Fuel presentation1
- 2. Avgas âĒ Aviation fuel is a specialized type of petroleum-based fuel used to power aircraft. âĒ Generally of a higher quality than fuels used in less critical applications such as heating or road transport, and often contains additives to reduce the risk of icing or explosion due to high temperatures, amongst other properties.
- 4. Avgas âĒ Avgas (aviation gasoline) is an aviation fuel used to power piston-engine aircraft. âĒ It can be distinguished from mogas (motor gasoline), which is the everyday petroleum spirit used in cars. âĒ Avgas is formulated for stability, safety, and predictable performance under a wide range of environments. âĒ Avgas is typically used in aircraft that use reciprocating or wankel engines. âĒ Dyes for the fuel are required in some countries.
- 5. Avgas âĒ Aviation fuels consist of blends of over a thousand chemicals: â primarily Hydrocarbons (paraffins, olefins, naphth enes, and aromatics) as well as additives such as antioxidants and metal deactivators, and impurities. â Principal components include n-octane, isooctane. â Like other fuels, blends of Aviation fuel used in piston engine aircraft are often described by their Octane rating.
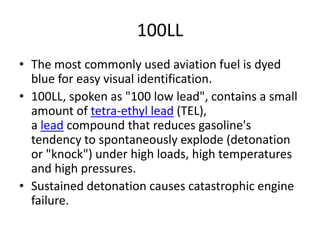
- 6. 100LL âĒ The most commonly used aviation fuel is dyed blue for easy visual identification. âĒ 100LL, spoken as "100 low lead", contains a small amount of tetra-ethyl lead (TEL), a lead compound that reduces gasoline's tendency to spontaneously explode (detonation or "knock") under high loads, high temperatures and high pressures. âĒ Sustained detonation causes catastrophic engine failure.
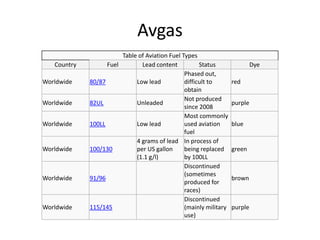
- 7. Avgas Table of Aviation Fuel Types Country Fuel Lead content Status Dye Phased out, Worldwide 80/87 Low lead difficult to red obtain Not produced Worldwide 82UL Unleaded purple since 2008 Most commonly Worldwide 100LL Low lead used aviation blue fuel 4 grams of lead In process of Worldwide 100/130 per US gallon being replaced green (1.1 g/l) by 100LL Discontinued (sometimes Worldwide 91/96 brown produced for races) Discontinued Worldwide 115/145 (mainly military purple use)
- 9. Donât Lie About Your Fuel State âĒ Iâve never overloaded my airplane âĒ I have the traffic in sight âĒ Yes, tower, I responded. You didn't hear me? âĒ You're not picking up my squawk code? Here, let me recycle the transponder âĒ I have the check-list memorized âĒ I broke out of the clouds right at minimums
- 10. Still???? âĒ http://www.google.com/search?um=1&hl=en &safe=off&biw=1024&bih=707&q=the%20run way%20behind%20you&ie=UTF- 8&sa=N&tab=iw#sclient=psy&hl=en&safe=off &biw=1024&bih=707&source=hp&q=aircraft+ crash+ran+out+of+fuel&aq=f&aqi=&aql=&oq= &pbx=1&bav=on.2,or.r_gc.r_pw.&fp=a316b5c db3fe9040
- 11. Weight & Balance âĒ Avgas has a density of 6.02 lb/U.S. gal at 15 °C, or 0.721 kg/l, and this density is commonly used for weight and balance computation. âĒ Density increases to 6.40 lb/US gallon at -40 °C, and decreases by about 0.5% per 5 °C (9 °F) increase in temperature. âĒ As you use fuel, your CG will move.
- 12. ?Hybrid?
- 13. Very Important
- 14. Whatâs Going In? âĒ Be present when Fuel is pumped. â Quantity â Quality â Correctness â Damage to A/C
- 15. Cases On March 2, 2008, a turbo-normalized Cirrus SR22 was destroyed when it crashed shortly after takeoff in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, killing all four people aboard. Shortly after the aircraft departed from Runway 20, the airplane's engine lost power, and the aircraft hit a building and exploded. Further investigation revealed that the aircraft had been refueled with Jet A instead of 100LL.
- 16. Effects of Contamination âĒ Zero Octane âĒ Instant destructive detonation âĒ You will loose the engine
- 17. The Fuel System âĒ Tanks âĒ Lines âĒ Vents âĒ Drains âĒ Primer âĒ Gauges âĒ Fuel Pump & Gravity Feed
- 18. Fuel Pump System âĒ Usually found in Low Wing Aircraft âĒ High Performance aircraft with Fuel Injected engines âĒ Usually will have a boost pump (Aux Pump)
- 19. Question In all fuel injected aircraft, if the engine fuel pump fails you will still be able to run the engine if the aux fuel pump is activated? False
- 20. Fuel Pressure Fuel Pressure Gauge Fuel Pump âĒ Cherokee Six âĒ Lycoming
- 21. The Relationship
- 22. Low Wing Design
- 23. High Wing Gravity Feed
- 24. Gravity Feed
- 25. Question In order to maximize range performance, on aircraft equipped with more than one fuel tank, it is common and safe to run a tank completely dry before switching fuel tanks. Vapor Lock
- 26. Question Once vapor lock is induced, there are steps a pilot can take while flying to counter it. False
- 27. Fuel Tank Venting/Overflow Drain
- 28. Fuel Gauges
- 29. The Digital Age
- 30. More Reasonable
- 32. Fuel Cross Feed
- 33. Question Using a fuel grade higher than specified can cause cylinder head and engine temperatures to exceed normal operating limits. False
- 34. Question You arrive at your aircraft for a flight and realize you need fuel. The fuel should be drained and checked immediately following the filling/adding of fuel to the fuel tanks. False
- 35. Fuel Tips âĒ Infrequently used fuel tanks should have their sumps drained before filling âĒ Agitation action of fuel entering the tank may suspend or entrain liquid water or other contaminants. âĒ After fueling, wait at least 15 minutes per foot of depth of the tank before sumping
- 36. AC-20-125 âĒ How much fuel says the FAA? â 10 ounces or more!! âĒ Cross feed and multiple tanks should be checked separately.
- 37. 3 Useless Things in Aviation ïThe runway behind you ïThe sky above you ïThe Fuel in the truck