Funtions of c programming. the functions of c helps to clarify all the tops
- 2. Introduction ŌĆó A function is a block of code that performs a specific task. ŌĆó A function is a set of statements that take inputs, do some specific computation and produces output. ŌĆó The idea is to put some commonly or repeatedly done task together and make a function, so that instead of writing the same code again and again for different inputs, we can call the function. ŌĆó Function helps in dividing complex problem into small components makes program easy to understand and use.
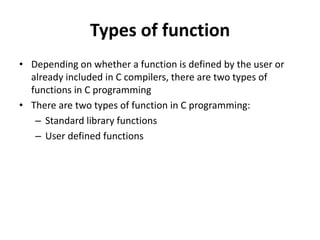
- 3. Types of function ŌĆó Depending on whether a function is defined by the user or already included in C compilers, there are two types of functions in C programming ŌĆó There are two types of function in C programming: ŌĆō Standard library functions ŌĆō User defined functions
- 4. Standard library functions ŌĆó The standard library functions are built-in functions in C programming to handle tasks such as mathematical computations, I/O processing, string handling etc. ŌĆó These functions are defined in the header file. When you include the header file, these functions are available for use. For example: ŌĆó The printf() is a standard library function to send formatted output to the screen (display output on the screen). This function is defined in "stdio.h" header file. ŌĆó There are other numerous library functions defined under "stdio.h", such as scanf(), fprintf(), getchar() etc. Once you include "stdio.h" in your program, all these functions are available for use.
- 5. User-defined function ŌĆó Functions created by the user are called user-defined functions. ŌĆó User defined function has basically following characteristics ŌĆō A function is named with unique name ŌĆō A function performs a specific task ŌĆō A function is independent ŌĆō A function may receive values from the calling program (caller) ŌĆō A function may return a value to the calling program
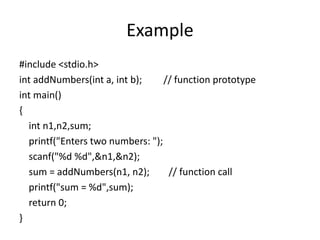
- 6. Example #include <stdio.h> int addNumbers(int a, int b); // function prototype int main() { int n1,n2,sum; printf("Enters two numbers: "); scanf("%d %d",&n1,&n2); sum = addNumbers(n1, n2); // function call printf("sum = %d",sum); return 0; }
- 7. int addNumbers(int a,int b) // function definition { int result; result = a+b; return result; // return statement }
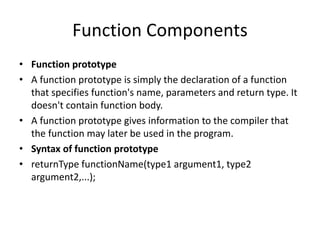
- 8. Function Components ŌĆó Function prototype ŌĆó A function prototype is simply the declaration of a function that specifies function's name, parameters and return type. It doesn't contain function body. ŌĆó A function prototype gives information to the compiler that the function may later be used in the program. ŌĆó Syntax of function prototype ŌĆó returnType functionName(type1 argument1, type2 argument2,...);
- 9. ŌĆó For example int addNumbers(int a, int b); ŌĆó It is the function prototype which provides following information to the compiler: ŌĆó name of the function is addNumbers() ŌĆó return type of the function is int ŌĆó two arguments of type int are passed to the function ŌĆó The function prototype is not needed if the user-defined function is defined before the main() function.
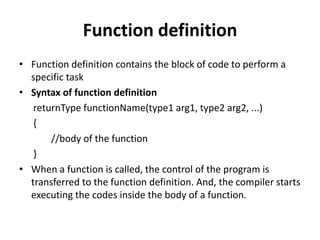
- 10. Function definition ŌĆó Function definition contains the block of code to perform a specific task ŌĆó Syntax of function definition returnType functionName(type1 arg1, type2 arg2, ...) { //body of the function } ŌĆó When a function is called, the control of the program is transferred to the function definition. And, the compiler starts executing the codes inside the body of a function.
- 11. Calling a function ŌĆó Control of the program is transferred to the user-defined function by calling it. ŌĆó Syntax of function call functionName(argument1, argument2, ...); ŌĆó For example void main() { addNumbers(n1,n2); }
- 12. Passing arguments to a function ŌĆó In programming, argument refers to the variable passed to the function. ŌĆó In the above example, two variables n1 and n2 are passed during function call. ŌĆó The parameters a and b accepts the passed arguments in the function definition. These arguments are called formal parameters of the function. ŌĆó The type of arguments passed to a function and the formal parameters must match, otherwise the compiler throws error. ŌĆó If n1 is of char type, a also should be of char type. If n2 is of float type, variable b also should be of float type. ŌĆó A function can also be called without passing an argument.
- 14. Return Statement ŌĆó The return statement terminates the execution of a function and returns a value to the calling function. ŌĆó The program control is transferred to the calling function after return statement. ŌĆó In the above example, the value of variable result is returned to the variable sum in the main() function.
- 16. Syntax of return statement ŌĆó return (expression); ŌĆó For example, ŌĆō return a; ŌĆō return (a+b); ŌĆó The type of value returned from the function and the return type specified in function prototype and function definition must match.
- 17. Types of User-defined Functions in C Programming ŌĆó No arguments passed and no return value ŌĆó No arguments passed but a return value ŌĆó Argument passed but no return value ŌĆó Argument passed and a return value
- 18. C Recursion ŌĆó A function that calls itself is known as a recursive function. And, this technique is known as recursion.
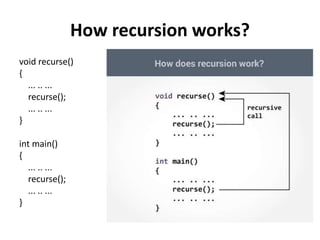
- 19. How recursion works? void recurse() { ... .. ... recurse(); ... .. ... } int main() { ... .. ... recurse(); ... .. ... }
- 20. ŌĆó The recursion continues until some condition is met to prevent it. ŌĆó To prevent infinite recursion, if...else statement (or similar approach) can be used where one branch makes the recursive call and other doesn't.
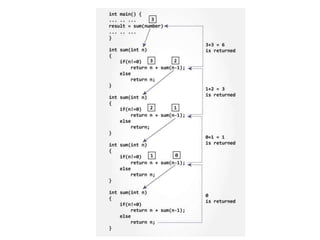
- 21. Sum of Natural Numbers Using Recursion #include <stdio.h> int sum(int n); int main() { int number, result; printf("Enter a positive integer: "); scanf("%d", &number); result = sum(number); printf("sum = %d", result); return 0; }
- 22. int sum(int num) { if (num!=0) return num + sum(num-1); // sum() function calls itself else return num; }
- 23. ŌĆó Initially, the sum() is called from the main() function with number passed as an argument. ŌĆó Suppose, the value of num is 3 initially. During next function call, 2 is passed to the sum() function. This process continues until num is equal to 0. ŌĆó When num is equal to 0, the if condition fails and the else part is executed returning the sum of integers to the main() function.
- 25. Advantages and Disadvantages of Recursion ŌĆó Recursion makes program elegant and more readable. However, if performance is vital then, use loops instead as recursion is usually much slower. ŌĆó Note that, every recursion can be modeled into a loop. ŌĆó Recursion Vs Iteration? Need performance, use loops, however, code might look ugly and hard to read sometimes. Need more elegant and readable code, use recursion, however, you are sacrificing some performance.
- 26. How to pass arrays to a function ŌĆó Passing One-dimensional Array to a Function ŌĆó Passing a single element of an array to a function is similar to passing variable to a function. #include <stdio.h> void display(int age) { printf("%d", age); } void main() { int a[] = {2, 3, 4}; display(a[2]); //Passing array element a[2] }
- 27. Passing an entire array to a function #include <stdio.h> float average(int []); void main() { float avg; int age[] = {23, 55, 22, 5, 40, 18}; avg = average(age); // Only name of an array is passed as an argument printf("Average age = %.2f", avg); }
- 28. float average(int age[]) { int i,sum=0; float avg; for (i = 0; i < 6; ++i) { sum += age[i]; } avg = (float)sum / 6; return avg; }
- 29. Passing Multi-dimensional Arrays to Function ŌĆó To pass multidimensional arrays to a function, only the name of the array is passed (similar to one dimensional array). #include <stdio.h> void displayNumbers(int num[2][2]); void main() { int num[2][2], i, j; printf("Enter 4 numbers:n"); for (i = 0; i < 2; ++i) for (j = 0; j < 2; ++j) scanf("%d", &num[i][j]); displayNumbers(num); // passing multi-dimensional array to a function }
- 30. void displayNumbers(int num[2][2]) { int i, j; printf("Displaying:n"); for (i = 0; i < 2; ++i) for (j = 0; j < 2; ++j) printf("%dn", num[i][j]); }



















![How to pass arrays to a function
ŌĆó Passing One-dimensional Array to a Function
ŌĆó Passing a single element of an array to a function is similar
to passing variable to a function.
#include <stdio.h>
void display(int age)
{
printf("%d", age);
}
void main()
{
int a[] = {2, 3, 4};
display(a[2]); //Passing array element a[2]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit7-240508025210-ad24d345/85/Funtions-of-c-programming-the-functions-of-c-helps-to-clarify-all-the-tops-26-320.jpg)
![Passing an entire array to a function
#include <stdio.h>
float average(int []);
void main()
{
float avg;
int age[] = {23, 55, 22, 5, 40, 18};
avg = average(age); // Only name of an array is passed as
an argument
printf("Average age = %.2f", avg);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit7-240508025210-ad24d345/85/Funtions-of-c-programming-the-functions-of-c-helps-to-clarify-all-the-tops-27-320.jpg)
![float average(int age[])
{
int i,sum=0;
float avg;
for (i = 0; i < 6; ++i) {
sum += age[i];
}
avg = (float)sum / 6;
return avg;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit7-240508025210-ad24d345/85/Funtions-of-c-programming-the-functions-of-c-helps-to-clarify-all-the-tops-28-320.jpg)
![Passing Multi-dimensional Arrays to Function
ŌĆó To pass multidimensional arrays to a function, only the name
of the array is passed (similar to one dimensional array).
#include <stdio.h>
void displayNumbers(int num[2][2]);
void main()
{
int num[2][2], i, j;
printf("Enter 4 numbers:n");
for (i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
for (j = 0; j < 2; ++j)
scanf("%d", &num[i][j]);
displayNumbers(num); // passing multi-dimensional array to a
function
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit7-240508025210-ad24d345/85/Funtions-of-c-programming-the-functions-of-c-helps-to-clarify-all-the-tops-29-320.jpg)
![void displayNumbers(int num[2][2])
{
int i, j;
printf("Displaying:n");
for (i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
for (j = 0; j < 2; ++j)
printf("%dn", num[i][j]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit7-240508025210-ad24d345/85/Funtions-of-c-programming-the-functions-of-c-helps-to-clarify-all-the-tops-30-320.jpg)