Freshwater Ecosystems
- 2. ïŽA fresh water ecosystem is an aquatic system that contains drinkable water or water of almost no salty content. It has habitats classified by different factors, including temperature, light penetration, and vegetation. Its resources include lakes, ponds, rivers, streams, reservoirs, wetlands as well as groundwater.
- 3. Kinds of freshwater habitats ïŽ Rivers, â â â streams Flowing freshwater Source: where it starts Mouth: where it ends ïŽ Lakes, ponds ïŽ Wetlands
- 4. All freshwater ecosystems ïŽ Just â a fraction of the Earthâs water .01% = one one-hundredth of one percent ïŽ Occupy surface less than 1 percent of the Earthâs
- 5. Rivers and streams ïŽMore than 3.5 million miles of rivers and streams - Just the U.S.! More than 140 times around the Earth. www.noaa.gov/str-plan/images/river.gif
- 6. Rivers A river is usually cold and full of oxygen and runs swiftly through a shallow riverbed. As a river flows down a mountain, a river may broaden, become warmer, wider, and slower, and decrease in oxygen.
- 7. Rivers Narrow headwaters Wide channels downstream
- 8. Lakes and ponds ïŽWhatâs â â â the difference? Ponds typically smaller May be seasonalâthat is, dry up part of the year Lakes exist hundreds or thousands of years ïŽBut, even lakes can fill in or dry up
- 9. Parts of a lake
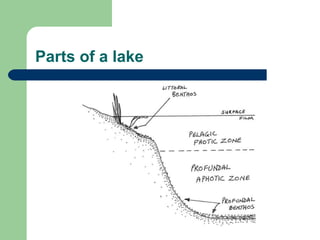
- 10. Parts of a lake ïŽ Littoral â â zone: near shore Nutrient rich, lots of plant and animal life Warm ïŽ Limnetic â â zone: near surface, open water Lots of light Lots of plankton ïŽ Profundal zone: deeper, little light ïŽ Benthic zone: the bottom, little light, low oxygen
- 11. Wetlands
- 12. Wetlands ïŽ Are those areas that are inundated or saturated by surface or ground water at a frequency and duration sufficient to support, and that under normal circumstances do support, a prevalence of vegetation typically adapted for life in saturated soil conditions. Wetlands generally include swamps, marshes, bogs and similar areas."
- 13. Wetlands ïŽMay be fresh or brackish ïŽFreshwater types include: Marsh â Swamp â Bog â Fen â
- 14. What good are wetlands? ïŽ Help â â clean water by acting like a filter The plants and slow water flow in a wetland help remove pollutants, leaving water cleaner downstream in a lake or river. Too much pollution can leave a wetland toxic to visiting animals, such as many birds.
- 15. What good are wetlands? ïŽ Protect shorelines from erosion ïŽ Erosion in this case came from grazing animals
- 16. Marsh ïŽ ïŽ ïŽ Most common freshwater wetland in U.S. Occur along streams or in depressions Characterized by organic, wet soils and non-woody (i.e., no trees) vegetation.
- 17. Marsh
- 18. Swamp ïŽ Wetland dominated by woody plants ïŽ Swamps occur on flat, poorly drained land often near streams.
- 19. Swamp
Editor's Notes
- #6: The miles of rivers and streams in the United States is equivalent to more than 140 times the circumference of the earth â 140 trips around the equator. Identify some of the regional rivers and streams known by the students.