Foot biomechanics
- 1. Dr. Deepak Anap M.P.Th.( Musculo) Asst. Professor ANKLE AND FOOT BIOMECHANICS
- 2. FOOT FACTS Average person logs 1,000 miles per year. One hour of running transfers 1 million lbs. of force through the feet. Walking places 1.5 times your body weight through your foot. Over 11 million medical office visits in 2003 due to foot and ankle problems.
- 3. Bone of the Ankle Talus Tibia Distal End of Fibula Articulations Distal tibfib Tibiotalor Fibiotalor Movements at the Ankle
- 4. Bones of the Foot Calcaneus Cuboid Navicular 3 Cuneiforms Metatarsal Phalanges
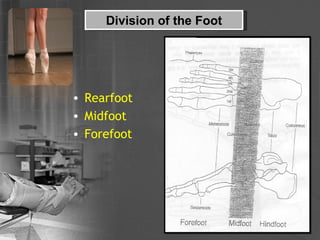
- 5. Division of the Foot Rearfoot Midfoot Forefoot
- 6. Hindfoot (Rearfoot) Subtalar joint: where the talus rests on and articulates with the calcaneus. This is a synovial joint with a weak capsule supported by medial, lateral, posterior & interosseous talocalcaneal ligaments. The interosseous talocalcaneal ligament (very strong) lies in the tarsal sinus (separates the anterior & posterior talocalcaneal joints). Anatomical subtalar joint- functionally a single synovial joint between the slightly concave articular surface of the talus and the convex posterior articular surface of the calcaneus.
- 7. Midfoot Composed of Navicular 3 cuneiforms cuboid Six Joints Talocalcaneonavicular Calcaneocuboid Cuboideonavicular Intercuneiform Cuneocuboid Cuneonavicular
- 8. Forefoot 5 MTĄŊs Proximally 1-3 articulate with cuneiforms Proximally 4-5 articulate with cuboid Bases articulate with: Phalanges
- 9. Ligaments of the Ankle and Foot Lateral Structures Anterior Talofibular Calcaneofibular Posterior Talofibular Distal Tibiofibular Medial Structures Deltoid Plantar Calcaneonavicular (Spring Ligament) Many intertarsal ligaments
- 10. Sagittal plane movement occurs at the talocrural joint One degree of freedom Axis is between tips of malleoli Oblique to anatomical planes Dorsiflexion (Extension) average range 20Ąã Plantar flexion (Flexion) average range 45Ąã (Note 0Ąã occurs where a line from the heel to the sesamoid bones under the big toe joint or 1 st metatarsophalangeal joint is perpendicular to the lower leg) KINEMATICS OF ANKLE & FOOT
- 11. 2 . Frontal (coronal) plane movement occurs at the subtalar joint Single Oblique axis Inversion average range 20Ąã Eversion average range 10Ąã (Note 0Ąã occurs where the sole of the foot at perpendicular to the lower leg in the frontal plane)
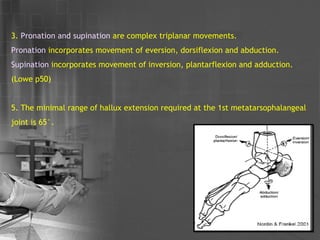
- 12. 3. Pronation and supination are complex triplanar movements. Pronation incorporates movement of eversion, dorsiflexion and abduction. Supination incorporates movement of inversion, plantarflexion and adduction. (Lowe p50) 5. The minimal range of hallux extension required at the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint is 65Ąã.
- 13. Arches of Foot Two arches held by tendons & ligaments Allow foot to support weight of the body: ball of foot ĻC 40% weight. Heel ĻC 60% weight Leverage for walking Fully developed by age 13 Longitudinal arch: medial and lateral parts Transverse arch
- 14. Arches of the Foot Medial Longitudinal Arch Calcaneus Talus Navicular 1-3 cuneiforms 1-3 MTĄŊs This arch is very tall (which is why the medial side of the foot is missing from a footprint ) and is extremely resilient due to its large number of component bones.
- 15. Arches of the Foot Medial Longitudinal Arch continued Ligament Support Plantar Calcaneonavicular Long Plantar Lig Deltoid Plantar fascia
- 16. Arches of the Foot Medial Longitudinal Arch continued Ligament Support Plantar Calcaneonavicular Long Plantar Lig Deltoid Plantar fascia
- 17. Arches of the Foot Medial Longitudinal Arch continued Ligament Support Plantar Calcaneonavicular Long Plantar Lig Deltoid Plantar fascia
- 18. Arches of the Foot Medial Longitudinal Arch continued Muscular Support Intrinsic Abductor Hallucis Flexor Digitorum Brevis Extrinsic Tibialis Posterior Flexor Hallucis Longus Flexor Digitorum Longus Tibialis Anterior Flexor Digitorm Longus
- 19. Arches of the Foot Lateral Longitudinal Arch Composed of Calcaneus Cuboid 4-5 th MTĄŊs Ligament Support Long & Short Plantar Plantar Fascia
- 20. Lateral Longitudinal Arch continued Muscle Support Intrinsic Abductor Digiti Minimi Flexor Digitorum Brevis Extrinisic Peroneus Longus, Brevis & Tertius
- 21. Arches of the Foot Transverse Arch Formed By: Ligament Support Intermetatarsal Ligaments Plantar Fascia Muscle Support All intrinsic muscles Extrinisic Tibialis Posterior Tibialis Anterior Peroneus Longus
- 22. In quiet stance body weight is transmitted through the talus bone and passed in equal measure backwards (into the calcaneum) and forwards. Weight distribution
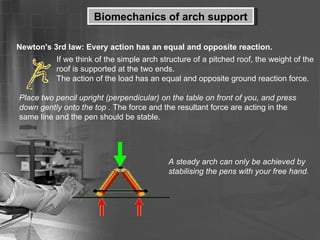
- 23. Biomechanics of arch support Newton's 3rd law: Every action has an equal and opposite reaction. If we think of the simple arch structure of a pitched roof, the weight of the roof is supported at the two ends. The action of the load has an equal and opposite ground reaction force. Place two pencil upright (perpendicular) on the table on front of you, and press down gently onto the top . The force and the resultant force are acting in the same line and the pen should be stable. A steady arch can only be achieved by stabilising the pens with your free hand.
- 24. In a stable arch the twisting moments are resisted by other structures, e.g a tie-beam in a pitched roof; pictured left. All pitched roofs are stabilised and supported, otherwise they would collapse. Biomechanics of arch support
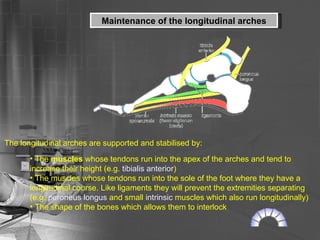
- 25. Maintenance of the longitudinal arches The longitudinal arches are supported and stabilised by: The muscles whose tendons run into the apex of the arches and tend to increase their height (e.g. tibialis anterior ) The muscles whose tendons run into the sole of the foot where they have a longitudinal course. Like ligaments they will prevent the extremities separating (e.g. peroneus longus and small intrinsic muscles which also run longitudinally) The shape of the bones which allows them to interlock
- 26. A variety of longitudinally arranged ligaments which prevent the extremities separating, for example the long and short plantar ligaments and by the plantar calcaneonavicular ("spring") ligament. The plantar aponeurosis links the extremities of the arches, and acts as the equivalent of a tie beam in an architectural arch Maintenance of the longitudinal arches
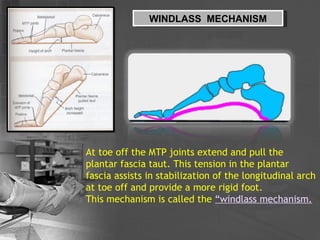
- 27. WINDLASS MECHANISM At toe off the MTP joints extend and pull the plantar fascia taut. This tension in the plantar fascia assists in stabilization of the longitudinal arch at toe off and provide a more rigid foot. This mechanism is called the Ą°windlass mechanism.
- 28. ?