Forces_and_Motion_Unit_Test.pdf
- 1. FORCES AND MOTION UNIT TEST Multiple Choice: Draw a Circle Completely around the ONE BEST answer. 1. A force acting on an object does no work if a. a machine is used to move the object. b. the force is not in the direction of the object’s motion. c. the force is greater than the force of friction. d. the object accelerates. 2. What is the speed of a bobsled whose distance- time graph indicates that it traveled 100 m in 25 seconds? a. 4 m/s c. 0.25 mph b. 250 m/s d. 100 m/s 3. What is the SI unit of pressure? a. a pascal c. a newton b. g/cm3 d. m/s2 4 . The operation of a hydraulic lift system is explained by a. Newton’s principle.
- 2. b. Bernoulli’s principle. c. Pascal’s principle. d. Archimedes’ principle. 5. The amount of matter in an object is called its a. inertia. c. balance. b. force. d. mass. 6. The force that one surface exerts on another when the two rub against each other is called a. gravity. c. inertia. b. friction. d. acceleration. 7. An object that travels around another object in space is called a(n) a. satellite. c. inertia. b. projectile. d. mass. 8. When you know both the speed and direction of an object’s motion, you know the a. average speed of the object. b. acceleration of the object. c. distance the object has traveled. d. velocity of the object.
- 3. 9. What is transferred by a force moving an object through a distance? a. motion c. energy b. force d. mass 10. The SI unit of power is the a. joule. c. newton. b. watt. d. newton-meter. 11. The basic SI unit of length is the a. inch. c. meter. b. foot. d. mile. 12. Based on your knowledge of energy conservation, which of the following statements is true? a. Manufacturers can increase a light bulb’s energy efficiency by using technology that increases the amount of electromagnetic energy the bulb converts from a given amount of electrical energy. b. Energy can be conserved by turning off lights when they are not in use. c. both a and b d. neither a nor b
- 4. 13. Which of the following is an example of exerting a force? a. a train speeding down a track b. a carpenter hammering a nail c. a child running through a field d. an airplane soaring through the sky 14. One way to increase acceleration is by a. decreasing force. b. increasing mass. c. decreasing mass. d. increasing both force and mass proportionally. 15. In order to calculate pressure exerted on a surface, what quantity is divided by the surface area? a. force c. volume b. mass d. altitude 16. Speed is the ratio of the distance an object moves to a. the displacement of the object. b. the motion of the object.
- 5. c. the amount of time needed to travel the distance. d. the direction the object moves. 17. An inclined plane reduces the effort force by a. reducing the work. b. reducing the effort distance. c. increasing the work. d. increasing the distance through which the force is applied. 18. The energy of motion is called a. thermal energy. c. work. b. kinetic energy. d. potential energy. 19. An ax is an example of a(an) a. lever. c. wedge. b. inclined plane. d. wheel and axle. 20. If you exert a force of 10.0 N to lift a box a distance of 0.75 m, how much work do you do? a. 75 J c. 7.5 J b. 0.075 J d. 10.75 J
- 6. 21. Which of the following increases when an object becomes warmer? a. chemical energy c. thermal energy b. elastic potential energy d. nuclear energy 22. According to Newton’s third law of motion, when a hammer strikes and exerts force on a nail, the nail a. disappears into the wood. b. exerts an equal force back on the hammer. c. moves at a constant speed. d. creates a friction with the hammer. 23. The power of a machine measures a. its strength. b. the work it does. c. its rate of doing work. d. the force it produces. 24. Which of the following materials conducts heat well? a. plastic c.metal b. wood d. glass Figure 11-1
- 7. 25. 25. Examine Figure 11-1. If you were standing under the tree, which object would appear to be moving? a. the tree c. the airplane b. the building d. the boy 26. When a pair of balanced forces acts on an object, the net force that results is a. greater in size than one of the forces. b. equal to zero.
- 8. c. equal in size to one of the forces. d. greater in size than both forces combined. 27. According to Newton’s second law of motion, the acceleration of an object equals the net force acting on the object divided by the object’s a. mass. c. momentum. b. velocity. d. weight. 28. Which of the following materials will sink in water? (The density of water 1.00 g/cm3 .) a. cooking oil (0.82 g/cm3 ) b. balsa wood (0.12 g/cm3 ) c. ethanol (0.798 g/cm3 ) d. steel (7.18 g/cm3 ) 29. The upward force acting on an object submerged in a fluid is called a. drag. c. weight. b. pressure. d. buoyant force. 30. A machine is classified as a compound machine if it a. has moving parts.
- 9. b. is made up of two or more simple machines that operate together. c. is very efficient. d. has an IMA greater than 1. 31. Energy from the sun reaches Earth mostly by a. convection. c. conduction. b. thermal expansion. d. radiation. 32. Which of the following universal forces is the most effective over long distances? a. gravitational c. strong nuclear b. magnetic d. electric 33. If a bicyclist travels 30 kilometers in two hours, her average speed is _______________. a. 60 km/h. b. 2 km/h. c. 30 km/h. d. 15 km/h. 34. Speed equals distance divided by __________ a. velocity. c. motion. b. size. d. time.
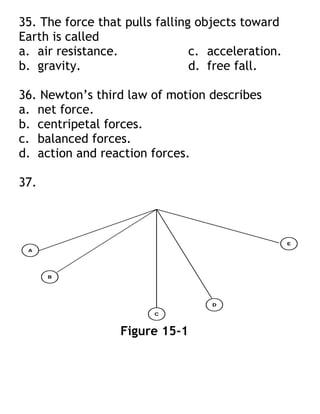
- 10. 35. The force that pulls falling objects toward Earth is called a. air resistance. c. acceleration. b. gravity. d. free fall. 36. Newton’s third law of motion describes a. net force. b. centripetal forces. c. balanced forces. d. action and reaction forces. 37. Figure 15-1
- 11. 37. The kinetic energy of the pendulum bob in Figure 15-1 increases the most between locations a. A and C. c. B and D. b. C and D. d. A and B. 38. Which of the following is a unit of temperature? a. calorie c. Celsius degree b. joule d. kilogram 39. How can a machine make work easier for you? a. by changing the direction of your force b. by decreasing the amount of work you do c. by increasing the work done by the machine d. none of the above 40. The SI unit of force is the a. meter. c. joule. b. kilogram. d. newton. 41. A horizontal line on a distance-time graph means the object is a. moving at a constant speed. b. moving faster. c. at rest.
- 12. d. slowing down. 42. A mechanical device requires 400 J of work to do 340 J of work in lifting a crate. What is the efficiency of the device? a. 0.9% c. 85% b. 60% d. 118% 43. What is the momentum of a 50-kilogram ice skater gliding across the ice at a speed of 2 m/s? a. 25 c. 48 kg m/s b. 50 kg d. 100 kg m/s 44. Which of the following is an example of a wheel and axle? a. a pencil b. a jar lid c. a doorknob d. an automobile steering wheel 45. Which of these is an example of deceleration? a. a roller coaster moving down a steep hill b. an airplane following a straight flight path c. a bird taking off for flight d. a car approaching a red light
- 13. 46. An orange might roll off your cafeteria tray when you stop suddenly because of a. the friction forces acting on the orange. b. the balanced forces acting on the orange. c. the centripetal force acting on the orange. d. the orange’s inertia. 47. An example of a compound machine is a a. crowbar. c. bicycle. b. seesaw. d. ramp. 48. The energy stored in gasoline is a. nuclear energy. b. chemical energy. c. electromagnetic energy. d. mechanical energy. 49. Which example identifies a change in motion that produces acceleration? a. a ball moving at a constant speed around a circular track b. a speed skater moving at a constant speed on a straight track
- 14. c. a particle moving in a vacuum at constant velocity d. a vehicle moving down the street at a steady speed 50. When an unbalanced force acts on an object, a. the object’s motion does not change. b. the inertia of the object increases. c. the weight of the object decreases. d. the object accelerates.


































![Long 50slideschapter 5 motion notes [autosaved]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/long50slideschapter5motionnotesautosaved-110126123317-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)

























