Frames
- 1. ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI) - KNOWLEDGE REPRESENTATION SCHEMESRuchi Sharmaruchisharma1701@gmail.comRuchi Sharma ruchisharma1701@gmail.com http://www.wiziq.com/tutor-profile/376074-Ruchi
- 2. ContentsQuick Recall – AI concept
- 3. Knowledge Representation – Concept & Features
- 4. Knowledge Representation - Techniques/Schemes
- 5. Understanding Semantic Networks – Facts
- 6. Understanding Semantic Networks – Examples
- 7. Understanding Frames – Facts
- 8. Understanding Frames – Examples
- 9. Understanding Propositional Logic & FOPL – Facts
- 10. Understanding Propositional Logic & FOPL - Examples
- 11. Understanding Rule-based Systems - Facts
- 12. Understanding Rule-based Systems - ExamplesRuchi Sharma ruchisharma1701@gmail.com http://www.wiziq.com/tutor-profile/376074-Ruchi
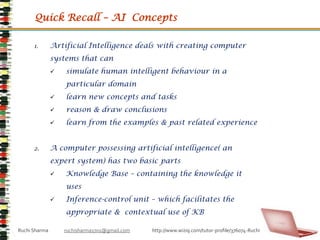
- 13. Quick Recall – AI ConceptsArtificial Intelligence deals with creating computer systems that can simulate human intelligent behaviour in a particular domain
- 14. learn new concepts and tasks
- 15. reason & draw conclusions
- 16. learn from the examples & past related experienceA computer possessing artificial intelligence( an expert system) has two basic parts Knowledge Base – containing the knowledge it uses
- 17. Inference-control unit – which facilitates the appropriate & contextual use of KBRuchi Sharma ruchisharma1701@gmail.com http://www.wiziq.com/tutor-profile/376074-Ruchi
- 18. Knowledge Representation – Concept & Features Knowledge representation is a method used to code knowledge in the knowledge base of an expert system. An ideal knowledge representation scheme should have inferencing capability
- 19. have a set of well defined syntax & semantics
- 20. allow the knowledge engineer to express knowledge in a language ( which can be inferred)
- 21. allow new knowledge to be inferred from the basic facts already stored in the KBRuchi Sharma ruchisharma1701@gmail.com http://www.wiziq.com/tutor-profile/376074-Ruchi
- 22. Knowledge Representation – Techniques/Schemes Different knowledge representation schemes are used today among which the most common are Semantic Networks
- 23. Frames
- 24. Propositional logic & FOPL
- 25. Rule-based systemRuchi Sharma ruchisharma1701@gmail.com http://www.wiziq.com/tutor-profile/376074-Ruchi
- 26. Understanding Semantic Networks - FactsA semantic network is a directed graph with labelled nodes & arrows. Nodes are commonly used for objects & the arrows for relations.
- 27. The pictorial representation of objects, their attributes & relationships between them & other entities make them better than many other representation schemes. Ruchi Sharma ruchisharma1701@gmail.com http://www.wiziq.com/tutor-profile/376074-Ruchi
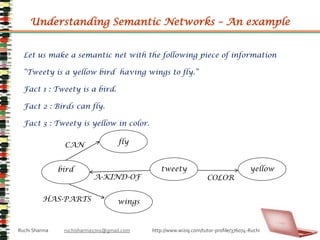
- 28. Understanding Semantic Networks – An exampleLet us make a semantic net with the following piece of information“Tweety is a yellow bird having wings to fly.”Fact 1 : Tweety is a bird.Fact 2 : Birds can fly.Fact 3 : Tweety is yellow in color.flyCANtweetyyellowbirdA-KIND-OFCOLORwingsHAS-PARTSRuchi Sharma ruchisharma1701@gmail.com http://www.wiziq.com/tutor-profile/376074-Ruchi
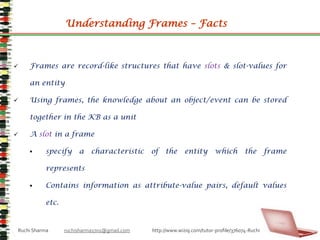
- 29. Understanding Frames – Facts Frames are record-like structures that have slots & slot-values for an entity
- 30. Using frames, the knowledge about an object/event can be stored together in the KB as a unit
- 31. A slot in a frame
- 32. specify a characteristic of the entity which the frame represents
- 33. Contains information as attribute-value pairs, default values etc.Ruchi Sharma ruchisharma1701@gmail.com http://www.wiziq.com/tutor-profile/376074-Ruchi
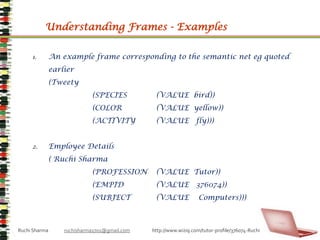
- 34. Understanding Frames - ExamplesAn example frame corresponding to the semantic net eg quoted earlier (Tweety (SPECIES (VALUE bird)) (COLOR (VALUE yellow)) (ACTIVITY (VALUE fly)))Employee Details ( Ruchi Sharma (PROFESSION (VALUE Tutor)) (EMPID (VALUE 376074)) (SUBJECT (VALUE Computers)))Ruchi Sharma ruchisharma1701@gmail.com http://www.wiziq.com/tutor-profile/376074-Ruchi
- 35. Understanding Propositional Logic – Facts Symbolic logic is a formalized system of logic which employs abstract symbols of various aspects of natural language.
- 36. Propositional logic is the simplest form of the symbolic logic, in which the knowledge is represented in the form of declarative statements called propositions.
- 37. Each proposition, denoted by a symbol, can assume either of the two values – true or false.EgP : It is raining.Q : The visibility is low. Ruchi Sharma ruchisharma1701@gmail.com http://www.wiziq.com/tutor-profile/376074-Ruchi
- 38. Understanding Propositional Logic – Facts (Contd.) Propositions are also called formulas or well-formed-formulas(wffs)
- 39. Formulas can be atomic or compound
- 40. Atomic formulas – elementary propositional sentences
- 41. Compound formulas – formed from the atomic formulas using logical connectives ( ^, V, !, ~, )eg R : It is raining and the visibility is low. Ruchi Sharma ruchisharma1701@gmail.com http://www.wiziq.com/tutor-profile/376074-Ruchi
- 42. Understanding Propositional Logic - ExamplesIf given the statements P, Q and S as : P : It is raining. Q : The visibility is low. S : I can’t drive. Then, the statement “It is raining and the visibility is low, so I can’t drive.” will be formalized as P ^ Q S If given the statements P & Q as : P : He needs a doctor. Q : He is unwell. we can conclude Q PRuchi Sharma ruchisharma1701@gmail.com http://www.wiziq.com/tutor-profile/376074-Ruchi
- 43. Understanding First order predicate logic (FOPL)FOPL was developed to extend the expressiveness of propositional logic.
- 44. It works by breaking a proposition into various parts & representing them as symbols.
- 45. The symbolic structure includes
- 46. individual symbols - some constants as names
- 47. variable symbols – as x, y, a, b etc
- 48. function symbols – as ‘product’
- 49. predicate symbols – as P, Q etc Ruchi Sharma ruchisharma1701@gmail.com http://www.wiziq.com/tutor-profile/376074-Ruchi
- 50. Understanding FOPL - ExampleGiven statements P: Every bird can fly. Q : Tweety is a bird. R : Tweety can fly.Using FOPL, lets define the following B(x) for x is a bird.F(x) for x can fly.P : V(x) ((B(x) F(X))Q : B(TWEETY))R : v(x)(B(x) F(x)) ^ B(TWEETY) F(TWEETY)Ruchi Sharma ruchisharma1701@gmail.com http://www.wiziq.com/tutor-profile/376074-Ruchi
- 51. Understanding Rule-based System – Facts A Rule-based system represents knowledge in the form of a set of rules .
- 52. Each rule represents a small chunk of knowledge relating to the given domain.
- 53. A number of related rules along with some known facts collectively may correspond to a chain of inferences.
- 54. An interpreter(inference engine) uses the facts & rules to derive conclusions about the current context & situation as presented by the user input. Ruchi Sharma ruchisharma1701@gmail.com http://www.wiziq.com/tutor-profile/376074-Ruchi
- 55. Understanding Rule-based System – Example Suppose a rule-based system has the following statements R1 : If A is an animal and A lays no eggs, then A is a mammal.F1 : Lucida is an animal.F2 : Lucida lays no eggs.The inference engine will update the rule base after interpreting the above set as : R1 : If A is an animal and A lays no eggs, then A is a mammal.F1 : Lucida is an animal.F2 : Lucida lays no eggs.F3 : Lucida is a mammal. Ruchi Sharma ruchisharma1701@gmail.com http://www.wiziq.com/tutor-profile/376074-Ruchi
- 56. Thank You Ruchi Sharma ruchisharma1701@gmail.com http://www.wiziq.com/tutor-profile/376074-Ruchi