Game as an interface
- 1. Game as an Interactive Interface Gameplay Usability Taras Korol, Ubisoft Kiev
- 2. Ubisoft approach Ubisoft Game Usability Criteria Avoid confusion ’é¦ Signs Make playing comfortable ’é¦ Minimum workload Cues to provoke action. Provide information about the state of the system ’é¦ Feedback A response to a playerŌĆÖs actions. Provides information about the consequences of these actions ’é¦ Perceptibility To be useful, information has to be seen / felt or heard, ie perceived. ’é¦ Consistency Actions outside the gameplay loop should require minimum efforts from the player ’é¦ Error management For actions not related to the game loop, help the players to prevent fatal errors and solve errors when they occur ’é¦ Flexibility Each player is unique. Players should be able to customize the game to suit their needs and preferences. Similar things have similar meanings & similar behaviors Taken from U-Learn Accessibility Training presentation
- 3. Introduction to UI and Cognetics ’é¦ Interface is a set of means for interaction between human and system ’é¦ Cognetics is an ergonomy of human mind and perception ’é¦ People are limited in their memory and processing resources
- 5. Attention limitations ’é¦ Locus of attention can only be allocated at one spot at a time Most of illusionist tricks are about manipulations with locus of attention. Multitasking in fact is an illusion that derives from the ability of rapidly switching the attention. Note that word ŌĆ£attentionŌĆØ does not have plural form in any of the languages. Simply because multiple attentions do not exist. Most commonly, locus of attention is allocated where the action is about to be applied, so it is likely to be where mouse cursor or crosshair is. Note that the cursor or crosshair itself is not the subject of attention. ’é¦ Switching between complex tasks takes about 10-20 seconds Experiments proved that performing two tasks one after another is significantly more effective than while constantly switching between them. This fact is especially important in real time strategy design where frequent switching of attention is very common thing.
- 6. Attention limitations ’é¦ Automaticity is a workaround to attention limitations Automated reflectory actions do not require attention which allows for example driving and talking at the same time. In game design, forming of reflexes plays a huge part in learning curve design. A game ŌĆ£This is the only levelŌĆØ is wholly based on tricks with automaticity ŌĆ£This is the only levelŌĆØ gameplay is wholly based around automaticity Nothing changed on stage 20 except the level is invisible. This is one of the easiest stages though ’é¦ Pitfalls of automaticity Automated actions are poorly manageable. Switch pedals in a car, warn the driver, place reminders before his eyes, but in critical situations reflexes will still take over.
- 7. Long-term memory ’é¦ People are unable to memorize random data The ability to memorize random data is in fact an ability to provide sense to meaningless patterns ’é¦ Memorizing via contextual connections The most common way to memorize things is to associate them with something previously known ’é¦ Memorizing via explanatory mechanisms ŌĆō the power of constrains There may be no need to memorize what can be recalled by applying logic. Thus a rhyme allowed bards of the past to remember very long poems by limiting or eliminating alternatives. ’é¦ Memorizing via repetition People can miss up to 60 % of spoken or written information. Repetition is another chance to create different association. If repetition involves physical actions it addresses a whole different layer of memory
- 8. Short-term and procedural memory ’é¦ Short-term memory is limited to average 7 entities 5-9 entities is all we can grasp at a time. This explains ŌĆ£Less is moreŌĆØ statement. People deal with this limitation by grouping entities. For example a car is a huge conglomerate of details, but is represented as a single entity in human mind ’é¦ Procedural memory Procedural memory is the type of memory responsible for remembering how to perform actions. A whole different part of the brain is used. In numerous brain-injury caused amnesia cases people didnŌĆÖt remember their life but remembered perfectly how to dress or how to eat. Mixing theory with practice is very effective because procedural memory can act as a reminder ŌĆō thatŌĆÖs why tutorial missions are better than briefings. ’é¦ Muscle memory Muscles have their own memory, so the hands ŌĆ£knowŌĆØ the movement they should perform. This is a type of procedural memory. Musician can forget how the melody sounds, but his finger still remember how to play it. Be careful with automatic adjustment of mouse sensitivity and screen resolution ŌĆō hands get used to it.
- 9. Designing for memory ’é¦ Do not rely on human memory!!! If your design suggests that player has to remember something to complete the game, it is a bad design. There always should be clues and reminders. Keep all gameimportant information stored in one place (journal, Civilopedia, diary, whatever) ’é¦ Limit the load on memory Give no more than 5-7 entities to remember at a time. The less is the better. ’é¦ Exploit associations Give you characters meaningful names (Max Payne, Blood Rayne, Alan Wake), give landmarks recognizable shapes, make them visible.
- 10. Designing for memory ’é¦ Merge entities into groups Grouping significantly reduces load on memory and attention. A car is an extremely complex conglomerate of elements but mind addresses to it as to one thing. This is how Mass Effect 2 HUD would look without grouping. Try to remember where is what.
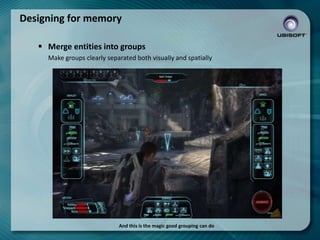
- 11. Designing for memory ’é¦ Merge entities into groups Make groups clearly separated both visually and spatially And this is the magic good grouping can do
- 12. Designing for memory ’é¦ Repeat It may be a good idea to build important dialogue using repetitive key words. This is a basic trick of NLP and rhetoric. Repetitive actions are a key to mastering the game and the amount of repetitions is directly related to learning curve ’é¦ Hide the unimportant Progressive disclosure allows showing less important things only when they are needed. ’é¦ Provide context where possible Information is interpreted depending on context. Context is a perfect reminder
- 13. Designing for memory ’é¦ Repeat It may be a good idea to build important dialogue using repetitive key words. This is a basic trick of NLP and rhetoric. Repetitive actions are a key to mastering the game and the amount of repetitions is directly related to learning curve ’é¦ Hide the unimportant Progressive disclosure or context awareness allows showing less important things only when they are needed. ’é¦ Provide context where possible Information is interpreted depending on context. Context is a perfect reminder
- 14. Visibility
- 15. Visibility ’é¦ Image Recognition Image recognition occurs in several stages each in a separate part of the brain. Reptilian brain is responsible for recognizing shapes, movement and basic colors such as red, green, blue and yellow. This happens much faster than recognition of a complex image. Team Fortress 2 developers consciously designed their characters for reptile brain perception. Simple shapes recognizable from any perspective and use of basic colors make sure that characters and their team alignement can be instantly recognized
- 16. Visibility ’é¦ HickŌĆÖs Law HickŌĆÖs law states that time of making a decision is exponentially dependent on amount of available choices 3 options at a time are enough to make a great game Homeworld would never be playable without a tactical pause ’é¦ Grouping Grouping splits decision making process in several stages thus decreasing time necessary to make a decision
- 17. Visibility ’é¦ FittsŌĆÖs Law FittsŌĆÖs Law states that time necessary to point an object is exponentially dependent on distance to the object and itŌĆÖs size Enemy proportions in Gears of War are designed for gameplay purpose . Shooting exaggerated bodies is easy even with gamepad and headshots are difficult but rewarding
- 18. Visibility ’é¦ Affordance Affordance is a self-explanatory purpose of an object. This is an important property that interactive game elements should possess. How many types of items in your pockets will fit that slot? Flat road surface is a natural choice for driving without additional explanations
- 19. Visibility ’é¦ Natural Mappings natural arrangements for the relations between controls and their movements to the outcome from such action into the world. Guess which knob is responsible for which burner And what about this case?
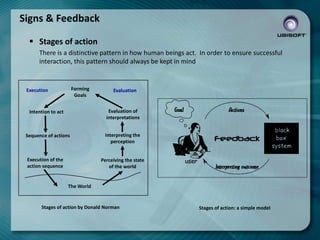
- 20. Signs & Feedback ’é¦ Stages of action There is a distinctive pattern in how human beings act. In order to ensure successful interaction, this pattern should always be kept in mind Forming Goals Execution Evaluation Intention to act Evaluation of interpretations Sequence of actions Interpreting the perception Execution of the action sequence Perceiving the state of the world The World Stages of action by Donald Norman Stages of action: a simple model
- 21. Signs & Feedback ’é¦ Gulf of evaluation Evaluation of system state before and after the action is crucial for successful interaction. Gulf of evaluation is amount of time spent on such evaluation. If the system fails to provide clear signs of its state and clear feedback on user action, the gulf of evaluation may be increased up to infinity causing frustration and anger.
- 22. Signs & Feedback ’é¦ Signs Sign is a display of system status. Rendering the design legible and underlining the rules of the game, the signs orientate the player in his actions. ’é¦ ’é¦ The display of this state is called Sign. ’é¦ Signs must be clear so the player knows what he can do. ’é¦ Signs can come from visuals, sounds or vibrations. ’é¦ Sign gives information about the system: The green cone is enemyŌĆÖs sight The system is always in a specific state. It should stress the ŌĆ£goodŌĆØ actions, so the player can learn from deduction and not from trial and error Taken from U-Learn Signs & Feedback presentation
- 23. Signs & Feedback ’é¦ Feedback Feedbacks are the direct answers of the game to the playerŌĆÖs actions. By providing information related to his performance, they help the player to play better. ’é¦ ’é¦ Feedbacks must be immediate so player could recognize the relation between his action and feedback. ’é¦ Feedbacks can come from visuals, sounds or vibrations. ’é¦ Sign gives information about the system: The green cone is enemyŌĆÖs sight Feedbacks must be clear so the player knows what he has accomplished. It should stress not only that the action took place but also the consequences (positive or negative), thus showing the player the ŌĆ£goodŌĆØ path. Taken from U-Learn Signs & Feedback presentation
- 24. Mental Models
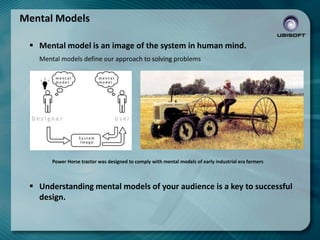
- 25. Mental Models ’é¦ Mental model is an image of the system in human mind. Mental models define our approach to solving problems Power Horse tractor was designed to comply with mental models of early industrial era farmers ’é¦ Understanding mental models of your audience is a key to successful design.
- 26. Consistency ’é¦ Things that look similar should behave similar A very common design mistake is inconsistent behavior of similar objects. In Splinter Cell players can climb on some pipes, but not on others ’é¦ Consistency and Occam's razor Entities must not be multiplied beyond necessity. By following this simple principle you will avoid many frustrations caused by misinterpretation of similarity. If you have only few artworks of locked doors, this may be enough for artistic diversity and easier for player to remember. Another good example is a single ŌĆ£useŌĆØ key that initiates different actions depending on context.
- 27. Consistency applications ’é¦ User experience and expectations It is important to keep in mind that users have previous experience and formed mental models. Try to be consistent with existing game design trends and the real world in order to meet user expectations. ’é¦ Terminology Consistent terminology is vital for unambiguous design. Avoid referring to gameplaymeaningful entities using different words. ’é¦ Behavior Consistency of behavior of different entities in dynamic environment makes sure that interaction is predictable and easy to learn ’é¦ Visual appearance Visual appearance is a key to recognizing things and their purpose. A fancy but ambiguous appearance is worse than simple but clear one if it relies to gameplay meaningful things
- 28. Modes ’é¦ Modes as the main reason of user errors Vast majority of user errors is caused by failure to recognize current mode of the system. Just remember how many errors were caused by Caps Lock. The main reason is that locus of attention is usually located on task, not on system state indicator. ’é¦ Examples of modes in games Player stances, difficulty levels, user settings, camera modes ’é¦ Modes as a valuable gameplay tool Disable shooting while running, allow healing while shooting, restrict movement while healing. These are all design choices that define gameplay experience and have a huge balancing potential. Make sure you are always conscious about modes in your game
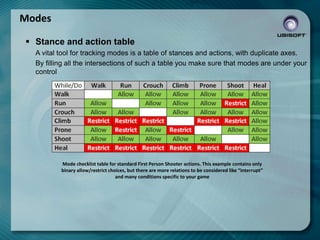
- 29. Modes ’é¦ Stance and action table A vital tool for tracking modes is a table of stances and actions, with duplicate axes. By filling all the intersections of such a table you make sure that modes are under your control Mode checklist table for standard First Person Shooter actions. This example contains only binary allow/restrict choices, but there are more relations to be considered like ŌĆ£interruptŌĆØ and many conditions specific to your game
- 30. Further Read ’é¦ The Design of Everyday Things This ŌĆ£bibleŌĆØ of design written by Donald Norman is for anyone who designs anything (technical manuals, software interfaces, machinery, consumer goods, clothes) and it is also for anyone who uses the items that are designed (that is, all of us). The purpose of the book is to encourage everyone to look at design, and to see how it corresponds to how people actually use things. ’é¦ The Humane Interface: New Directions for Designing Interactive Systems Written by Jeff Raskin the designer of Apple and Apple II, this book puts forward a large number of interface design suggestions, from obvious to radical ones. It gives a good insight on how usability can actually be measured ’é¦ Human Information Processing A cornerstone in cognitive psychology by Peter Lindsay and Donald Norman for those who really want to dig the subject in depth.