foundationsofindividualbehaviour-160808151709.pptx
- 1. FOUNDATIONS OF INDIVIDUAL BEHAVIOUR Ō×ó ATTITUDE Ō×ó PERSONALITY Ō×ó PERCEPTIONS Ō×ó LEARNING Ō×ó MOTIVATION
- 2. ATTITUDES Definition Attitude is the mental state of readiness, learned and organized through experience, exerting a specific influence on personŌĆÖs response to people, object and situations with which it is related. Attitudes are learned predispositions towards aspects of our environment. They may be positively or negatively directed towards certain people, service or institutions.
- 3. Characteristics of Attitudes Ō£ō Attitudes are learned Ō£ōAttitudes are predispositions to respond to a set of facts Ō£ō Attitudes are evaluative statements. Ō£ōEverybody, irrespective of age or social status, hold attitudes.
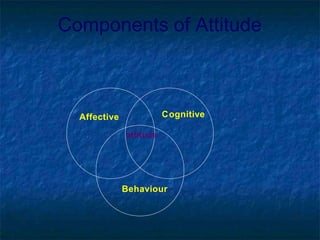
- 4. Components of Attitude Affective Cognitive Behaviour attitude
- 5. ABC Model Ō×óAffective component : feelings, sentiments, moods and emotions about a person, event, idea or object. Ō×ó Behavioural component : predisposition to form a favourable / unfavourable evaluation of something. Also called overt component. Ō×ó Cognitive component : beliefs, opinion, knowledge or information held by the individual. STIMULUS AFFECT COGNITION BEHAVIOUR
- 6. Formation of attitudes attitudes Experience Associations Economic status Family Neighbourhood
- 7. Influence of Attitudes ŌØ¢ Influence perceptions ŌØ¢ Job- satisfaction ŌØ¢ Job involvement ŌØ¢ Organizational commitment
- 8. Attitudes Vs Values Ō¢¬Values : represent long lasting beliefs about what is important. Ō¢¬ Evaluative standards that help us define what is right or wrong. Ō¢¬General beliefs about life, and stands in relation to some custom / cultural practice or norms. Ō¢¬ Enduring and resistant to change. VALUES LAY THE FOUNDATION FOR ATTITUDES AND MOTIVATION
- 9. PERCEPTIONS Definition It is the intellectual process by which a person acquires information from the environment , organizes it and obtains meaning from it.
- 10. Process of Perception PERCEPTUAL ORGANIZATION INPUTS OUTPUT Objects Events People Selection Organization Interpretation Actions Attitudes Beliefs Feelings
- 11. Selection Selective perception involves two psychological principles : ŌØ¢ ŌØ¢ Figure ground principle Relevancy
- 14. Organization Grouping : people/things can be grouped together due to similarity or proximity Closure : tendency to fill in gaps due to incomplete information to make them more meaningful. Simplicity : ignoring less important information and focus on important to overcome problem of overloading & complication.
- 15. Interpretation Interpretation is a subjective and judgmental process. this process is influenced by : ŌØ¢ ŌØ¢ ŌØ¢ ŌØ¢ Halo effect Stereotyping Attribution Projection
- 16. Factors influencing Perception Internal factors : Needs & desires Personality Experience External factors : Size Intensity Frequency Status Contrast