Very high severity ranking when a potential failure mode affects safe vehicle operation and/or involves noncompliance with government regulation. Failure will occur without warning. 10 ’āś Hazardous- with warning Many endanger machine or assembly operator. Very high severity ranking when a potential failure mode affects safe vehicle operation and/or involves noncompliance with government regulation. Failure will occur with warning. 9 ’āś Very High Major disruption to production line. 100% of product may have to be scrapped. Vehicle/item inoperable, loss of primary function. Customer very dissatisfied. 8 ’āś High Minor disruption to production line. Product may have to be sorted and a portion (less than 100%) scrapped. Vehicle/item operable, but at a reduced level of performance. Customer dissatisfied. 7 ’āś Moderate Minor disruption to production line. A portion (less than 100%) of the product may have to be scrapped ( no sorting). Vehicle/item operable, but some comfort/convenience item(s) inoperable. Customers experiences discomfort. 6 ’āś Low Minor disruption to production line. 100% of product may have to be reworked. Vehicle/item operable, but some comfort/convenience item(s) operable ’āś at reduced level of performance. Customers experiences discomfort. 5 ’āś Very Low Minor disruption to production line. The product may have to be sorted and a portion (less than 100 %) reworked. Fit & Finish/squeak & Rattle item does not conform. Defect noticed by most customers. 4 ’āś Minor disruption to production line. A portion (less than 100 %) of the product may have reworked on-line but out-of-station. Fit & Finish/squeak & Rattle item does not conform. Defect noticed by average customers. 3 ’āś Very Minor Minor disruption to production line. A portion (less than 100 %) of the product have to be reworked on-line but in-station. Fit & Finish/squeak & Rattle item does not conform. Defect noticed by discriminating customers. 2 ’āś None No effect 1
- 14. Evaluation Criteria for OCCURRENCE ’āś PROBABILITY OF FAILURE POSSIBLE FAILURE RATES CpK RANKING ’āś Very High: Failure is almost inevitable ’é│ 1 in 2 ’Ć╝ 0.33 10 ’āś 1 in 3 ’é│ 0.33 9 ’āś High: Generally associated with processes ’āś similar to previous processes that have often failed 1 in 8 ’é│ 0.51 7 ’āś Moderate: Generally associated with processes 1 in 80 ’é│ 0.83 6 ’āś similar to previous processes which have experienced 1 in 400 ’é│ 1.00 5 ’āś occasional failures, but not in major proportions 1 in 2000 ’é│ 1.17 4 ’āś Low: Isolated failures associated with similar 1 in 15,000 ’é│ 1.33 3 processes ’āś Very Low: Only isolated failures associated with 1 in 1,50,000 ’é│ 1.50 2 ’āś almost identical processes ’āś Remote: failure is unlikely. No failures ever associated ’éŻ 1 in 15,00,000 ’é│ 1.67 1 with almost identical processes
- 15. Evaluation Criteria for DETECTION ’āś DETECTION Criteria : Likelihood the existence of a defect will be detected by process RANKING controls before next or subsequent process, or before part or component leaves the manufacturing or assembly location ’āś Almost Impossible No known control(s) available to detect failure mode 10 ’āś Very remote Very remote likelihood current control(s) will detect failure mode 9 ’āś Remote Remote likelihood current control(s) will detect failure mode 8 ’āś Very Low Very low likelihood current control(s) will detect failure mode 7 ’āś Low Low likelihood current control(s) will detect failure mode 6 ’āś Moderate Moderate likelihood current control(s) will detect failure mode 5 ’āś Moderately High Moderately high likelihood current control(s) will detect failure mode 4 ’āś High High likelihood current control(s) will detect failure mode 3 ’āś Very High Very high likelihood current control(s) will detect failure mode 2 ’āś Almost Certain Current control(s) almost certain to detect the failure mode. Reliable detection controls are known with similar processes 1
- 16. REFERENCE MATERAIL ’āś Books: ’āś The Root Cause Analysis handbook. ’āś FMEA - Theory to execution. ’āś The FMEA pocket handbook. ’āś Internet sites: ’āś www.fmeainfocentre.com ’āś www.fmeca.com ’āś www.amsup.com ’āś Softwares: ’āś FMEA Facilitator, Relex
- 17. Thank you