genetic code.pptx
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes249 views
The genetic code is the set of rules by which ribosomes translate nucleic acid sequences into amino acid sequences during biological protein synthesis. It is summarized in a genetic code table that shows the relationships between codons and amino acids. The genetic code is nearly universal across all living organisms and has several key properties: it is triplet, non-overlapping, commaless, and specifies both start and stop signals. There are some minor exceptions to the universal genetic code, such as reassignment of stop codons or dual coding of some codons.
1 of 16
Download to read offline














Recommended
Riboswitches 



Riboswitches rajani prabhu
Ěý
Riboswitches are RNA elements found in the 5' untranslated region of mRNA that can bind to specific metabolites and undergo a conformational change to regulate gene expression. They are classified based on the ligand they bind and their secondary structure. Examples include TPP, lysine, glycine, FMN, purine, and cobalamin riboswitches. A riboswitch has two domains - an aptamer domain that binds the ligand and an expression platform domain that can adopt two structures to control transcription or translation. Binding of a metabolite can induce formation of a terminator stem loop to terminate transcription, mask the ribosome binding site to inhibit translation initiation, or trigger self-cleavage of the mRNA.Wobble hypothesis



Wobble hypothesissubhananthini jeyamurugan
Ěý
- Crick proposed the "wobble hypothesis" to explain how more than one codon can direct the synthesis of a single amino acid, given there are fewer tRNAs than codons.
- The hypothesis suggests the third nucleotide in a codon is not as important in binding to the tRNA anticodon. The first two nucleotides specify the amino acid.
- At the wobble position, the third nucleotide in the codon can bind in non-standard ways ("wobble") to the first nucleotide in the anticodon, allowing a single tRNA to bind to multiple codons and explain the degeneracy of the genetic code.Translation Initiation in Eukaryotes



Translation Initiation in EukaryotesZohaib HUSSAIN
Ěý
Translation initiation in eukaryotes is a highly regulated and rate-limiting process that involves the assembly of numerous transient complexes containing over a dozen eukaryotic initiation factors. This process culminates in the accommodation of a start codon at the appropriate ribosomal site. Structural biology has provided insights into the mammalian mitochondrial translation initiation complex and other key complexes and factors involved in the process, such as eIF3, the eIF2 ternary complex, and the DHX29 helicase. Dysregulation of translation initiation can contribute to diseases like cancer and metabolic disorders.Genetic code



Genetic codeRinaldo John
Ěý
The document discusses the genetic code, including its key characteristics and discoveries. It notes that the genetic code is a triplet code where each set of 3 nucleotides (codon) codes for a specific amino acid. There are 64 possible codons that can code for 20 standard amino acids. The code is nearly universal across all organisms and is characterized by being unambiguous, non-overlapping, and comma-less.Control of gene expression



Control of gene expressionGurdeepSingh358
Ěý
Definition, Principle, gene expression in eukaryotes, levels of gene control, genes and regulatory elements, Operon systemTranslational machinery



Translational machineryvishnu prasad
Ěý
This document discusses the process of translation in cells. It defines translation as the process by which the genetic information in messenger RNA (mRNA) is used to direct the synthesis of proteins. The key components involved in translation are mRNA, transfer RNA (tRNA), aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, and ribosomes. Translation involves tRNAs carrying amino acids to the ribosome, where they are linked together into a polypeptide chain according to the codons in the mRNA.Dna binding motiffs



Dna binding motiffsIndrajaDoradla
Ěý
This document discusses different DNA binding motifs that allow proteins to interact with DNA without disrupting the hydrogen bonds between the DNA bases. It describes several conserved structural motifs common to many DNA binding proteins, including the helix-turn-helix motif, zinc finger domains, and leucine zipper domains. The helix-turn-helix motif contains two short alpha helices separated by a beta turn. Zinc finger domains use cysteine or histidine residues to coordinate a zinc ion, stabilizing their structure. Leucine zipper domains contain repeated leucine residues that allow dimerization of regulatory proteins.Genetic Code



Genetic CodeBalaji Thorat
Ěý
1) The document discusses the genetic code, which determines how DNA and mRNA sequences are translated into proteins.
2) Marshall Nirenberg and others were the first to elucidate the nature of codons in 1961 and determine that codons consist of three DNA bases.
3) The genetic code is universal, uses triplets of nucleotides, has no commas, does not overlap, is not ambiguous, but is degenerate meaning several codons can code for the same amino acid.Ribozyme



RibozymeMUMTHAS P K - KANNUR UNIVERSITY, CAMPUS, KANNUR
Ěý
Ribozymes are RNA molecules that act as enzymes and catalyze biochemical reactions. Some key points:
- Ribozymes were first proposed in the 1960s and discovered in the 1980s by Thomas Cech and Sidney Altman, who shared the 1989 Nobel Prize for the discovery.
- Common ribozyme activities include splicing and cleaving RNA and DNA. Ribozymes in the ribosome help link amino acids during protein synthesis.
- Major types of ribozymes include group I and group II introns, hammerhead, hairpin, and RNase P ribozymes. They use mechanisms like metal ion coordination and nucleophilic attacks to catalyze reactions.
- Reukaryotic translation initiation and its regulation



eukaryotic translation initiation and its regulationnida rehman
Ěý
The document summarizes eukaryotic translation initiation. It describes how the 43S preinitiation complex is formed and recruits to the 5' end of mRNA with the help of initiation factors. The complex then scans the 5' UTR until it recognizes the start codon, after which the 60S subunit joins to form the 80S ribosome. Initiation factors are regulated by phosphorylation and proteolysis. Translation can also be controlled by RNA-binding proteins and the length of the poly-A tail.DNA structure



DNA structureNagaraju Yalavarthi
Ěý
DNA is the genetic material found in cells. It exists in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in the form of a double helix composed of two strands bound together by hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous base pairs. The four bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine in DNA or uracil in RNA. DNA can take on different structures depending on its sequence and environment, including A, B, C, D, E, and Z forms. Eukaryotic DNA is linear and contained within the nucleus, while prokaryotic DNA exists as a single circular chromosome. RNA also exists as a single strand and plays important roles in protein synthesis and gene regulation.Translation in eukaryotes



Translation in eukaryotesHETAKUMARI PILUDARIA
Ěý
Translation in Eukaryotes
The third part of Central Dogma
Transferring the information from RNA to Protein
For BSc students
Transcriptional and post transcriptional regulation of gene expression



Transcriptional and post transcriptional regulation of gene expressionDr. Kirti Mehta
Ěý
Gene expression is regulated at the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. Transcriptional regulation involves proteins binding to promoter and enhancer sequences to control RNA polymerase recruitment and initiation of transcription. Eukaryotic gene expression requires transcription factors, coactivators, and basal transcription factors to assemble the transcription initiation complex. Post-transcriptional regulation influences RNA processing, transport, translation, and degradation.Transcription Regulation 



Transcription Regulation IshaqueAbdulla
Ěý
This document provides an overview of regulation of transcription in eukaryotes. It discusses that transcription is primarily controlled at the initiation stage by proteins binding to regulatory sequences. These sequences include promoters near the transcription start site as well as enhancers that can be located farther away. Enhancers stimulate transcription through DNA looping. Gene expression is also regulated by chromatin structure and DNA methylation. Transcription factors have distinct DNA-binding and activation domains and include zinc finger and helix-turn-helix motifs.Translation in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes



Translation in Prokaryotes and EukaryotesShiv Nadar University
Ěý
This document summarizes translation mechanisms in prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems. It discusses that translation is the process of protein synthesis from mRNA, involving ribosomes, tRNAs, and enzymes. The three main steps of translation - initiation, elongation, and termination - are described for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems. Key differences between the two systems are the use of Shine-Dalgarno sequences and initiation factors in prokaryotes versus Kozak sequences and more complex initiation factor involvement in eukaryotes. Termination and ribosome recycling mechanisms are also compared between prokaryotes and eukaryotes.HELIX-LOOP-HELIX, HELIX-TURN-HELIX



HELIX-LOOP-HELIX, HELIX-TURN-HELIXnaren
Ěý
ALL BASIC AND IMPORTANT CONTENT REGARDING HELIX LOOP HELIX AND HELIX TURN HELIX.. ALL ITS FUNCTION AND SUMMARY.
HOPE YOU WILL FIND IT EASY..Transposibleelements.pptx



Transposibleelements.pptxYoGeshSharma834784
Ěý
This document discusses transposable elements, which are mobile genetic elements that can move within genomes. It describes different types of transposable elements in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In prokaryotes, examples discussed include insertion sequence (IS) elements and transposons. In eukaryotes, examples of transposable elements found in corn, yeast, and Drosophila are described. The mechanisms of both replicative and non-replicative transposition are summarized. Barbara McClintock's pioneering discoveries of transposable elements in corn through her studies of kernel color are also highlighted.Arabinose operon and their regulation and arac 



Arabinose operon and their regulation and arac VijiMahesh1
Ěý
arabinose operon and their detalied explanation about the operon conceptt and their regulation both positive and negative and the detailed explanation of the promoter ,operator,inducer,structural gene,arac protein Translation: Protein synthesis



Translation: Protein synthesisDr. Mafatlal Kher
Ěý
Translation is the process by which the genetic code stored in mRNA is used to synthesize proteins. It occurs on ribosomes using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to add amino acids to a growing polypeptide chain. There are three sites on the ribosome - the A site binds incoming tRNA, the P site holds tRNA with the polypeptide chain, and the E site releases tRNA. Through the repetitive binding of tRNA to mRNA codons and formation of peptide bonds, proteins specified by the mRNA are assembled from amino acids based on the genetic code.Phage Gene Regulation.pptx



Phage Gene Regulation.pptxDepartment of Biotechnology, Kamaraj college of engineering and technology
Ěý
A bacteriophage is a virus that infects bacteria. Lambda phage is a temperate bacteriophage that has two life cycle choices: lytic and lysogenic. During lysogeny, the lambda repressor binds to the operator region (OR) on the phage DNA and represses transcription of lytic genes, allowing the phage genome to remain dormant as a prophage integrated into the bacterial chromosome.Translation in prokaryotes



Translation in prokaryotesshishtasharma1
Ěý
This document summarizes the key steps of translation: initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation involves assembly of the ribosomal subunits and initiator tRNA on the mRNA. Elongation consists of aminoacyl-tRNA delivery, peptide bond formation, and translocation. Termination occurs when a stop codon enters the A site, triggering release factors to cleave the polypeptide from tRNA and dissociate the ribosomal subunits.Prokaryotic DNA replication



Prokaryotic DNA replicationMoumita Paul
Ěý
DNA replication in prokaryotes begins with the unwinding of DNA at the origin of replication by enzymes like DnaA and DnaB helicase. This produces two replication forks that move in opposite directions. The leading strand is replicated continuously while the lagging strand is replicated discontinuously in short segments called Okazaki fragments. DNA polymerase III is the main enzyme that synthesizes new DNA. Replication terminates at the terminus region when the DnaB helicase is stopped by protein Tus bound to Ter sequences.Genetic code - 



Genetic code - Ashok Katta
Ěý
The genetic code is the system by which nucleotide sequences in mRNA determine the amino acid sequences in proteins. The genetic code uses triplets of nucleotides called codons to specify which amino acid will be incorporated into the growing polypeptide chain. There are 64 possible codons but only 20 standard amino acids, so most amino acids have multiple codons. Three codons act as stop signals to end protein synthesis. The genetic code is nearly universal across all life due to its high degree of specificity and redundancy.Translation In Eukaryotes



Translation In EukaryotesUmer Farooq
Ěý
Translation is the process by which proteins are synthesized from messenger RNA (mRNA) in eukaryotes, which are organisms with membrane-bound nuclei. Translation involves mRNA being decoded on ribosomes into a polypeptide chain. It occurs through three main steps - initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation involves the small ribosomal subunit binding to the 5' end of mRNA and scanning for the start codon. Elongation is the sequential addition of amino acids specified by the mRNA codons. Termination occurs when a stop codon is reached and release factors cause the ribosome to dissociate and release the completed protein.Translation



TranslationRinaldo John
Ěý
1. Translation is the process by which the information contained in mRNA is used to synthesize proteins from amino acids. It occurs on ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
2. Ribosomes contain three binding sites (A, P, and E sites) that facilitate the sequential addition of amino acids to form a polypeptide chain. tRNAs carry specific amino acids and recognize mRNA codons through complementary base pairing of their anticodons.
3. The genetic code consists of three-nucleotide sequences called codons that specify which of 20 amino acids will be added during translation. Most amino acids are specified by multiple codons. Translation proceeds through initiation, elongation, translocation, and termination phases.Galactose operon and Histidine operon 



Galactose operon and Histidine operon PunithKumars6
Ěý
The document discusses the galactose and histidine operons. It describes the structural organization and regulation of the galactose operon, including the Leloir pathway for D-galactose metabolism and repression/induction by galactose. It also summarizes the structural organization and two mechanisms of regulation (feedback inhibition and repression control) for the histidine operon. Finally, it explains attenuation control of the histidine operon through transcriptional termination or anti-termination depending on histidine availability.Dna binding proteins



Dna binding proteinsHari Sharan Makaju
Ěý
The document discusses DNA binding proteins. It describes how DNA is wrapped around histone proteins to form nucleosomes, which resemble "beads on a string". There are five main types of histone proteins - H1, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Histone proteins can be modified through processes like acetylation and methylation, which affect gene expression. Other non-histone proteins use motifs like zinc fingers and helix-turn-helix to bind DNA in a sequence-specific manner and regulate transcription.Regulation of gene expression in prokaryotes



Regulation of gene expression in prokaryotesgohil sanjay bhagvanji
Ěý
This document discusses various mechanisms of gene expression regulation in prokaryotes. It introduces the concepts of induction and repression using the example of beta-galactosidase in E. coli. Inducers activate gene expression while corepressors repress it. The operon model of the lac and tryptophan operons is explained in detail. Other mechanisms discussed include transcriptional, translational, and post-transcriptional regulation. Feedback inhibition is also summarized.Genetic code2



Genetic code2piya1apiya
Ěý
1. The genetic code is composed of nucleotide triplets called codons that specify individual amino acids.
2. Experiments confirmed that the genetic code is a triplet code and that each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid, with some codons coding for the same amino acid (degenerate).
3. Key properties of the genetic code include it being triplet-based, non-overlapping, unambiguous, degenerate, and nearly universal across organisms.Genetic code slide



Genetic code slideDr.M.SANKARESWARAN
Ěý
Genetic code is a dictionary that corresponds with sequence of nucleotides and sequence of amino acids.
Genetic code is a set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material(DNA or RNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells.
Term given By ″ Goerge Gamow ʺ
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Ribozyme



RibozymeMUMTHAS P K - KANNUR UNIVERSITY, CAMPUS, KANNUR
Ěý
Ribozymes are RNA molecules that act as enzymes and catalyze biochemical reactions. Some key points:
- Ribozymes were first proposed in the 1960s and discovered in the 1980s by Thomas Cech and Sidney Altman, who shared the 1989 Nobel Prize for the discovery.
- Common ribozyme activities include splicing and cleaving RNA and DNA. Ribozymes in the ribosome help link amino acids during protein synthesis.
- Major types of ribozymes include group I and group II introns, hammerhead, hairpin, and RNase P ribozymes. They use mechanisms like metal ion coordination and nucleophilic attacks to catalyze reactions.
- Reukaryotic translation initiation and its regulation



eukaryotic translation initiation and its regulationnida rehman
Ěý
The document summarizes eukaryotic translation initiation. It describes how the 43S preinitiation complex is formed and recruits to the 5' end of mRNA with the help of initiation factors. The complex then scans the 5' UTR until it recognizes the start codon, after which the 60S subunit joins to form the 80S ribosome. Initiation factors are regulated by phosphorylation and proteolysis. Translation can also be controlled by RNA-binding proteins and the length of the poly-A tail.DNA structure



DNA structureNagaraju Yalavarthi
Ěý
DNA is the genetic material found in cells. It exists in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in the form of a double helix composed of two strands bound together by hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous base pairs. The four bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine in DNA or uracil in RNA. DNA can take on different structures depending on its sequence and environment, including A, B, C, D, E, and Z forms. Eukaryotic DNA is linear and contained within the nucleus, while prokaryotic DNA exists as a single circular chromosome. RNA also exists as a single strand and plays important roles in protein synthesis and gene regulation.Translation in eukaryotes



Translation in eukaryotesHETAKUMARI PILUDARIA
Ěý
Translation in Eukaryotes
The third part of Central Dogma
Transferring the information from RNA to Protein
For BSc students
Transcriptional and post transcriptional regulation of gene expression



Transcriptional and post transcriptional regulation of gene expressionDr. Kirti Mehta
Ěý
Gene expression is regulated at the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. Transcriptional regulation involves proteins binding to promoter and enhancer sequences to control RNA polymerase recruitment and initiation of transcription. Eukaryotic gene expression requires transcription factors, coactivators, and basal transcription factors to assemble the transcription initiation complex. Post-transcriptional regulation influences RNA processing, transport, translation, and degradation.Transcription Regulation 



Transcription Regulation IshaqueAbdulla
Ěý
This document provides an overview of regulation of transcription in eukaryotes. It discusses that transcription is primarily controlled at the initiation stage by proteins binding to regulatory sequences. These sequences include promoters near the transcription start site as well as enhancers that can be located farther away. Enhancers stimulate transcription through DNA looping. Gene expression is also regulated by chromatin structure and DNA methylation. Transcription factors have distinct DNA-binding and activation domains and include zinc finger and helix-turn-helix motifs.Translation in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes



Translation in Prokaryotes and EukaryotesShiv Nadar University
Ěý
This document summarizes translation mechanisms in prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems. It discusses that translation is the process of protein synthesis from mRNA, involving ribosomes, tRNAs, and enzymes. The three main steps of translation - initiation, elongation, and termination - are described for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems. Key differences between the two systems are the use of Shine-Dalgarno sequences and initiation factors in prokaryotes versus Kozak sequences and more complex initiation factor involvement in eukaryotes. Termination and ribosome recycling mechanisms are also compared between prokaryotes and eukaryotes.HELIX-LOOP-HELIX, HELIX-TURN-HELIX



HELIX-LOOP-HELIX, HELIX-TURN-HELIXnaren
Ěý
ALL BASIC AND IMPORTANT CONTENT REGARDING HELIX LOOP HELIX AND HELIX TURN HELIX.. ALL ITS FUNCTION AND SUMMARY.
HOPE YOU WILL FIND IT EASY..Transposibleelements.pptx



Transposibleelements.pptxYoGeshSharma834784
Ěý
This document discusses transposable elements, which are mobile genetic elements that can move within genomes. It describes different types of transposable elements in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In prokaryotes, examples discussed include insertion sequence (IS) elements and transposons. In eukaryotes, examples of transposable elements found in corn, yeast, and Drosophila are described. The mechanisms of both replicative and non-replicative transposition are summarized. Barbara McClintock's pioneering discoveries of transposable elements in corn through her studies of kernel color are also highlighted.Arabinose operon and their regulation and arac 



Arabinose operon and their regulation and arac VijiMahesh1
Ěý
arabinose operon and their detalied explanation about the operon conceptt and their regulation both positive and negative and the detailed explanation of the promoter ,operator,inducer,structural gene,arac protein Translation: Protein synthesis



Translation: Protein synthesisDr. Mafatlal Kher
Ěý
Translation is the process by which the genetic code stored in mRNA is used to synthesize proteins. It occurs on ribosomes using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to add amino acids to a growing polypeptide chain. There are three sites on the ribosome - the A site binds incoming tRNA, the P site holds tRNA with the polypeptide chain, and the E site releases tRNA. Through the repetitive binding of tRNA to mRNA codons and formation of peptide bonds, proteins specified by the mRNA are assembled from amino acids based on the genetic code.Phage Gene Regulation.pptx



Phage Gene Regulation.pptxDepartment of Biotechnology, Kamaraj college of engineering and technology
Ěý
A bacteriophage is a virus that infects bacteria. Lambda phage is a temperate bacteriophage that has two life cycle choices: lytic and lysogenic. During lysogeny, the lambda repressor binds to the operator region (OR) on the phage DNA and represses transcription of lytic genes, allowing the phage genome to remain dormant as a prophage integrated into the bacterial chromosome.Translation in prokaryotes



Translation in prokaryotesshishtasharma1
Ěý
This document summarizes the key steps of translation: initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation involves assembly of the ribosomal subunits and initiator tRNA on the mRNA. Elongation consists of aminoacyl-tRNA delivery, peptide bond formation, and translocation. Termination occurs when a stop codon enters the A site, triggering release factors to cleave the polypeptide from tRNA and dissociate the ribosomal subunits.Prokaryotic DNA replication



Prokaryotic DNA replicationMoumita Paul
Ěý
DNA replication in prokaryotes begins with the unwinding of DNA at the origin of replication by enzymes like DnaA and DnaB helicase. This produces two replication forks that move in opposite directions. The leading strand is replicated continuously while the lagging strand is replicated discontinuously in short segments called Okazaki fragments. DNA polymerase III is the main enzyme that synthesizes new DNA. Replication terminates at the terminus region when the DnaB helicase is stopped by protein Tus bound to Ter sequences.Genetic code - 



Genetic code - Ashok Katta
Ěý
The genetic code is the system by which nucleotide sequences in mRNA determine the amino acid sequences in proteins. The genetic code uses triplets of nucleotides called codons to specify which amino acid will be incorporated into the growing polypeptide chain. There are 64 possible codons but only 20 standard amino acids, so most amino acids have multiple codons. Three codons act as stop signals to end protein synthesis. The genetic code is nearly universal across all life due to its high degree of specificity and redundancy.Translation In Eukaryotes



Translation In EukaryotesUmer Farooq
Ěý
Translation is the process by which proteins are synthesized from messenger RNA (mRNA) in eukaryotes, which are organisms with membrane-bound nuclei. Translation involves mRNA being decoded on ribosomes into a polypeptide chain. It occurs through three main steps - initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation involves the small ribosomal subunit binding to the 5' end of mRNA and scanning for the start codon. Elongation is the sequential addition of amino acids specified by the mRNA codons. Termination occurs when a stop codon is reached and release factors cause the ribosome to dissociate and release the completed protein.Translation



TranslationRinaldo John
Ěý
1. Translation is the process by which the information contained in mRNA is used to synthesize proteins from amino acids. It occurs on ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
2. Ribosomes contain three binding sites (A, P, and E sites) that facilitate the sequential addition of amino acids to form a polypeptide chain. tRNAs carry specific amino acids and recognize mRNA codons through complementary base pairing of their anticodons.
3. The genetic code consists of three-nucleotide sequences called codons that specify which of 20 amino acids will be added during translation. Most amino acids are specified by multiple codons. Translation proceeds through initiation, elongation, translocation, and termination phases.Galactose operon and Histidine operon 



Galactose operon and Histidine operon PunithKumars6
Ěý
The document discusses the galactose and histidine operons. It describes the structural organization and regulation of the galactose operon, including the Leloir pathway for D-galactose metabolism and repression/induction by galactose. It also summarizes the structural organization and two mechanisms of regulation (feedback inhibition and repression control) for the histidine operon. Finally, it explains attenuation control of the histidine operon through transcriptional termination or anti-termination depending on histidine availability.Dna binding proteins



Dna binding proteinsHari Sharan Makaju
Ěý
The document discusses DNA binding proteins. It describes how DNA is wrapped around histone proteins to form nucleosomes, which resemble "beads on a string". There are five main types of histone proteins - H1, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Histone proteins can be modified through processes like acetylation and methylation, which affect gene expression. Other non-histone proteins use motifs like zinc fingers and helix-turn-helix to bind DNA in a sequence-specific manner and regulate transcription.Regulation of gene expression in prokaryotes



Regulation of gene expression in prokaryotesgohil sanjay bhagvanji
Ěý
This document discusses various mechanisms of gene expression regulation in prokaryotes. It introduces the concepts of induction and repression using the example of beta-galactosidase in E. coli. Inducers activate gene expression while corepressors repress it. The operon model of the lac and tryptophan operons is explained in detail. Other mechanisms discussed include transcriptional, translational, and post-transcriptional regulation. Feedback inhibition is also summarized.Phage Gene Regulation.pptx



Phage Gene Regulation.pptxDepartment of Biotechnology, Kamaraj college of engineering and technology
Ěý
Similar to genetic code.pptx (20)
Genetic code2



Genetic code2piya1apiya
Ěý
1. The genetic code is composed of nucleotide triplets called codons that specify individual amino acids.
2. Experiments confirmed that the genetic code is a triplet code and that each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid, with some codons coding for the same amino acid (degenerate).
3. Key properties of the genetic code include it being triplet-based, non-overlapping, unambiguous, degenerate, and nearly universal across organisms.Genetic code slide



Genetic code slideDr.M.SANKARESWARAN
Ěý
Genetic code is a dictionary that corresponds with sequence of nucleotides and sequence of amino acids.
Genetic code is a set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material(DNA or RNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells.
Term given By ″ Goerge Gamow ʺ
GENETIC CODE.pptx



GENETIC CODE.pptxGRThapliyal
Ěý
The genetic code is the set of rules by which ribosomes translate nucleic acid sequences into amino acid sequences during biological protein synthesis. It is based on triplets of nucleotides called codons, with 64 possible codons composed of combinations of four nucleotides. Codons are read sequentially in groups of three and each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid, with some codons corresponding to termination signals. The genetic code is nearly universal across all living organisms and is non-overlapping, non-ambiguous, and degenerate.Genetic Code and Protein Biosynthesis.pptx



Genetic Code and Protein Biosynthesis.pptxDeepanshuBanyal
Ěý
The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences) is translated into proteins (amino acid sequences) by living cells.
Each codon is a triplet of nucleotides, 64 codons in total and three out of these are Non Sense codons, 61 codons for 20 amino acids.
The letters A, G, T and C correspond to the nucleotides found in DNA. They are organized into codons. The collection of codons is called Genetic code.
For 20 amino acids there should be 20 codons. Each codon should have 3 nucleotides to impart specificity to each of the amino acid for a specific codon:
• 1 Nucleotide- 4 combinations
• 2 Nucleotides- 16 combinations
• 3 Nucleotides- 64 combinations ( Most suited for 20 amino acids)
Genetic Information Transfer (Biology for Engineers)



Genetic Information Transfer (Biology for Engineers)Dr. Arun Sharma
Ěý
Information Transfer: Purpose: The molecular basis of coding and
decoding genetic information is universal. Molecular basis of information
transfer. DNA as a genetic material. Hierarchy of DNA structure- from
single stranded to double helix to nucleosomes. Concept of genetic code.
Universality and degeneracy of genetic code. Define gene in terms of
complementation and recombination.Genetic code.pptx



Genetic code.pptxAliya Fathima Ilyas
Ěý
• The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences) is translated into proteins (amino acid sequences) by living cells.
• The genetic code, once thought to be identical in all forms of life, has been found to diverge slightly in certain organisms and in the mitochondria of some eukaryotes.
• Nevertheless, these differences are rare, and the genetic code is identical in almost all species, with the same codons specifying the same amino acids.
Genetic code 



Genetic code DhirendraKumar175
Ěý
Genetic code describes codons that code amino acids. Contents are well defined according to process central dogma specially Translation mechanism.Concept of genetic code and its properties



Concept of genetic code and its propertiesVishrut Ghare
Ěý
These slides contain information about genetic code and properties, Start codon and stop codon, Wobble hypothesisGenetic code



Genetic codeRachana Choudhary
Ěý
Genetic code is the term we use for the way that the four bases of DNA--the A, C, G, and Ts--are strung together in a way that the cellular machinery, the ribosome, can read them and turn them into a protein. In the genetic code, each three nucleotides in a row count as a triplet and code for a single amino acid.Genetic code



Genetic codeSHALINIBARA
Ěý
The genetic code is composed of triplets of nucleotide bases that correspond to specific amino acids. There are 64 possible codon combinations from sequences of the 4 nucleotide bases, with 61 coding for 20 amino acids and 3 serving as stop codons. The genetic code is universal across all living organisms, specifying the same amino acids for each codon. It is read in sets of 3 bases moving in the 5' to 3' direction on mRNA, and mutations in the code can result in silent, missense, nonsense, or frameshift changes to the specified protein.Genetic code a presentation on genetic code how a gene express themselves



Genetic code a presentation on genetic code how a gene express themselvesrushinstagoor
Ěý
The genetic code consists of triplet nucleotide sequences in mRNA that code for amino acids in proteins. There are 64 possible codon combinations using the four nucleotide bases, with 61 codons coding for 20 amino acids. Three codons act as stop signals. The genetic code is universal across organisms, specific in its codon-amino acid mapping, non-overlapping in reading frames, and degenerate with multiple codons coding for single amino acids. Codons are recognized by anticodons in tRNA through Watson-Crick base pairing, with some third base wobble according to Wobble hypothesis. Mutations can alter codons and cause changes to protein sequences.Genetic code



Genetic codeIqraSami3
Ěý
The sequence ofĚýnucleotidesĚýinĚýdeoxyribonucleic acidĚý(DNA) andĚýribonucleic acidĚý(RNA) that determines theĚýamino acidĚýsequence of proteins. Though the linear sequence of nucleotides in DNA contains the information forĚýproteinĚýsequences, proteins are not made directly from DNA. Instead, aĚýmessenger RNAĚý(mRNA) molecule is synthesized from the DNA and directs the formation of the protein. RNA is composed of four nucleotides: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), andĚýuracil."(U)." Genetic code deciphering propertie and code dictionary.



Genetic code deciphering propertie and code dictionary.HEENA KAUSAR
Ěý
The genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material into proteinsGenetic code - Charateristics



Genetic code - CharateristicsJigar Patel
Ěý
The genetic code is the sequence of nitrogen bases in mRNA that contains the information for protein synthesis. A codon is three nitrogen bases that code for a single amino acid. Nirenberg and Mathaei experimentally proved that codons determine amino acids. The genetic code is universal, uses non-overlapping triplets to specify amino acids in a linear, commaless fashion, and employs initiation and termination codons.Genetic Code. A comprehensive overview..pdf



Genetic Code. A comprehensive overview..pdfmughalgumar440
Ěý
The genetic code serves as nature's instruction manual, dictating how genetic information is translated into proteins essential for life. Comprised of codons which code for specific amino acid or signaling the start or end of protein synthesis. This code exhibits redundancy and universality across organisms, In essence, the genetic code is the foundation of biological diversity and functionality, shaping the characteristics and functions of all living beings.Genetic code and transcription



Genetic code and transcriptionAnfal Izaldeen AL KATEEB
Ěý
Genetic information is stored in DNA by means of a triplet code that is nearly universal to all living things on Earth.
The genetic code is initially transferred from DNA to RNA, in the process of transcription.
Genetic code and transcription



Genetic code and transcriptionAnfal Izaldeen AL KATEEB
Ěý
Genetic information is stored in DNA by means of a triplet code that is nearly universal to all living things on Earth.
The genetic code is initially transferred from DNA to RNA, in the process of transcription.
deciphering the genetic code and its features



deciphering the genetic code and its featuresRANJITHA512994
Ěý
A brief description of the genetic code and its features. Genetic Code and Translation.pdf



Genetic Code and Translation.pdfuniversity of karachi
Ěý
The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in DNA is translated into proteins by living cells. It specifies how sequences of nucleotides in mRNA are used to direct protein synthesis through codon-anticodon interactions between mRNA and tRNA. The genetic code is nearly universal, with some minor variations, and is written in the 5' to 3' direction on mRNA. It uses 64 possible codon combinations to specify 20 standard amino acids and 3 stop codons.Genetic code and translation



Genetic code and translationSafder Abbas
Ěý
The genetic code is universal and specifies how nucleotides in DNA and mRNA are translated to amino acids in proteins. It uses 64 codons consisting of 3 nucleotides each to encode the 20 standard amino acids. The code is degenerate, with most amino acids specified by multiple codons. It also has start and stop codons to initiate and terminate translation. Wobble base pairing in the third codon position allows fewer tRNAs to recognize all codons.Recently uploaded (20)
communication in pharmacovigilance for B pharmacy and Pharm D



communication in pharmacovigilance for B pharmacy and Pharm DNashrahnasreen
Ěý
communication in pharmacovigilance
pharmacovigilance for B pharmacy and pharm D ABNORMALITIES OF PLACENTA & UMBILICAL CORD.pptx



ABNORMALITIES OF PLACENTA & UMBILICAL CORD.pptxSREEVIDYA UMMADISETTI
Ěý
DESCRIBES ABNORMALITIES OF PLACENTA AND UMBILICAL CORDEquation Of Motion In Mechanical Ventilation Application



Equation Of Motion In Mechanical Ventilation ApplicationFaisalRawagah1
Ěý
Presentation Title: Equation of Motion in Mechanical Ventilation: Clinical Applications and Insights
Presenter: Dr. Faisal MA Rawagah (Minimally Invasive Bariatric Surgeon and Intensivist)
Description:
This comprehensive presentation delves into the Equation of Motion and its critical role in understanding mechanical ventilation dynamics. Designed for intensivists, pulmonologists, respiratory therapists, and critical care professionals, the slides explore key concepts such as:
Core Components of the Equation:
Pressure (P), Resistance (R), Volume (V), Compliance (C), and PEEP.
Clinical Parameters:
Resistance Pressure, Peak Inspiratory Pressure (PIP), Plateau Pressure (Pplat), Driving Pressure, and Stress Index (SI).
Practical Applications:
Calculating resistance and compliance in ventilator management.
Interpreting P/V loops and time constants (Ď„ = RĂ—C).
Stress Index analysis for optimizing ventilation strategies.
Case Examples:
Step-by-step breakdowns of pressure equations and their real-world implications.
Learn how to translate theoretical principles into actionable clinical decisions, enhance patient outcomes, and avoid common pitfalls in ventilator settings. The presentation also addresses advanced topics like the "Equation of the Monster" (time constant) and the significance of slow P/V loops.
Presenter Credentials:
Dr. Faisal MA Rawagah combines expertise in minimally invasive surgery and critical care, offering a unique perspective on bridging surgical and intensive care practices.
Contact:
For inquiries, reach Dr. Rawagah at f.rawagah@gmail.com or +962 7 75 44 1427.
Ideal for:
Medical professionals seeking to deepen their understanding of mechanical ventilation mechanics and improve bedside practice.DEFIBRILLATORS.pptx created by KIRAN KARETHA



DEFIBRILLATORS.pptx created by KIRAN KARETHAKIRAN KARETHA
Ěý
Defibrillation is a process in which an electronic device sends an electric shock to the heart to stop an extremely rapid, irregular heartbeat, and restore the normal heart rhythm.
Defibrillator is an electronic apparatus used to counteract atrial or ventricular fibrillation by application of a brief electric shock to the heart.
Drugs acting on Respiratory System: Anti-Athmatic Drugs.pptx



Drugs acting on Respiratory System: Anti-Athmatic Drugs.pptxSivaGanesh552177
Ěý
The topic " Anti-Asthmatic Drugs" is covered under Unit I of the Pharmacology of Drugs Acting on the Respiratory System, which is included in the course of Pharmacology III with course code BP602.Adverse Drug Reactions (ADR). .



Adverse Drug Reactions (ADR). .Department of Pharmaceutical science, Gurugram University
Ěý
Adverse Drug Reactions are
unintended and harmful responses resulting from the
administration of medication; these may range
from mild side effects to life threatening conditions,
reflecting the complexity of
individual pharmacological
responses presented by Sant Kumar from Department of Pharmaceutical science, Gurugram University
HYPERTENSIVE DISORDERS.pptx TOXAEMIA OF PREGNANCY



HYPERTENSIVE DISORDERS.pptx TOXAEMIA OF PREGNANCYSREEVIDYA UMMADISETTI
Ěý
DESCRIBES PREGNANCY INDUCED HYPERTENSION AND PRE ECLAMPSIAIntroduction to the Clinical Laboratory.pdf



Introduction to the Clinical Laboratory.pdfShafqat Hussain
Ěý
Introduction to Laboratory
Introduction to diagnostic laboratory
What is lab
Learning Objectives
• What is a Laboratory
• Different types of Laboratory
• Understand the role of the clinical laboratory in healthcare.
• Identify the different types of laboratory departments.
• Clinical Lab Instruments
What is a Laboratory?
•A laboratory is a controlled environment where scientific experiments, tests, and analyses are
conducted.
•It is equipped with specialized instruments, tools, and reagents to perform specific tasks.
•Laboratories play a critical role in advancing science, medicine, and technology.
What is a Clinical Laboratory?
•A facility where tests are performed on clinical
specimens to diagnose, monitor, and treat diseases.
•Provides critical information for patient care.ADOLESCENT PREGNANCY.pptx TEENAGE PREGNANCY



ADOLESCENT PREGNANCY.pptx TEENAGE PREGNANCYSREEVIDYA UMMADISETTI
Ěý
ADOLESCENT PREGNANCY OR TEENAGE PREGNANCYDynamic and Flexible Fullstack NGS Pipelines in VSWarehouse 3



Dynamic and Flexible Fullstack NGS Pipelines in VSWarehouse 3Golden Helix
Ěý
As clinical variant analysis grows in complexity, laboratories face challenges in unifying diverse pipelines, optimizing infrastructure, and ensuring seamless collaboration between bioinformaticians and clinicians. In this webcast, we explore how VarSeq and VSWarehouse 3 (WH3) provide a scalable and customizable solution to integrate secondary and tertiary analysis pipelines within a single workspace.
Through real-world examples, we will demonstrate how WH3 enables flexible deployment, whether on-premises, in the cloud, or hybrid, to accommodate a variety of workflows, from whole-genome sequencing (WGS) trios to high-throughput panel processing. Attendees will gain insights into:
Unifying disparate secondary analysis pipelines in WH3 for a streamlined workflow.
Customizing pipelines with user-defined inputs, modular steps, and external tool integration.
Leveraging WH3’s infrastructure flexibility to optimize performance for specific project needs.
Seamlessly connecting secondary pipelines to tertiary analysis for efficient variant interpretation.
Join us as we showcase how WH3 empowers clinical labs with the adaptability and scalability needed to meet the evolving demands of genomic analysis.RADIOLOGY OF CANCER CERVIX BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATRO



RADIOLOGY OF CANCER CERVIX BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATROKanhu Charan
Ěý
RADIOLOGY OF CANCER CERVIX BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATROINTRA UTERINE DEATH.pptx INTRA UTERINE FETAL DEATH



INTRA UTERINE DEATH.pptx INTRA UTERINE FETAL DEATHSREEVIDYA UMMADISETTI
Ěý
IUFD OR IUD DESRIBES ABOUT INTRA UTERINE FETAL DEATHIntegrating Biomarker Testing Into Alzheimer’s Disease Workflows: Tools and S...



Integrating Biomarker Testing Into Alzheimer’s Disease Workflows: Tools and S...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
Ěý
Chair and Presenter, Suzanne E. Schindler, MD, PhD, Tammie L.S. Benzinger, MD, PhD, and Lawren VandeVrede, MD, PhD, prepared useful Practice Aids pertaining to Alzheimer’s disease for this CME/MOC/AAPA activity titled “Integrating Biomarker Testing Into Alzheimer’s Disease Workflows: Tools and Strategies for Specialty Care.” For the full presentation, downloadable Practice Aids, and complete CME/MOC/AAPA information, and to apply for credit, please visit us at https://bit.ly/3YLJ5EX. CME/MOC/AAPA credit will be available until March 17, 2026.Thrombotic Microangiopathies in Pregnancy



Thrombotic Microangiopathies in PregnancyChristos Argyropoulos
Ěý
Review of the syndromes , pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of TMA (aHUS/TTP) in pregnancyLet's Talk About It: Breast Cancer (The Unspoken Emotions of Cancer Survivors...



Let's Talk About It: Breast Cancer (The Unspoken Emotions of Cancer Survivors...RheannaRandazzo
Ěý
Sadness and worry are often discussed as common emotional responses to cancer survivorship, but what about the quieter, heavier feelings—resentment, regret, bitterness, or anger? These "darker feelings" are just as valid and normal, yet they often go unspoken and unprocessed.
Join us on Wednesday, February 19th, for an open and compassionate conversation about these less-discussed emotions. Together, we’ll create a safe space to explore and understand them, building a path toward healing, self-awareness, and acceptance.
Let’s talk about it.SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHROMATOUS/ SLE - Pharm D Notes .pptx



SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHROMATOUS/ SLE - Pharm D Notes .pptxAyesha Fatima
Ěý
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease associated with autoantibody production. SLE is a multisystem disease.
The term “lupus” (Latin for wolf) was first used in the 13th century to describe erosive lesions that looked like skin that had been gnawed by a wolf.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
SLE occur most frequently in women of reproductive age (15–50 years old)
Rates are nine times higher in women than in men.
It is affected by ethnicity, which includes genetic, geographic,
cultural, social, and other aspects within a group.
Rates are higher in non - whites than in the white population.
It is most common in those of African origin.
ETIOLOGY
The exact etiology for SLE is unknown but many factors have been identified that appear to play a role in the disease.
Predisposing factors
Genetic influences :
First-degree relatives of patients with SLE are 20 times more likely to develop the disease than those in a general population.
The genetic predisposition to SLE is a result of the interplay of a combination of genes.
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II alleles HLA-DR2 and HLA-DR3 are known to be linked to SLE.
Epigenetic regulation of gene expression :
Gene expression is regulated by deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) methylation and histone modifications.
These epigenetic changes can cause alterations that may influence SLE.
Hydralazine and procainamide, two drugs that may induce lupus, inhibit DNA methylation.
Environmental factors :
Cigarette smoke is phototoxic and associated with cutaneous lupus.
Ultraviolet light can cause keratinocytes in the skin to release nuclear material that can further stimulate the immune system and autoantibody production by B cells.
Viruses Epstein–Barr virus.
Other include : infections, medications (eg, vaccines and biologics) psychological stress, silica dust, hydralazines, petroleum, solvents (eg, nail polish remover and metal cleaners), dyes, and pesticides.
Hormones, and
Abnormalities in immune cells and cytokines
Pathogenesis is related in large part to production of increased quantities and immunogenic forms of nucleic acids and other self-antigens, which drive autoimmune-inducing activation of innate immunity, autoantibodies, and T cells.
Interactions between genes, environment, and epigenetic changes drive increased autophagy, Ag presentation, neutrophil NETosis, autoantibody formation with increased plasma cells, and production of pathogenic effector T cells in Th1, Th17, and Tfh subsets, with ineffective regulatory networks.
The exact mechanism of autoantibody tissue destruction is unclear.
Immune complexes form when autoantibodies bind to nuclear material and deposit in tissues.
They activate the complement cascade, leading to an influx of inflammatory cells and tissue injury.
Autoantibodies might also directly react with proteins in tissues.
There are increased T helper cells type 2 and 17 and diminished number and function of T regulatory (Treg) cells.
Cytokines. Integrating Biomarker Testing Into Alzheimer’s Disease Workflows: Tools and S...



Integrating Biomarker Testing Into Alzheimer’s Disease Workflows: Tools and S...PVI, PeerView Institute for Medical Education
Ěý
genetic code.pptx
- 1. GENETIC CODE Presentation By: Nageen Talib Department: IBAHS
- 2. Outlines • What is genetic code? • Genetic code table • Wobble Hypothesis • Properties of genetic code • Exceptions to the code
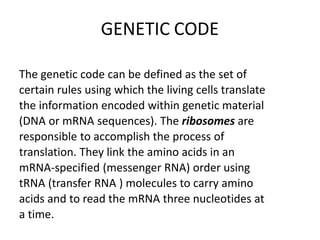
- 3. GENETIC CODE The genetic code can be defined as the set of certain rules using which the living cells translate the information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences). The ribosomes are responsible to accomplish the process of translation. They link the amino acids in an mRNA-specified (messenger RNA) order using tRNA (transfer RNA ) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time.
- 4. The complete set of relationships among amino acids and codons is said to be a genetic code which is often summarized in a table.
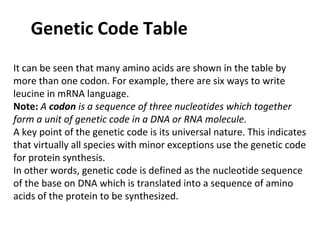
- 5. Genetic Code Table It can be seen that many amino acids are shown in the table by more than one codon. For example, there are six ways to write leucine in mRNA language. Note: A codon is a sequence of three nucleotides which together form a unit of genetic code in a DNA or RNA molecule. A key point of the genetic code is its universal nature. This indicates that virtually all species with minor exceptions use the genetic code for protein synthesis. In other words, genetic code is defined as the nucleotide sequence of the base on DNA which is translated into a sequence of amino acids of the protein to be synthesized.
- 6. The Wobble Hypothesis • There are more than one codon for one amino acid. This is called degeneracy of genetic code. • To explain the possible cause of degeneracy of codons, in 1966, Francis Crick proposed “the Wobble hypothesis”. • According to this hypothesis, only the first two bases of the codon have a precise pairing with the bases of the anticodon of tRNA, while the pairing between the third bases of codon and anticodon may Wobble (wobble means to sway or move unsteadily). • The phenomenon permits a single tRNA to recognize more than one codon. Therefore, although there are 61 codons for amino acids, the number of tRNA is far less (around 40) which is due to wobbling.
- 7. • The first two bases of the codon make normal (canonical) H-bond pairs with the 2nd and 3rd bases of the anticodon. • At the remaining position, less stringent rules apply and non- canonical pairing may occur. The wobble hypothesis thus proposes a more flexible set of base-pairing rules at the third position of the codon. • The relaxed base-pairing requirement, or “wobble,” allows the anticodon of a single form of tRNA to pair with more than one triplet in mRNA. • The rules: first base U can recognize A or G, first base G can recognize U or C, and first base I can recognize U, C or A.
- 10. Properties of Genetic Code • Triplet code • Non-ambiguous and Universal • Degenerate code • Non-overlapping code • Commaless • Start and Stop Codons • Polarity
- 11. Triplet code A codon or a code word is defined as a group of bases that specify an amino acid. There is strong evidence, which proves that a sequence of three nucleotides codes for an amino acid in the protein, i.e., the code is a triplet. The four bases of nucleotide i.e, (A, G, C, and U) are used to produce three-base codons. The 64 codons involve sense codons (that specify amino acids). Hence, there are 64 codons for 20 amino acids since every codon for one amino acid means that there exist more than one code for the same amino acid. Commaless code No room for punctuation in between which indicates that every codon is adjacent to the previous one without any nucleotides between them.
- 12. Nonoverlapping code The code is read sequentially in a group of three and a nucleotide which becomes a part of triplet never becomes part of the next triplet. For example 5’-UCU-3’ codes for Serine 5’-AUG-3’ codes for methionine Polarity Each triplet is read from 5’ → 3’ direction and the beginning base is 5’ followed by the base in the middle then the last base which is 3’. This implies that the codons have a fixed polarity and if the codon is read in the reverse direction, the base sequence of the codon would reverse and would specify two different proteins. Degenerate code Every amino acid except tryptophan (UGG) and methionine (AUG) is coded by various codons, i.e, a few codons are synonyms and this aspect is known as the degeneracy of genetic code.
- 13. Start and Stop Codons Generally, AUG codon is the initiating or start codon. The polypeptide chain starts either with eukaryotes (methionine) or prokaryotes (N- formylmethionine). On the other hand, UAG, UAA and UGA are called as termination codons or stop codons. These are not read by any tRNA molecules and they never code for any amino acids. Non-ambiguous and Universal The genetic code is non-ambiguous which means a specific codon will only code for a particular amino acid. Also, the same genetic code is seen valid for all the organisms i.e. they are universal.
- 14. Exceptions to the Code The genetic code is universal since similar codons are assigned to identical amino acids along with similar START and STOP signals in the majority of genes in microorganisms and plants. However, a few exceptions have been discovered and most of these include assigning one or two of the STOP codons to an amino acid. Apart from this, both the codons GUG and AUG may code for methionine as a starting codon, although GUG is meant for valine. This breaks the property of non-ambiguousness. Thus, it can be said that few codes often differs from the universal code or non- ambiguous code.
- 15. Codon Universal code Human mitochondrial code AGA Arg Stop AGG Arg Stop AUA Ile Met



