friend function(c++)
- 2. Access privileges in C++. You have access privileges in C++ such as public, protected and private that helps in encapsulation of data at various level.
- 3. Private If data are declared as private in a class then it is accessible by the member functions of the class where they are declared. The private member functions can be accessed only by the members of the class. By default, any member of the class is considered as private by the C+ + compiler, if no specifier is declared for the member. Public The member functions with public access specifier can be accessed outside of the class. This kind of members is accessed by creating instance of the cass.
- 4. ïProtected Protected members are accessible by the class itself and it's sub- classes. The members with protected specifier act exactly like private as long as they are referenced within the class or from the instance of the class. This specifier specially used when you need to use inheritance facility of C++. The protected members become private of a child class in case of private inheritance, public in case of public inheritance, and stay protected in case of protected inheritance.
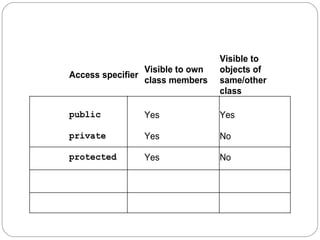
- 5. Access specifier Visible to own class members Visible to objects of same/other class public Yes Yes private Yes No protected Yes No
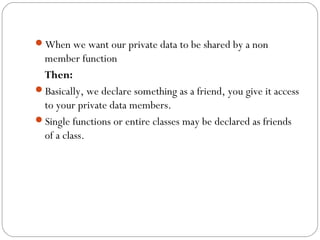
- 6. ïWhen we want our private data to be shared by a non member function Then: ïBasically, we declare something as a friend, you give it access to your private data members. ïSingle functions or entire classes may be declared as friends of a class.
- 7. âĒ A Friend function is a non-member function of the class that has been granted access to all private members of the class. âĒ We simply declare the function within the class by a prefixing its declaration with keyword friend. âĒ Function definition must not use keyword friend. âĒ Definition of friend function is specified outside the class body and is not treated as a part of the class. âĒ The major difference b/w member function and friend function is that the member function is accessed through the object while friend function requires object to be passed as parameter.
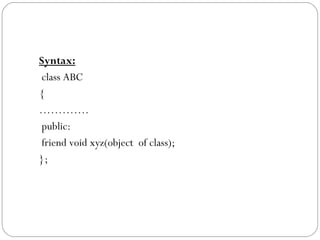
- 8. Syntax: class ABC { âĶâĶâĶâĶ. public: friend void xyz(object of class); };
- 9. Friend function characterstics ïIt is not in scope of class. ïIt cannot be called using object of that class. ïIt can be invoked like a normal function. ïIt should use a dot operator for accessing members. ïIt can be public or private. ïIt has objects as arguments. ïPerhaps the most common use of friend functions is overloading << and >> for I/O.
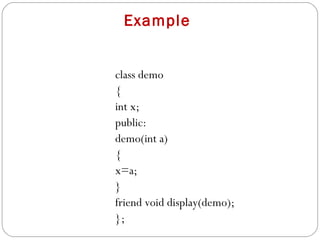
- 10. Example class demo { int x; public: demo(int a) { x=a; } friend void display(demo); };
- 11. void display(demo d1) { cout<<d1.x; } void main() { demo d2(5); display(d2); }
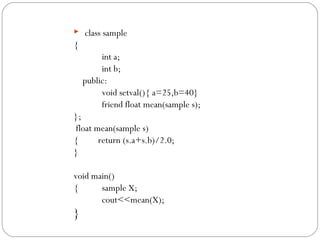
- 12. ï― class sample { int a; int b; public: void setval(){ a=25,b=40} friend float mean(sample s); }; float mean(sample s) { return (s.a+s.b)/2.0; } void main() { sample X; cout<<mean(X); }
- 13. Friend class ïIn previous section of class we declared only one function as a friend of another class.but it is possible that all member of the one class can be friend of another class.this is friend class
- 14. Friends (a few gory details) ïFriendship is not inherited, transitive, or reciprocal. ïDerived classes donât receive the privileges of friendship (more on this when we get to inheritance in a few classes). ïThe privileges of friendship arenât transitive. If class A declares class B as a friend, and class B declares class C as a friend, class C doesnât necessarily have any special access rights to class A. ïIf class A declares class B as a friend (so class B can see class Aâs private members), class A is not automatically a friend of class B (so class A cannot necessarily see the private data members of class B). ïFriendship is not inherited, transitive, or reciprocal.
- 15. Example class demo { private: int x,y; public: demo(int a,int b) { x=a; y=b; } friend class frnd; };
- 16. class frnd { public: void display(demo d1) { cout<<âx is=âd1.x; cout<<ây is=âd1.y; } };
- 17. void main() { demo d2(10,40); frnd f1; f1.display(d2); getch(); }
- 18. This pointer Every object in C++ has access to its own address through an important pointer called this pointer. The this pointer is an implicit parameter to all member functions. Therefore, inside a member function, this may be used to refer to the invoking object. Friend functions do not have a this pointer, because friends are not members of a class. Only member functions have a this pointer.