Folate deficiency anemia .pdf
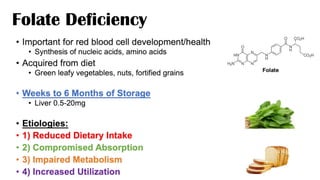
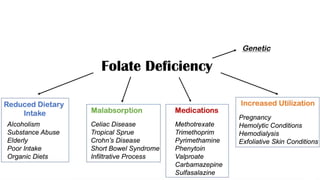
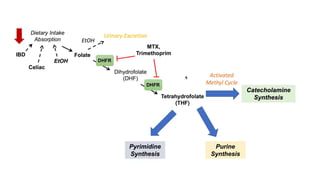
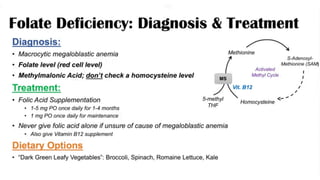
Folate deficiency anaemia: folate is essential for the development and synthesis of red blood cells the synthesis of nucleic acids, and amino acids. The ethologies include Reduced Dietary Intake, Compromised Absorption, impaired metabolism CO2H CO.H, Increased Utilisation. the pathophysiological mechanism based on tetrahydrofolate giving synthesis of catecholamine, purine, and pyrimidine. Symptoms of Anemia Pallor, shortness of breath, fatigue, dyspnea on exertion, mild jaundice, mouth ulcers, Diarrhea, Neurological symptoms less common, Confusion, Fatigue, Irritability, Cognitive Decline. In pregnancy, Increased Utilization of Folate in Pregnancy can lead to folate deficiency ŌĆó Daily required folate appears to be m,0g04cwhereas folate fortification only provides around 160mcg ŌĆó Folate seems to be required for proper neural tube closure, which occurs at approximately 2weeksofgestation ŌĆó Folate deficiency can lead to Neural Tube Defects (NTD) ŌĆó recommended that all women of reproductive age take a folic acid supplement. diagnosis is based on laboratory tests which include complete blood count, methylmalonic acid and homocysteine. treatment is usually supplements like folic acid and vitamin b12 in appropriate dosages to treat the deficiency and maintain the normal level. Dietary options include Dark Green Leafy Vegetables: Broccoli, Spinach, Romaine Lettuce, and Kale.