GASTRULATION, NOTOCHORD AND NEURULATION.pptx
- 1. GASTRULATION, NOTOCHORD AND NEURULATION COURSETITLE: General Embryology LECTURER: Dr Sabiu B. SOJA UNIT: Epigenetics/ Developmental Anatomy DATE : 27TH October 2024
- 2. GASTRULATION 2 ŌĆó Is the process that establishes 3 germ cell layers: Trilaminar germ disc at the 3rd week of embryonic development ŌĆó Begins with formation of primitive streak on surface of epiblast ŌĆó Which has an orientation with the cephalic end marked by the primitive node and pit
- 3. GASTRULATION (CONTŌĆÖD) 3 ŌĆó Epiblast cells migrate to the primitive streak, detach and slip underneath, ŌĆó Displacing the hypoblast and becoming the endoderm ŌĆó Subsequent layer of cells develops between this endoderm and the epiblast- these form the mesoderm ŌĆó The remaining epiblast now is referred to as the ectoderm.
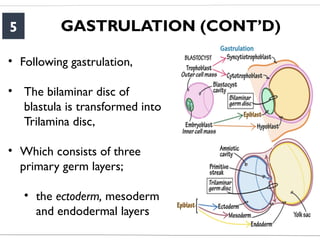
- 5. GASTRULATION (CONTŌĆÖD) 5 ŌĆó Following gastrulation, ŌĆó The bilaminar disc of blastula is transformed into Trilamina disc, ŌĆó Which consists of three primary germ layers; ŌĆó the ectoderm, mesoderm and endodermal layers
- 6. NOTOCHORDAL FORMATION 6 ŌĆó Invagination cells that migrate cephalad form the prechodal plate, that is significant in induction of the forebrain ŌĆó It is situated close to the buccopharnyngeal membrane ŌĆó Also , the migrating cells form the notochord ŌĆó That extends from the prechordal plate cranially to the primitive pit caudally.
- 7. NOTOCHORDAL FORMATION 7 ŌĆó The Cloacal membrane is formed at the caudal end of the embryonic disk- formed
- 8. NEURULATION 8 ŌĆó Is the formation of the neural tube ŌĆó Notochord induces the overlying ectoderm to thicken and form the neural plate ŌĆó At the end of 3rd week, neural folds and neural groove are established.
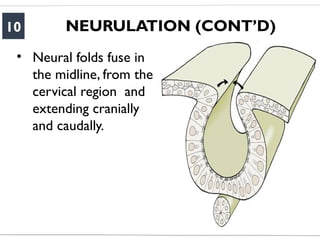
- 10. NEURULATION (CONTŌĆÖD) 10 ŌĆó Neural folds fuse in the midline, from the cervical region and extending cranially and caudally.
- 12. NEURULATION (CONTŌĆÖD) 12 ŌĆó Neural tube is formed and invade into the embryo body
- 13. NEURULATION 13 ŌĆó The broader cephalic portion of the neural tube transforms into primary brain vesicles ŌĆó The narrower part develops into the spinal cord
- 14. NEURULATION (CONTŌĆÖD) 14 Primary and Secondary Vesicle Stages of Development The embryonic brain develops complexity through enlargements of the neural tube called vesicles; (a) The primary vesicle stage has three regions, and (b) the secondary vesicle stage has five regions. Credit: OpenStax.
- 15. SOMITES 15 ŌĆó Mesodermal cells on each side of the neural tube begin to form a row of regular, compact structures called somites
- 16. SOMITES (CONTŌĆÖD) 16 A. Dorsal view of a human embryo at about day 22 B. Dorsal view of a human embryo at about day 23. ŌĆó The nervous system is in connection with the amniotic cavity through the cranial and caudal neuropores ŌĆó Closure of the cranial neuropore happens at about day 25(18-20-somite stage) ŌĆó Posterior neuropore closes at approximately day 27 (25- somite stage)
- 17. NEURAL CREST CELLS 17 ŌĆó Along the line of fusion of the neural folds, some of the cells break free and become migratory within the mesodermal layer. ŌĆó These are the neural crest cells, and are shown here as tan-coloured clusters of cells resembling 'teardrops' alongside the neural tube Neural crest cell
- 18. NEURAL CREST CELLS (CONTŌĆÖD) 18
- 19. 19
- 20. CLINICAL CONSIDERATION 20 ŌĆó NTDŌĆÖs occur due to defect in the midline fusion of neural tube ŌĆó Resulting in cranial or spinal dysraphism, and may involve nerve roots, spinal cord, or bony vertebrae. ŌĆó They can be open or closed types NEURALTUBE DEFECTS(NTDŌĆÖs)
- 21. CLINICAL CONSIDERATION 21 ŌĆó The causes are mostly multifactorial, including both genetic and environmental causes. ŌĆó Mutations in several genes, especially genes involved in folic acid metabolism, have been found
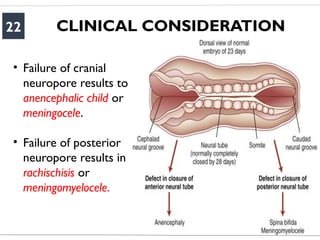
- 22. CLINICAL CONSIDERATION 22 ŌĆó Failure of cranial neuropore results to anencephalic child or meningocele. ŌĆó Failure of posterior neuropore results in rachischisis or meningomyelocele.