Formwork
- 1. Formwork Dr. D. K. Jain Professor and Head, Department of Civil Engineering, Oriental Institute of Science and Technology, Bhopal
- 2. Definition â—¦ Formwork is a die or a mould including all supporting structures, used to shape and support the concrete until it attains sufficient strength to carry its own weight. It should be capable of carrying all imposed dead and live loads apart from its own weight. â—¦ The horizontal (or vertical) planks or plates directly in contact with concrete are called forms or shuttering while the supporting frame (steel pipes or wooden ballies etc.) is called centering. The centering and shuttering together is usually referred as formwork.
- 3. Material â—¦ Material for formwork can be any of the following â—¦ Wood (Solid timber as well as plywood) â—¦ Steel â—¦ Aluminum â—¦ Plastic â—¦ Wooden planks and ballies were the most common formwork in small construction works which are being replaced by steel plates and props with increase in their availability. As steel formwork gives better strength, faster assembly and better control over the quality and finish of concrete., the same is preferred in all Government works in India. â—¦ Aluminum formwork is being adopted in large repetitive construction works like very tall buildings for faster construction.
- 4. Qualities of Good Formwork â—¦ It should be strong enough to take the weight of concrete, reinforcement, labour, equipment etc. safely. â—¦ It should be designed and constructed so as to remain sufficiently rigid during placing and compaction of concrete. â—¦ It should be capable of forming desired shape with ease and accuracy. â—¦ It should be sufficiently water tight so that no loss of slurry takes place. â—¦ It should be easy to work and handle. â—¦ It should be economical. â—¦ It should be reusable.
- 5. Cleaning and Treatment of Formwork â—¦ Before placing concreting, the formwork should be thoroughly cleaned and all dust, dirt and rubbish removed from it. â—¦ The surface of formwork coming in contact with concreting should be treated with thin and uniform layer of form release agent e.g. commercial shuttering oils, raw linseed oil, soap solution. â—¦ The form release agent should not coat the reinforcement otherwise proper bond of reinforcement with concrete will not be there.
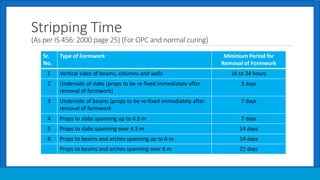
- 6. Stripping Time (As per IS 456: 2000 page 25) (For OPC and normal curing) Sr. No. Type of Formwork Minimum Period for Removal of Formwork 1 Vertical sides of beams, columns and walls 16 to 24 hours 2 Underside of slabs (props to be re-fixed immediately after removal of formwork) 3 days 3 Underside of beams (props to be re-fixed immediately after removal of formwork 7 days 4 Props to slabs spanning up to 4.5 m 7 days 5 Props to slabs spanning over 4.5 m 14 days 6 Props to beams and arches spanning up to 6 m 14 days Props to beams and arches spanning over 6 m 21 days
- 7. Web Resources â—¦ For formwork & centering some good presentations can be seen at the following links; â—¦ http://www.slideshare.net/rithikarockingravishankar/formwork-construction-in-structures â—¦ http://www.slideshare.net/ahbiahlee/formwork-presentation-for-construction-technology?qid=eb4fc339-2a18-418b-a3f4- 7f08c311cf45&v=default&b=&from_search=10 â—¦ For formwork and scaffolding a good presentation can be seen at the following link; â—¦ http://www.slideshare.net/hamo92/building-construction-8-formworks-and-scaffoldings â—¦ For safety aspect of scaffolding a good presentation can be seen at the following link; â—¦ http://www.slideshare.net/tamersafety/scaffolds-ppt-construction?qid=032d7b01-260d-47df-ac03- 6045b0218c6d&v=default&b=&from_search=1