foresight session TRANSLATOR 2030
- 2. Foresight Session: TRANSLATOR 2030 In Moscow on May 16, 2017, School of Translation Didactics held for the first time ┬½Foresight Session: Translator 2030┬╗. Participants: ÔÇó representatives of professional associations, unions of translators, translation groups, professional translators and freelance translators; ÔÇó representatives of universities, tertiary schools and colleges for translators; ÔÇó executives of translation agencies, companies employing translation services; ÔÇó representatives of translation software companies.
- 3. FORESIGHT Technology ÔÇó foresight ÔÇô the ability to see what will or might happen in the future ÔÇó is widely used to make long-term forecasts, and represents a way to create a consistent and reasonable vision of the future. ÔÇó FORESIGHT - ┬½the process involved in systematically attempting to look into the longer-term future of science, technology, the economy and society with the aim of identifying the areas of strategic research and the emerging generic technologies likely to yield the greatest economic and social benefits┬╗ [B. Martin]. ÔÇó Result is ┬½a map of the future┬╗.
- 4. Session subject: translation profession. Thematic focus: translation (literary and sectoral), interpreting (consecutive/simultaneous) and audiovisual translation. Time map involved 3 periods: short-term (2017 - 2020); medium-term (2020 - 2025); long-term (2025 - 2030 ð│ð¥ð┤Ðï). Session object ÔÇô to use foresight technology to organize a discussion which allows putting on the time map the most adequate, important and interesting proposals on the fate of translators.
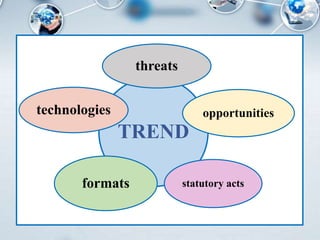
- 5. Key concepts of the foresight session ÔÇó ┬½Trends┬╗ are processes which allow to improve and complement the content of the future translation profession. ÔÇó ┬½Technologies┬╗ allow the specific trend to be implemented in the future. Inventions and technical innovations are considered as technologies. ÔÇó ┬½Format┬╗ allows to present forms/formats of interaction. ÔÇó ┬½Opportunities and risks┬╗ which may occur when implementing a specific trend. ÔÇó ┬½Statutory act┬╗ allows to formalize results of the trend at official (legislative) level.
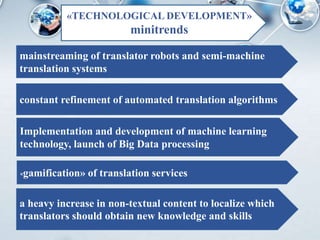
- 8. ð×Ðüð¢ð¥ð▓ð¢ÐïðÁ ÐéÐÇðÁð¢ð┤Ðï ┬½TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENT┬╗ minitrends mainstreaming of translator robots and semi-machine translation systems constant refinement of automated translation algorithms Implementation and development of machine learning technology, launch of Big Data processing ┬½gamification┬╗ of translation services a heavy increase in non-textual content to localize which translators should obtain new knowledge and skills
- 9. ┬½TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENT┬╗ threats decrease in demand for human translation drop in income of classical translators translatorsÔÇÖ unpreparedness for rapid software development machines start evaluating human translator skills, which leads to the risk of an inadequate assessment translators canÔÇÖt keep up with market demands for software use professional degradation: the more robots can do, the less human translators are capable of
- 10. creation of new secondary/interdisciplinary professions or additional skills for translators return of demand for creativity and cognitive skills demand for highly professional translators to train robots «TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENT» opportunities
- 11. ð×Ðüð¢ð¥ð▓ð¢ÐïðÁ ÐéÐÇðÁð¢ð┤Ðï┬½Decrease in demand for experts in translation industry┬╗ minitrends-1 Translator transition to related industries Further inability of training system to keep up with market realities Professional degradation, decline in prestige and internal skills Blurring of professional boundaries Emergence of new specialities in translation profession Expansion of translation capabilities ÔÇô cultural mediation
- 12. ð×Ðüð¢ð¥ð▓ð¢ÐïðÁ ÐéÐÇðÁð¢ð┤Ðï┬½Decrease in demand for experts in translation industry┬╗ minitrends -2 Growing gap between elite translators and the rest Absence of certification for translators, which allows for dumping by less competent specialists Temporary deterioration of teaching staff skills, slow process of professional training of new teachers Search function replaces analysis function Dissolution of large educational institutions
- 13. «Decrease in demand for experts in translation industry» threats translation quality deterioration at times of avalanche like growth of localization content further inability of training system to keep up with market realities translation industry «stratification» and widening gap between elite translators and other representatives of the profession expert translators leaving the industry due to the drop in income
- 14. «Decrease in demand for experts in translation industry» opportunities - 1 growth of demand for highly-skilled professionals a chance to change specialties within boundaries of the profession improving the process of professional personnel selection flexibility and ability to adapt to market demands, and opportunity for professional self-fulfillment creation of a flexible system for further education and reorientation of translators throughout their professional lives
- 15. «Decrease in demand for experts in translation industry» opportunities - 2 need to preserve, process and use cumulative knowledge of translation studies in the profession of a translator will give rise to translator- researchers personality-centered education for future translators considering their skills and wishes achieving a greater role of research and scientific advances emergence of new educational institutions (smaller than classical universities) able to provide a large amount of knowledge in response to future translator demands synergistic dynamics in translator training process, emergence of many interdisciplinary translation specialties related to other areas
- 16. ð×Ðüð¢ð¥ð▓ð¢ÐïðÁ ÐéÐÇðÁð¢ð┤Ðï┬½Steady decline in income┬╗ minitrends A steady decline in freelance translator income due to the onset of translation companies A large number of ill-trained translators willing to work at low translation rates Growing dumping on the part of translators from neighboring countries Computer-based translation share growth Negative effect of CAT-tools on ┬½classical┬╗ translation rates
- 17. SECONDARY TRENDS Decrease in textual content share (medium-term trend) Consumer mosaic thinking (short-term trend) Hybridization of communication formats and hybridization of translation activities as a result (medium-term trend) Return to analytical thinking (long-term trend)
- 18. FORMATS ÔÇócommercial translation 101 courses. ÔÇóstate services portal for freelance translators. ÔÇóa portal to preserve and share translation research works. ÔÇóassociation of translation companies.
- 19. TECHNOLOGIES ÔÇó development of adaptive training courses. ÔÇó improving the means of communication with robots (voice input/output of data, a new level of software, etc.) ÔÇó development of criteria for expert evaluating of translator competence levels. ÔÇó expert systems to identify professional inclinations. ÔÇó creation of online learning platforms. ÔÇó development of new learning technologies: gamification, use of social media, etc. ÔÇó customized courses for professional advancement. ÔÇó building of networking cooperation to deter unscrupulous clients. ÔÇó a portal with a list of opportunities and possible ways to study various types of translation. ÔÇó project-based learning (PB-learning), Life Long Learning.
- 20. Statutory Acts ÔÇó a request to the Ministry of Labour to register professions of new translator qualifications. ÔÇó creation of a unified lobbying institution for language services industry. ÔÇó creation of accreditation centers for translators. ÔÇó creation of the occupational standard for translators, inclusion of translation profession in the unified register of professions. ÔÇó creation of educational standard for translators based on the occupational standard. ÔÇó creation of offices for expert evaluation of translations.
- 21. BLACK SWANS ┬½the black swan┬╗ (Engl. TBS, The Black Swan) ÔÇô a term introduced by Nassim Nicholas Taleb, an American economist - a hard-to-predict and rare event which may have significant effects on the matter in hand.
- 22. ┬½Black swans┬╗ for translation industry 2017-2020 2020-2025 2025-2030 Return of the ┬½Iron Curtain┬╗. Border closure Lifting of sanctions The loss of critical reading skills by younger generations Creation of a unified global translation market Sudden and erratic interference of state agencies in activities of the industry Internet censorship introduction Tightening of regulatory control of cash payments Internet shutdown RussiaÔÇÖs entry into the EU
- 23. Map of the future «Translator 2030»



![FORESIGHT Technology
ÔÇó foresight ÔÇô the ability to see what will or might happen
in the future
ÔÇó is widely used to make long-term forecasts, and
represents a way to create a consistent and reasonable
vision of the future.
ÔÇó FORESIGHT - ┬½the process involved in systematically
attempting to look into the longer-term future of science,
technology, the economy and society with the aim of
identifying the areas of strategic research and the
emerging generic technologies likely to yield the
greatest economic and social benefits┬╗ [B. Martin].
ÔÇó Result is ┬½a map of the future┬╗.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ptxen-170719073006/85/foresight-session-TRANSLATOR-2030-3-320.jpg)