GENETIC ALGORITHM
- 1. GENETIC ALGORITHM @Harsh_Sinha Presented by : HARSHWARDHAN SINHA (3rd SEM C.S.E 2017 -21) SSIPMT RAIPUR
- 2. 1. This Presentation contains only 25 slides @Harsh_Sinha
- 3. We will see â Introduction â Terminology â Flow chart â Advantages, disadvantages and applications. â Conclude with an example @Harsh_Sinha
- 4. GENETIC ALGORITHM â Optimization Algorithm â Nature inspired approach based on Darwinâs law of âsurvival of the fittestâ and bio-inspired operators such as Pairing, crossover and mutation â Frequently used to find optimal or near- optimal solutions of difficult problems 4@Harsh_Sinha
- 5. GENETIC ALGORITHM â It is not an smart algorithm neither an intelligence algorithm Rather it reflects the changes and response to it very quickly, so it called Genetic algorithm. 5@Harsh_Sinha
- 6. OPTIMIZATION â Optimization is the process of making something better â Finding the values of inputs in such a way that we get the âbestâ output value. 6@Harsh_Sinha
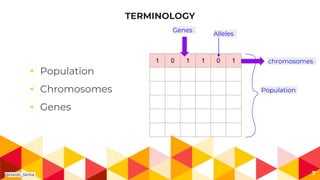
- 7. TERMINOLOGY â Population â Chromosomes â Genes 7 1 0 1 1 0 1 Population Genes chromosomes Alleles @Harsh_Sinha
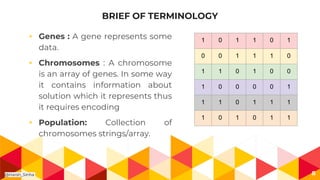
- 8. BRIEF OF TERMINOLOGY â Genes : A gene represents some data. â Chromosomes : A chromosome is an array of genes. In some way it contains information about solution which it represents thus it requires encoding â Population: Collection of chromosomes strings/array. 8 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 @Harsh_Sinha
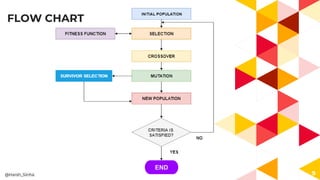
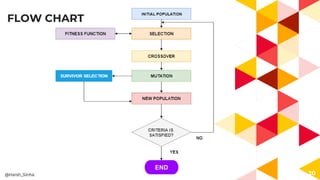
- 10. GENETIC OPERATORS â Selection â Crossover â Mutation 10@Harsh_Sinha
- 11. SELECTION Selection individual for creating the next generation(better generation). In terms of CS selecting the data so to reach optimal solution. Selection is done by applying fitness function. 11@Harsh_Sinha
- 12. FITNESS & FITNESS FUNCTION Fitness: The value assigned to an individual based on how far or close an individual is from solution; greater the fitness value better the solution it contains. Fitness Function: A function that assigns fitness value to the individual.It is problem specific. 12@Harsh_Sinha
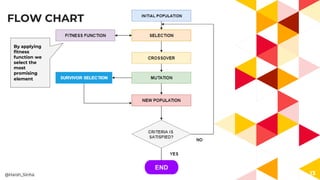
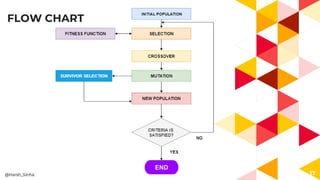
- 13. FLOW CHART 13 By applying fitness function we select the most promising element @Harsh_Sinha ENDEND
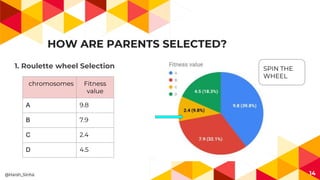
- 14. HOW ARE PARENTS SELECTED? 1. Roulette wheel Selection 14 chromosomes Fitness value A 9.8 B 7.9 C 2.4 D 4.5 SPIN THE WHEEL @Harsh_Sinha
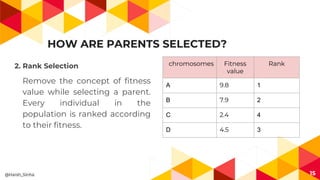
- 15. HOW ARE PARENTS SELECTED? 2. Rank Selection Remove the concept of fitness value while selecting a parent. Every individual in the population is ranked according to their fitness. 15 chromosomes Fitness value Rank A 9.8 1 B 7.9 2 C 2.4 4 D 4.5 3 @Harsh_Sinha
- 16. HOW ARE PARENTS SELECTED? 3. STOCHASTIC UNIVERSAL SAMPLING(SUS): Multiple fixed points, all the parents are chosen in just one spin of the wheel. 4.TOURNAMENT SELECTION: Select k individuals from the population at random and select the best out of these to become a parent, same process is repeated for selecting the next parent. 16@Harsh_Sinha
- 18. CROSSOVER Crossover is a genetic operator that combines(mates) two chromosomes(parents) to produce a new chromosome(offspring). The crossover operators are of many types: 1. One simple ways is one-point crossover. 2. The others are two-point, uniform, arithmetic and heuristic crossovers. They are selected based on the way chromosomes are encoded. (Encoded because it is computer science and not biology.) 18@Harsh_Sinha
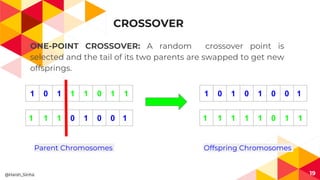
- 19. CROSSOVER ONE-POINT CROSSOVER: A random crossover point is selected and the tail of its two parents are swapped to get new offsprings. 19 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 Parent Chromosomes Offspring Chromosomes @Harsh_Sinha
- 21. MUTATION â Small random tweak in the chromosome, to get a new solution. Types 1. Bit-flip mutation: Select one or more random bits and flip them. 1. Swap mutation: Select two random bits and swap them. 21 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 @Harsh_Sinha
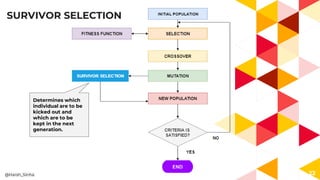
- 22. 22 Determines which individual are to be kicked out and which are to be kept in the next generation. SURVIVOR SELECTION @Harsh_Sinha END
- 23. When are Genetic Algorithms Useful? There are at least three situations where genetic algorithms are useful: 1. The objective function is not smooth (i.e., not differentiable). 2. There are multiple local optima. 3. Useful when the search space is very large and there are a large number of parameters (the meaning of âlargeâ keeps changing). 4. Provides a list of âgoodâ solutions and not just a single solution For details about each point refer to: https://www.burns-stat.com/documents/tutorials/an-introduction-to-genetic- algorithms/ 23@Harsh_Sinha
- 24. ITS APPLICATION 1. Optimized Telecommunications Routing 2. Trip, Traffic and Shipment Routing 3. Encryption and Code Breaking 4. Evolvable Hardware 5. Joke and Pun Generation These are few of them. For more we can refer to : https://www.brainz.org/15-real-world-applications-genetic-algorithms/ 24@Harsh_Sinha
- 25. Drawbacks 1. Computationally expensive as fitness value is calculated repeatedly 2. Not suited for all problems, especially problems which are simple and for which derivative information are available 3. GA may not converge to the optimal solutions,if not implemented properly. 25@Harsh_Sinha