G4 - Forces and Motion (1) balanced and unbalanced forces.pptx
- 1. The Science Behind Tug-of-War Balanced and Unbalanced Forces
- 2. Have you played Tug-of-War? Let's unveil the science behind this game!
- 3. Effects of Force and Motion Grade 4 Quarter 3 - Module 1
- 4. Learning Outcomes • explain the effects of force when applied to an object; • describe the force exerted by a magnet; and • practice safety measures in physical activities and proper handling of materials.
- 5. Questions: Today's • What is the difference between balanced and unbalanced forces? • How do forces act on objects?
- 6. What is Force? Push Pull Force is a push or pull that changes an object's state of rest or motion. It is a vector quantity which has a magnitude and direction.
- 7. A balanced force results when two forces with the same amount are applied in opposite directions. Same force In this scene of tug-of-war, both teams pull away with the same force. There are no changes in the direction or motion of object. Balanced Force Team A Team B
- 8. Unbalanced Force Less force An unbalanced force results when one of the two forces applied in opposite directions is greater than the other. Greater force In this tug-of-war scene, Team B pulls away with greater force than Team A. The tie on the rope moves closer to Team B. Unbalanced force Team A Team B
- 9. Let's Think Two forces of opposite directions are acted upon the box. What do you think is the direction of the boxes' movement? Same force A B Less force Greater force
- 10. Contact Forces occur when two objects are in physical contact with each other. In order for contact force to occur, there must be a point of direct contact between the objects.
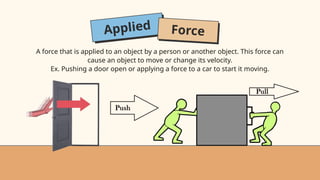
- 11. Applied Force A force that is applied to an object by a person or another object. This force can cause an object to move or change its velocity. Ex. Pushing a door open or applying a force to a car to start it moving.
- 12. Air Resistance A type of force that is exerted by the air particles in the atmosphere. It is directed opposite to the direction of motion of the object moving in the air. Objects that are moving fast experience greater air resistance. Ex. When you ride a bicycle, air resistance pushes against you as you move forward.
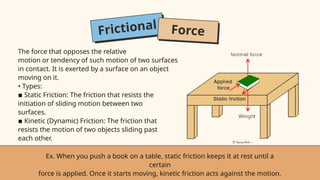
- 13. Frictional Force The force that opposes the relative motion or tendency of such motion of two surfaces in contact. It is exerted by a surface on an object moving on it. • Types: ▪ Static Friction: The friction that resists the initiation of sliding motion between two surfaces. ▪ Kinetic (Dynamic) Friction: The friction that resists the motion of two objects sliding past each other. Ex. When you push a book on a table, static friction keeps it at rest until a certain force is applied. Once it starts moving, kinetic friction acts against the motion.
- 15. Recall When unbalanced forces are acted upon an object at rest, the object will move in the direction pushed or pulled by the stronger force. Which way will the boxes move?
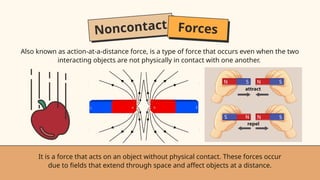
- 16. Noncontact Forces Also known as action-at-a-distance force, is a type of force that occurs even when the two interacting objects are not physically in contact with one another. It is a force that acts on an object without physical contact. These forces occur due to fields that extend through space and affect objects at a distance.
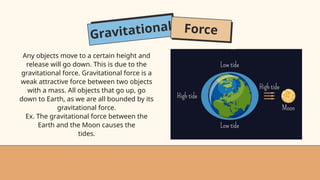
- 17. Gravitational Force Any objects move to a certain height and release will go down. This is due to the gravitational force. Gravitational force is a weak attractive force between two objects with a mass. All objects that go up, go down to Earth, as we are all bounded by its gravitational force. Ex. The gravitational force between the Earth and the Moon causes the tides.
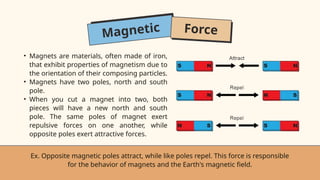
- 18. Magnetic Force • Magnets are materials, often made of iron, that exhibit properties of magnetism due to the orientation of their composing particles. • Magnets have two poles, north and south pole. • When you cut a magnet into two, both pieces will have a new north and south pole. The same poles of magnet exert repulsive forces on one another, while opposite poles exert attractive forces. Ex. Opposite magnetic poles attract, while like poles repel. This force is responsible for the behavior of magnets and the Earth's magnetic field.
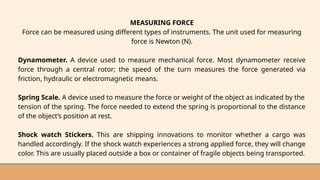
- 19. MEASURING FORCE Force can be measured using different types of instruments. The unit used for measuring force is Newton (N). Dynamometer. A device used to measure mechanical force. Most dynamometer receive force through a central rotor; the speed of the turn measures the force generated via friction, hydraulic or electromagnetic means. Spring Scale. A device used to measure the force or weight of the object as indicated by the tension of the spring. The force needed to extend the spring is proportional to the distance of the object’s position at rest. Shock watch Stickers. This are shipping innovations to monitor whether a cargo was handled accordingly. If the shock watch experiences a strong applied force, they will change color. This are usually placed outside a box or container of fragile objects being transported.
- 21. EFFECTS OF FORCES APPLIED ON OBJECTS
- 22. EFFECTS OF FORCE A. Force on Change in Speed The applied force can be easily visualized, especially if we are the ones to exert it. On the other hand, other types of forces cannot be seen directly, and their effects are the only indicators that they exist. • An unbalanced force is needed to change the motion of an object. • A net force greater than zero can make the object at rest move, and an object in motion stop. • Increasing the amount of force acting on an object changes its speed, making it faster to reach a farther distance, and decreasing the force acting on it makes the object move slower to travel a shorter distance.
- 23. EFFECTS OF FORCE B. Force on Change in Direction • The amount of force acting on an object affects the direction of motion. • If the pair of forces with opposing directions are not equal, the direction of the force is dependent on where the stronger force is directed, and if the pair of forces with opposing directions are equal, the objects tend to be at rest or in no motion at all.
- 24. EFFECTS OF FORCE C. Force on Change in Shape • When you tear, stretch, and squeeze on an object, you change its size and shape. • Stretching is an applied force that increase the length of an object while shearing or compressing force is a force that decreases the length or size through squeezing or pressing. • Aside from stretching and shearing, another type of contact force is twisting. It is another type of applied force that changes the orientation of the object.
- 25. DESCRIBING THE FORCE EXERTED BY A MAGNET
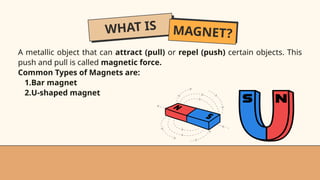
- 26. WHAT IS MAGNET? A metallic object that can attract (pull) or repel (push) certain objects. This push and pull is called magnetic force. Common Types of Magnets are: 1.Bar magnet 2.U-shaped magnet
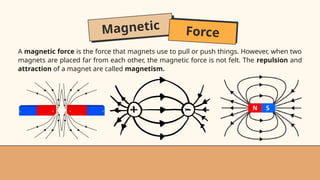
- 27. Magnetic Force A magnetic force is the force that magnets use to pull or push things. However, when two magnets are placed far from each other, the magnetic force is not felt. The repulsion and attraction of a magnet are called magnetism.
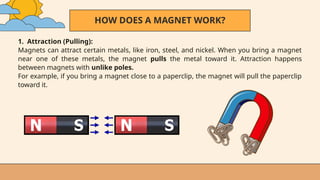
- 28. HOW DOES A MAGNET WORK? 1. Attraction (Pulling): Magnets can attract certain metals, like iron, steel, and nickel. When you bring a magnet near one of these metals, the magnet pulls the metal toward it. Attraction happens between magnets with unlike poles. For example, if you bring a magnet close to a paperclip, the magnet will pull the paperclip toward it.
- 29. HOW DOES A MAGNET WORK? 2. Repulsion (Pushing): If you take two magnets and bring the same poles (the north and north, or south and south) close together, the magnets will push each other away. This is called repelling. For example, if you try to push the north poles of two magnets together, they will push away from each other
- 30. TYPES OF MAGNETIC FORCE • Magnet’s North and South Poles: Every magnet has two ends (called poles)—a north pole and a south pole. The force from a magnet is invisible, but you can feel it when the magnet pulls or pushes objects around it o Opposite poles attract: The north pole of one magnet will attract the south pole of another magnet. o Same poles repel: Two north poles or two south poles will push away from each other. Example: • If you hold a magnet above a paperclip, the magnet will pull the paperclip toward it. This is because the magnet exerts a magnetic force. • If you have two magnets and bring the same poles (north to north, or south to south) close together, you will feel them push away. This is the force of repelling.
- 31. Resource Page Happy designing! Don't forget to delete this page before presenting. Use these icons and illustrations in your Canva Presentation.
- 32. Press these keys while on Present mode! for a drumroll for bubbles for blur for unveil for mic drop for quiet for confetti Any number from 0-9 for a timer B Resource Page C Q D M O U 0 - 9
- 33. Kindly delete this note before downloading. Thank you! Try this background for online class.