Genetic algorithm
- 1. Genetic Algorithm Presented by Harshada Gurav CADME 2015-16 Roll No. 05
- 2. INTRODUCTION ï Introduced by Prof. John Holland in 1975. ï Genetic algorithms are categorized as global search heuristic algorithm. ï Genetic algorithms are a particular class of evolutionary algorithms that use techniques inspired by evolutionary biology such as inheritance, mutation, selection, and crossover (also called recombination).
- 3. FITNESS FUNCTION F(x) ïDerived from objective function f(x) ïMost often used function is F(x) = 1/(1+f(x))
- 5. REPRODUCTION ï It selects good (above average) strings in a population and forms a mutation pool. ï The probability for selecting ith string is n = population size ï One way to implement the selection scheme is roulette-wheel selection mechanism.
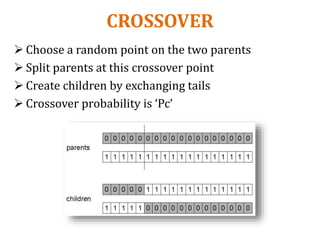
- 6. CROSSOVER ï Choose a random point on the two parents ï Split parents at this crossover point ï Create children by exchanging tails ï Crossover probability is âPcâ
- 7. MUTATION ï The mutation operator is applied to the new strings with a specific small mutation probability, pm. ï The mutation operator changes the binary digit 1 to 0 and vice versa. ï pm is called the mutation rate ïTypically between 1/pop_size and 1/ chromosome_length ï It maintains diversity in the population
- 8. Steps in GA 1. Choose a coding to represent problem parameters, a selection operator, a crossover operator, mutation operator, population size, crossover probability and mutation probability. 2. Initialize random population of strings of size l, tmax, set t = 0. 3. Evaluate each string in population 4. If t > tmax or other termination criteria is satisfied, terminate 5. Perform reproduction on the population 6. Perform crossover on random pairs of string 7. Perform mutation on every string 8. Evaluate strings in the new population. Set t = t+1 and go to step 3.
- 9. ADVANTAGES ï It is very potential algorithm. ï Used for complex engineering problems ï A population of points is used for starting the procedure instead of a single design point. ï GAs use only the values of the objective function. The derivatives are not used in the search procedure. ï The objective function value corresponding to a design vector plays the role of fitness in natural genetics. ï GA efficiently explore the new combinations with the available knowledge to find a new generation with better fitness value.