Fuels from crude oil
- 1. Topic: Introduction – the alkanes
- 2. • Intoduction • Cycloalkanes • Structure of an alkane • Structure of Saturated hydrocarbons • Crude oil • Fractional distillation • Videos 14.1 – 14.2 (pg. 215-217)
- 3. Crude oil is a mixture of compounds called hydrocarbons. Many useful materials can be produced from crude oil. It can be separated into different fractions using fractional distillation, and some of these can be used as fuels. Unfortunately, there are environmental consequences when fossil fuels such as crude oil and its products are used. • Hydrocarbons Most of the compounds in crude oil are hydrocarbons. This means that they only contain hydrogen and carbon atoms, joined together by chemical bonds. There are different types of hydrocarbon, but most of the ones in crude oil are alkanes. • Alkanes The alkanes are a family of hydrocarbons that share the same general formula. This is: CnH2n+2 The general formula means that the number of hydrogen atoms in an alkane is double the number of carbon atoms, plus two. For example, methane is CH4 and ethane is C2H6. Alkane molecules can be represented by displayed formulae in which each atom is shown as its symbol (C or H) and the chemical bonds between them by a straight line.
- 4. Cycloalkanes Cycloalkanes again only contain carbon-hydrogen bonds and carbon-carbon single bonds, but this time the carbon atoms are joined up in a ring. The smallest cycloalkane is cyclopropane. If you count the carbons and hydrogens, you will see that they no longer fit the general formula CnH2n+2. By joining the carbon atoms in a ring, you have had to lose two hydrogen atoms. You are unlikely to ever need it, but the general formula for a cycloalkane is CnH2n. Don't imagine that these are all flat molecules. All the cycloalkanes from cyclopentane upwards exist as "puckered rings". This is known as the "chair" form of cyclohexane - from its shape which vaguely resembles a chair.
- 7. Crude oil Crude oil forms naturally over millions of years from the remains of living things. Most of the compounds in crude oil are hydrocarbons. These are compounds that contain hydrogen and carbon atoms only, joined together by chemical bonds called covalent bonds. There are different types of hydrocarbon, but most of the ones in crude oil are alkanes.
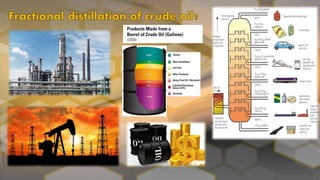
- 9. • Fractional distillation is different from distillation in that it separates a mixture into a number of different parts, called fractions. • A tall column is fitted above the mixture, with several condensers coming off at different heights. • The column is hot at the bottom and cool at the top. Substances with high boiling points condense at the bottom and substances with lower boiling points condense on the way to the top. • The crude oil is evaporated and its vapors condense at different temperatures in the fractionating column. • Each fraction contains hydrocarbon molecules with a similar number of carbon atoms.
- 10. Because they have different boiling points, the substances in crude oil can be separated using fractional distillation. The crude oil is evaporated and its vapours allowed to condense at different temperatures in the fractionating column. Each fraction contains hydrocarbon molecules with a similar number of carbon atoms. As you go up the fractionating column, the hydrocarbons have: •lower boiling points •lower viscosity (they flow more easily) •higher flammability (they ignite more easily). This means that in general hydrocarbons with small molecules make better fuels than hydrocarbons with large molecules.