Functions of motherboard
- 1. Presented By Aman Sharma Anuj Gupta Yash Bhoir
- 2. Introduction ’é× A motherboard, also known as the primary circuit inside the computer, and where the central processing unit(CPU), Memory slots, drives and other peripherals. ’é× A motherboard provides the electrical connections by which the other components of the system communicate. it also connects the central processing unit and hosts other subsystems and devices. ’é× An important component of a motherboard is the microprocessor's supporting chipset, which provides the supporting interfaces between the CPU and the various buses and external components. This chipset determines, to an extent, the features and capabilities of the motherboard.
- 3. Form Factor ’é× An important component of a motherboard is the microprocessor's supporting chipset, which provides the supporting interfaces between the CPU and the various buses and external components. This chipset determines, to an extent, the features and capabilities of the motherboard. ’é× Motherboard form factor Determines the size of the board Drives selection of power supply, case, CPU, cards ’é× ATX: most popular motherboard form factor ’é× BTX: the latest motherboard form factor ’é× Three types of motherboards you can select: ’éŚ A board providing the most room for expansion ’éŚ A board suiting the computerŌĆÖs current configuration ’éŚ A board falling in between current and future needs
- 6. Micro ATX motherboard ŌĆó Laptop computers generally use highly integrated, miniaturized and customized motherboards. This is one of the reasons that laptop computers are difficult to upgrade and expensive to repair. ŌĆó Often the failure of one laptop component requires the replacement of the entire motherboard, which is usually more expensive than a desktop motherboard due to the large number of integrated components.
- 7. Motherboard Components 1.Clock Generator 2. CPU socket 3. Memory Socket Memory error checking 4. ROM Bios 5. CMOS Ram 6. Battery 7. Chipset 8. Expansion Slot 9. AGP Port 10. IDE Ports 10.1 IDE Port continue 10.2 IDE Port continue 10.3 IDE Port with Raid 10.4 Serial ATA 11. Floppy Disk port 12. IO Connectors/USB ports USB port add more printer ports 13. Main Power Connector1 14. Front Panel Connecting Pin
- 8. ’é× A chipset is a set of electronic components in an integrated circuit that manages the data flow between the processor, memory and peripherals. It is usually found in the motherboard of a computer. Chipsets are usually designed to work with a specific family of microprocessors. Because it controls communications between the processor and external devices, the chipset plays a crucial role in determining system performance. CHIPSET
- 9. Internal Structure of North bridge & South bridge
- 10. Memory Socket( DIMM socket) ’é× There are 3 types of memory that currently popular used in the PC, 1. RD RAM 2. DDR RAM 3. SD RAM
- 11. ContinueŌĆ”. RDRAM Memory -Used in Pentium 4 motherboard - 2 Notches -highest performance and is most expensive. DDR ram -128 MB, 256 MB, 512 MB. -medium high performance and medium price. SDRAM -lowest performance and lowest price.
- 12. CPU Socket ’é× A CPU socket or slot is an electrical component that attaches to a printed circuit board (PCB) and is designed to house a CPU (also called a microprocessor). ’é× It is a special type of integrated circuit socket designed for very high pin counts. ’é× CPU sockets on the motherboard can most often be found in most desktop and server computers (laptops typically use surface mount CPUs), particularly those based on the Intelx86 architecture.
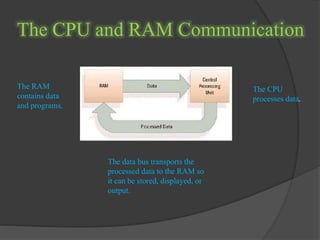
- 13. The CPU and RAM Communication The CPU processes data. The RAM contains data and programs. The data bus transports the processed data to the RAM so it can be stored, displayed, or output.
- 14. Read-Only Memory can be read but not changed. It is non-volatile storage: it remembers its contents even when the power is turned off. ROM chips are used to store the instructions a computer needs during start-up, called firmware. Some kinds of ROM are PROM, EPROM, EEPROM, and CD-ROM. ROM BIOS
- 15. CMOS Battery ŌĆó This is a 3 volt battery, this battery supplies the power to CMOS ram for CMOS ram to retain the information during system powered off, the battery may be last for 5 or 6 years.
- 16. Expansion Slot ( PCI type ) ’é× Expansion slot or Expansion bus is the slot that enable the user to add the adapter card for additional function to the system Ex. -Sound card or Multimedia - LAN card. -SCSI controller card. - Internal Modem card. -TV tuner card. -Additional hard disc controller card.
- 17. AGP Port AGP ( Accelerated Graphic Port ) port is a high speed data transfer port, this port is used by the display adapter card that demands so much data with in short period of time.
- 19. Bibliography ’é× http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motherboard ’é× http://www.oocities.org/inhs_iloilo/Refere nces/motherboard.pdf ’é× http://www.beyourownit.com/motherboar d-basics.html ’é× http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CPU_socket