GABA neurotransmitter
- 1. G A B A - N E U R O T R A N S M I T T E R ( g a m m a - a m i n o b u t y r i c a c i d ) P R E S E N T E D B Y : N O O R A F S H A N M E M O N ( B M - 8 6 - 2 0 1 8 ) R I M S H A A Z M AT ( B M - 8 7 - 2 0 1 8 ) A I S H A JA M A L I ( B M - 8 5 - 2 0 1 8 )
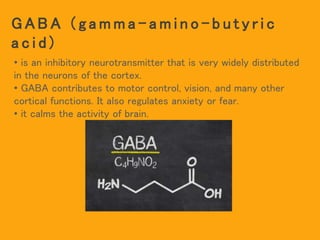
- 2. G A B A ( g a m m a - a m i n o - b u t y r i c a c i d ) • is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that is very widely distributed in the neurons of the cortex. • GABA contributes to motor control, vision, and many other cortical functions. It also regulates anxiety or fear. • it calms the activity of brain.
- 3. D I S C O V E R Y O F G A B A : • in 19th century, it was known as the metabolite of plants & micro organisms. • in 20th century , through the process of chromatography it was isolated as amino acid from the brain of the mouse. • In 1950, Robert & Frankel discovered that GABA acts as a inhibitory neurotransmitter in human brain.
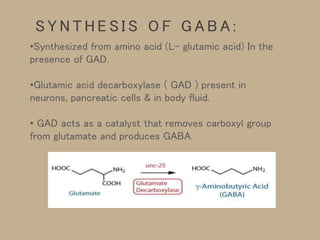
- 4. •Synthesized from amino acid (L- glutamic acid) In the presence of GAD. •Glutamic acid decarboxylase ( GAD ) present in neurons, pancreatic cells & in body fluid. • GAD acts as a catalyst that removes carboxyl group from glutamate and produces GABA. S Y N T H E S I S O F G A B A :
- 5. S TO R A G E O F G A B A : • Newly synthesized GABA is stored in synaptic vesicle by means of vesicular transporter. •These are stored at post synaptic terminal until action potential is released. R E L E A S I N G O F G A B A : •The stored GABA releases into synaptic cleft stimulated by depolarization of pre synaptic neurons. •GABA diffuses across the cleft to target receptors on post synaptic surface. •The action of GABA is terminated by presynaptic nerve terminal & glial cells
- 7. THANK-YOU!!