GEOMETRICAL OPTICS (REFRACTION) physical sciences G11
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes30 views
Based on refraction only in the physics geometric optics
1 of 15
Download to read offline













Recommended
Laws of reflection



Laws of reflectionLABISHETTY CHARAN
╠²
Geometrical optics describes the laws of reflection and refraction of light. When light travels from one medium to another, it can be reflected, refracted, scattered, or absorbed at the interface. Reflection follows the law that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Refraction is described by Snell's law, which relates the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction to the refractive indices of the media. The bending of light occurs due to changes in speed as it passes between materials of different refractive indices. Prisms are used to demonstrate refraction and dispersion of light into its component wavelengths.1 reflection and refraction



1 reflection and refractionMissingWaldo
╠²
Light can be thought of as travelling in rays that change direction through reflection and refraction. Reflection occurs when light strikes a surface, following the laws that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Refraction occurs when light passes from one medium to another of different density, bending according to Snell's law that relates the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction through the refractive indices. The refractive index quantifies how much light slows down in a medium relative to a vacuum. Common refractive indices include air as 1, water as 1.33 and glass around 1.5.Geometrical optics



Geometrical opticsSiyavula
╠²
Geometrical optics is the study of how light interacts with materials and their shapes. Light rays reflect off surfaces according to the law of reflection, where the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Refraction occurs when light travels from one medium to another and its speed changes, causing it to change direction. Snell's law describes the relationship between the refractive indices and angles of incidence and refraction between two media. Total internal reflection occurs when light travels from an optically dense to a less dense medium at an angle greater than the critical angle, and the light is fully reflected back into the first medium.Pin Hole Imaging, Reflection & Refraction



Pin Hole Imaging, Reflection & RefractionRabia Ammer
╠²
This document discusses several optical phenomena including pinhole imaging, reflection, refraction, and total internal reflection. It begins by explaining how pinhole imaging works to form an inverted image without the use of lenses due to the collimating effect of a small aperture. Next, it covers the fundamentals of reflection including the law of reflection and diffuse reflection. Refraction is then summarized, including Snell's law and how light bends when passing through different media based on their refractive indices. Finally, the document briefly discusses the phenomenon of total internal reflection that occurs when light passes from an optically dense to rare medium at an angle greater than the critical angle.Basic optics



Basic opticsAmer Ghazi Attari
╠²
The document summarizes the ray model of light, which describes light traveling in straight lines called rays. It discusses how light rays change direction upon reflection off surfaces or when passing between materials with different refractive indices. This redirection of light rays is governed by two laws: the law of reflection, which states that the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence, and Snell's law of refraction, which relates the refractive indices of materials to how much a light ray bends when passing between them. Total internal reflection can occur when light passes from a higher to lower refractive index material at an angle greater than the critical angle, causing all the light to be reflected back into the first material.Semiconductor LASERS ( 8 Lectures )Review of Laser Physics



Semiconductor LASERS ( 8 Lectures )Review of Laser PhysicsSitamarhi Institute of Technology
╠²
Review of Laser Physics; Rate equations for carrier- and Photon-Density and their Steady state solutions, Laser Dynamics, Relaxation oscillations, Input-Output characteristics of Lasers. Semiconductor Laser: Structure, Materials, Device characteristics and figures of Merit; DFB, DBR, and verticalcavity Surface-Emitting Lasers (vecsel), Tunable Semiconductor Lasers.5 refraction, snells law (8.2)



5 refraction, snells law (8.2)Jason Whittle
╠²
1) Light bends when moving between materials with different densities, called refraction.
2) The degree that light bends depends on the change in speed according to Snell's law, which relates the angle of incidence and refraction based on the refractive indices of the materials.
3) Higher refractive index means lower speed of light, so light bends more when moving from lower to higher indices.Total internal reflection



Total internal reflectionramalakshmi54
╠²
The document discusses the principles of light propagation in optical fibers, including total internal reflection. It explains that total internal reflection occurs when light travels from a higher density medium to a lower density medium at an angle greater than the critical angle. This causes the light ray to reflect back into the first medium rather than refracting into the second. Total internal reflection is the mechanism that allows light to propagate along the length of an optical fiber with little loss of intensity.0511 week10 second_reflection



0511 week10 second_reflectionSubas Nandy
╠²
This document provides a summary of key concepts in reflection and refraction of light:
- Light was originally thought to consist of particles (1000 AD) but was later explained as a wave by Huygens in the 1600s and Maxwell in 1865. Planck later showed it has particle-like properties as well.
- Reflection follows the law that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Refraction follows Snell's law, which relates the indices of refraction and angles of the materials. Dispersion is the dependence of the index of refraction on wavelength.
- Huygen's principle treats each point on a wavefront as a secondary source, and the new wavefront is tangent to these secondaryEngineering Physics Ereflect&refract.ppt



Engineering Physics Ereflect&refract.pptEngrNoumanMemon
╠²
This document provides a history of theories about the nature of light and summarizes key concepts about reflection and refraction of light. It describes how light was initially thought to consist of particles, then was explained as a wave by Huygens, and was later found to have both wave-like and particle-like properties. The document outlines the laws of reflection and refraction, including Snell's law, total internal reflection, and their explanations via Huygens' principle. It also discusses applications such as fiber optics, rainbows, and dispersion.LIGHT.pdf



LIGHT.pdfguntikarthikkumar
╠²
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that interacts with the retina to produce the sensation of sight. It is the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, ranging from 400-700 nm. Light travels as a transverse wave and exhibits properties of both waves and particles. The interaction of light with matter can be explained using wave optics concepts like interference and diffraction, or quantum optics concepts like absorption and scattering. Geometrical optics describes how lenses and mirrors form images through reflection and refraction according to Snell's law. Total internal reflection occurs when light passes from an optically dense to rare medium at an angle greater than the critical angle.Refraction through a glass slab and the refractive index



Refraction through a glass slab and the refractive indexSharan Raj
╠²
This document discusses refraction through a rectangular glass slab and the refractive index. It begins by defining refraction as the change in direction of a wave when passing from one medium to another. It then explains Snell's law, which relates the angles of incidence and refraction. The refractive index is defined as the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in a medium. Examples of refraction in everyday life are given, as well as the history and uses of the refractive index. An experiment is described to measure the angles of incidence, refraction, and emergence using a glass slab.Refraction and snells_law



Refraction and snells_lawAtharShah7
╠²
Refraction and Snell's Law describes how light bends when passing from one medium to another due to a change in speed. Refraction occurs at the boundary between two media, with the incident ray entering the first medium at an angle of incidence, and the refracted ray exiting the second medium at an angle of refraction. Snell's law states that the ratio of the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction is equal to the ratio of the indices of refraction of the two media. This relationship is written as an equation that can be used to calculate angles of refraction based on the incident angle and refractive indices. Each material has its own index of refraction value that determines how much light will bend whenOptics and Laser (1).pptx physics notess



Optics and Laser (1).pptx physics notessShahnailMemon
╠²
This document summarizes key concepts in optics and lasers. It discusses how optics studies light and its interactions with matter. It then covers the nature of light, including reflection, refraction, Snell's law, total internal reflection, and fiber optics. It defines lasers as devices that produce coherent and monochromatic beams of light via stimulated emission of radiation. Lasers have properties of being highly directional and able to focus energy in a small area. The document explains the laser process of exciting a gain medium's atoms and photons stimulating the emission of more photons with the same properties.LIGHTS-REFRACTIONS-AND-REFLECTIONSS.pptx



LIGHTS-REFRACTIONS-AND-REFLECTIONSS.pptxMajSisonRevicente
╠²
This will help you understand basic concepts of light.REFRACTION.



REFRACTION.SRAJARAJESWARI
╠²
INTRO, CAUSE OF REFRACTION, LAWS OF REFRACTION, REFRACTIVE INDEX, APPLICATION OF REFRACTIVE INDEX, CRITICAL ANGLE, TOTAL INTERNAL REFLECTION.
Lateral shift



Lateral shiftZenblade 93
╠²
Refraction is the change in direction of a wave passing from one medium to another due to a change in its speed. When light travels from one medium to another at an angle, it bends and experiences lateral shift. Lateral shift is the perpendicular distance between the incident and emergent rays and depends on factors like the thickness and refractive index of the medium, as well as the angle of incidence. Snell's law relates the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction to the refractive indices of the media and can be used to calculate lateral shift experimentally.Refraction plane power point presentaion 



Refraction plane power point presentaion SRINIVASAREDDYCHINTA
╠²
This document discusses the fundamentals of refraction of light, including definitions of key terms like medium, rarer medium, denser medium, absolute refractive index, and relative refractive index. It explains that refraction occurs when light travels from one medium to another at a different speed, causing a change in direction. Snell's law is presented as relating the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction to the refractive indices of the media. Total internal reflection and applications are also mentioned.Polarization by reflection at a dielectric and verifying fresnelŌĆÖs equations



Polarization by reflection at a dielectric and verifying fresnelŌĆÖs equationsQahtan Al-zaidi
╠²
This document describes an experiment to verify Fresnel's equations for reflection at a dielectric surface. The experiment involves measuring the reflection coefficients and rotation of the polarization plane for light reflected at various angles of incidence off a glass prism. The reflection coefficients will be measured for perpendicular and parallel polarization and plotted against angle of incidence. The refractive index of the glass will be determined. The measured reflection coefficients and polarization rotation will be compared to values calculated using Fresnel's equations to test the equations. Key concepts covered include Brewster's angle, reflection and transmission coefficients, polarization, and Fresnel's equations.geometrical Optics



geometrical OpticsMae William- Ganaca
╠²
1. The document discusses principles of geometrical optics including pinhole imaging, mirrors, lenses, and light propagation.
2. Key terms are defined such as object and image characteristics, magnification, and refractive index.
3. Principles of reflection, refraction, and dispersion are explained according to Snell's law and the refractive indices of common optical materials.Refraction of light



Refraction of lightVASUDEV03
╠²
This document discusses the refraction of light. It defines refraction as the change in direction of light when passing from one medium to another. It states that light bends away from the normal when traveling to a less dense medium, and toward the normal when traveling to a denser medium. Snell's law is introduced, which states that the ratio of sines of the angle of incidence and refraction is a constant. Refractive index is defined as the ratio of speed of light in a vacuum to that in a medium. Lens equations and image formation by convex and concave lenses are briefly covered.Luc 2 chapter35



Luc 2 chapter35Khadiga Ali
╠²
This document provides an overview of key concepts in geometric optics, including:
- Light exhibits both wave and particle properties, with different experiments supporting each model.
- Ray optics approximates light propagation using straight line paths. Reflection and refraction cause changes in light's direction at material boundaries.
- The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Refraction is governed by Snell's law.
- Total internal reflection occurs when light passes from a high to low refractive index material beyond the critical angle, and is used in applications like fiber optics.Refraction of light



Refraction of lightMahekJais
╠²
This topic seems difficult to make a ppt on! But I hope this helps :) Feedbacks or any tips are welcomes. All the best for the presentation or your exam! Lights and Optics - reflection, refraction and dispersion of light



Lights and Optics - reflection, refraction and dispersion of lightButterflyWaltz
╠²
Light can be defined as electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, but also includes radiation with frequencies above and below the visible spectrum. Many properties of light can be explained by the wave theory that describes light as a transverse wave with electrical and magnetic properties. The speed of light varies when passing through different materials, which can be explained by this wave theory.U10 Cn1 Refraction Intro



U10 Cn1 Refraction IntroAlexander Burt
╠²
Refraction occurs when light passes from one medium to another and changes speed, causing it to bend at the boundary. The amount of bending depends on the difference in speed of light in the two media, with more bending occurring when there is a greater difference in speed. Snell's law can be used to calculate the angle of refraction given the angle of incidence and the indices of refraction of the two media.light



lightpratham gupta
╠²
Light is the part of the EM spectrum which we can see.Light travels in straight lines called rays.A bundle of rays is known as a beam of light.
Reflection and Refraction



Reflection and Refractionmeenng
╠²
Light is part of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. It travels in straight lines called rays. Reflection is when light bounces off a surface, following the laws that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection and that the incident, normal, and reflected rays lie in the same plane. Refraction is when light changes speed and direction as it passes from one medium to another due to the different refractive indices, following Snell's law. Total internal reflection occurs when light cannot pass from an optically denser medium to a less dense one if the angle of incidence exceeds the critical angle.NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION - 5TH SEM.pdf



NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION - 5TH SEM.pdfDolisha Warbi
╠²
NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION, Introduction, definition, types - macronutrient and micronutrient, food pyramid, meal planning, nutritional assessment of individual, family and community by using appropriate method, nutrition education, nutritional rehabilitation, nutritional deficiency disorder, law/policies regarding nutrition in India, food hygiene, food fortification, food handling and storage, food preservation, food preparation, food purchase, food consumption, food borne diseases, food poisoningMore Related Content
Similar to GEOMETRICAL OPTICS (REFRACTION) physical sciences G11 (20)
0511 week10 second_reflection



0511 week10 second_reflectionSubas Nandy
╠²
This document provides a summary of key concepts in reflection and refraction of light:
- Light was originally thought to consist of particles (1000 AD) but was later explained as a wave by Huygens in the 1600s and Maxwell in 1865. Planck later showed it has particle-like properties as well.
- Reflection follows the law that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Refraction follows Snell's law, which relates the indices of refraction and angles of the materials. Dispersion is the dependence of the index of refraction on wavelength.
- Huygen's principle treats each point on a wavefront as a secondary source, and the new wavefront is tangent to these secondaryEngineering Physics Ereflect&refract.ppt



Engineering Physics Ereflect&refract.pptEngrNoumanMemon
╠²
This document provides a history of theories about the nature of light and summarizes key concepts about reflection and refraction of light. It describes how light was initially thought to consist of particles, then was explained as a wave by Huygens, and was later found to have both wave-like and particle-like properties. The document outlines the laws of reflection and refraction, including Snell's law, total internal reflection, and their explanations via Huygens' principle. It also discusses applications such as fiber optics, rainbows, and dispersion.LIGHT.pdf



LIGHT.pdfguntikarthikkumar
╠²
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that interacts with the retina to produce the sensation of sight. It is the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, ranging from 400-700 nm. Light travels as a transverse wave and exhibits properties of both waves and particles. The interaction of light with matter can be explained using wave optics concepts like interference and diffraction, or quantum optics concepts like absorption and scattering. Geometrical optics describes how lenses and mirrors form images through reflection and refraction according to Snell's law. Total internal reflection occurs when light passes from an optically dense to rare medium at an angle greater than the critical angle.Refraction through a glass slab and the refractive index



Refraction through a glass slab and the refractive indexSharan Raj
╠²
This document discusses refraction through a rectangular glass slab and the refractive index. It begins by defining refraction as the change in direction of a wave when passing from one medium to another. It then explains Snell's law, which relates the angles of incidence and refraction. The refractive index is defined as the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in a medium. Examples of refraction in everyday life are given, as well as the history and uses of the refractive index. An experiment is described to measure the angles of incidence, refraction, and emergence using a glass slab.Refraction and snells_law



Refraction and snells_lawAtharShah7
╠²
Refraction and Snell's Law describes how light bends when passing from one medium to another due to a change in speed. Refraction occurs at the boundary between two media, with the incident ray entering the first medium at an angle of incidence, and the refracted ray exiting the second medium at an angle of refraction. Snell's law states that the ratio of the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction is equal to the ratio of the indices of refraction of the two media. This relationship is written as an equation that can be used to calculate angles of refraction based on the incident angle and refractive indices. Each material has its own index of refraction value that determines how much light will bend whenOptics and Laser (1).pptx physics notess



Optics and Laser (1).pptx physics notessShahnailMemon
╠²
This document summarizes key concepts in optics and lasers. It discusses how optics studies light and its interactions with matter. It then covers the nature of light, including reflection, refraction, Snell's law, total internal reflection, and fiber optics. It defines lasers as devices that produce coherent and monochromatic beams of light via stimulated emission of radiation. Lasers have properties of being highly directional and able to focus energy in a small area. The document explains the laser process of exciting a gain medium's atoms and photons stimulating the emission of more photons with the same properties.LIGHTS-REFRACTIONS-AND-REFLECTIONSS.pptx



LIGHTS-REFRACTIONS-AND-REFLECTIONSS.pptxMajSisonRevicente
╠²
This will help you understand basic concepts of light.REFRACTION.



REFRACTION.SRAJARAJESWARI
╠²
INTRO, CAUSE OF REFRACTION, LAWS OF REFRACTION, REFRACTIVE INDEX, APPLICATION OF REFRACTIVE INDEX, CRITICAL ANGLE, TOTAL INTERNAL REFLECTION.
Lateral shift



Lateral shiftZenblade 93
╠²
Refraction is the change in direction of a wave passing from one medium to another due to a change in its speed. When light travels from one medium to another at an angle, it bends and experiences lateral shift. Lateral shift is the perpendicular distance between the incident and emergent rays and depends on factors like the thickness and refractive index of the medium, as well as the angle of incidence. Snell's law relates the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction to the refractive indices of the media and can be used to calculate lateral shift experimentally.Refraction plane power point presentaion 



Refraction plane power point presentaion SRINIVASAREDDYCHINTA
╠²
This document discusses the fundamentals of refraction of light, including definitions of key terms like medium, rarer medium, denser medium, absolute refractive index, and relative refractive index. It explains that refraction occurs when light travels from one medium to another at a different speed, causing a change in direction. Snell's law is presented as relating the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction to the refractive indices of the media. Total internal reflection and applications are also mentioned.Polarization by reflection at a dielectric and verifying fresnelŌĆÖs equations



Polarization by reflection at a dielectric and verifying fresnelŌĆÖs equationsQahtan Al-zaidi
╠²
This document describes an experiment to verify Fresnel's equations for reflection at a dielectric surface. The experiment involves measuring the reflection coefficients and rotation of the polarization plane for light reflected at various angles of incidence off a glass prism. The reflection coefficients will be measured for perpendicular and parallel polarization and plotted against angle of incidence. The refractive index of the glass will be determined. The measured reflection coefficients and polarization rotation will be compared to values calculated using Fresnel's equations to test the equations. Key concepts covered include Brewster's angle, reflection and transmission coefficients, polarization, and Fresnel's equations.geometrical Optics



geometrical OpticsMae William- Ganaca
╠²
1. The document discusses principles of geometrical optics including pinhole imaging, mirrors, lenses, and light propagation.
2. Key terms are defined such as object and image characteristics, magnification, and refractive index.
3. Principles of reflection, refraction, and dispersion are explained according to Snell's law and the refractive indices of common optical materials.Refraction of light



Refraction of lightVASUDEV03
╠²
This document discusses the refraction of light. It defines refraction as the change in direction of light when passing from one medium to another. It states that light bends away from the normal when traveling to a less dense medium, and toward the normal when traveling to a denser medium. Snell's law is introduced, which states that the ratio of sines of the angle of incidence and refraction is a constant. Refractive index is defined as the ratio of speed of light in a vacuum to that in a medium. Lens equations and image formation by convex and concave lenses are briefly covered.Luc 2 chapter35



Luc 2 chapter35Khadiga Ali
╠²
This document provides an overview of key concepts in geometric optics, including:
- Light exhibits both wave and particle properties, with different experiments supporting each model.
- Ray optics approximates light propagation using straight line paths. Reflection and refraction cause changes in light's direction at material boundaries.
- The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Refraction is governed by Snell's law.
- Total internal reflection occurs when light passes from a high to low refractive index material beyond the critical angle, and is used in applications like fiber optics.Refraction of light



Refraction of lightMahekJais
╠²
This topic seems difficult to make a ppt on! But I hope this helps :) Feedbacks or any tips are welcomes. All the best for the presentation or your exam! Lights and Optics - reflection, refraction and dispersion of light



Lights and Optics - reflection, refraction and dispersion of lightButterflyWaltz
╠²
Light can be defined as electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, but also includes radiation with frequencies above and below the visible spectrum. Many properties of light can be explained by the wave theory that describes light as a transverse wave with electrical and magnetic properties. The speed of light varies when passing through different materials, which can be explained by this wave theory.U10 Cn1 Refraction Intro



U10 Cn1 Refraction IntroAlexander Burt
╠²
Refraction occurs when light passes from one medium to another and changes speed, causing it to bend at the boundary. The amount of bending depends on the difference in speed of light in the two media, with more bending occurring when there is a greater difference in speed. Snell's law can be used to calculate the angle of refraction given the angle of incidence and the indices of refraction of the two media.light



lightpratham gupta
╠²
Light is the part of the EM spectrum which we can see.Light travels in straight lines called rays.A bundle of rays is known as a beam of light.
Reflection and Refraction



Reflection and Refractionmeenng
╠²
Light is part of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. It travels in straight lines called rays. Reflection is when light bounces off a surface, following the laws that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection and that the incident, normal, and reflected rays lie in the same plane. Refraction is when light changes speed and direction as it passes from one medium to another due to the different refractive indices, following Snell's law. Total internal reflection occurs when light cannot pass from an optically denser medium to a less dense one if the angle of incidence exceeds the critical angle.Recently uploaded (20)
NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION - 5TH SEM.pdf



NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION - 5TH SEM.pdfDolisha Warbi
╠²
NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION, Introduction, definition, types - macronutrient and micronutrient, food pyramid, meal planning, nutritional assessment of individual, family and community by using appropriate method, nutrition education, nutritional rehabilitation, nutritional deficiency disorder, law/policies regarding nutrition in India, food hygiene, food fortification, food handling and storage, food preservation, food preparation, food purchase, food consumption, food borne diseases, food poisoningAI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...



AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria
╠²
AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publication, UGC-MMTTC, MANUU, 25/02/2025, Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria, University of Delhi, vinodpr111@gmail.comHow to create security group category in Odoo 17



How to create security group category in Odoo 17Celine George
╠²
This slide will represent the creation of security group category in odoo 17. Security groups are essential for managing user access and permissions across different modules. Creating a security group category helps to organize related user groups and streamline permission settings within a specific module or functionality.ASP.NET Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



ASP.NET Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠²
ASP.NET Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatFull-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Full-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠²
Full-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatRRB ALP CBT 2 Mechanic Motor Vehicle Question Paper (MMV Exam MCQ)



RRB ALP CBT 2 Mechanic Motor Vehicle Question Paper (MMV Exam MCQ)SONU HEETSON
╠²
RRB ALP CBT 2 Mechanic Motor Vehicle Question Paper. MMV MCQ PDF Free Download for Railway Assistant Loco Pilot Exam.Hannah Borhan and Pietro Gagliardi OECD present 'From classroom to community ...



Hannah Borhan and Pietro Gagliardi OECD present 'From classroom to community ...EduSkills OECD
╠²
Hannah Borhan, Research Assistant, OECD Education and Skills Directorate and Pietro Gagliardi, Policy Analyst, OECD Public Governance Directorate present at the OECD webinar 'From classroom to community engagement: Promoting active citizenship among young people" on 25 February 2025. You can find the recording of the webinar on the website https://oecdedutoday.com/webinars/
How to Configure Proforma Invoice in Odoo 18 Sales



How to Configure Proforma Invoice in Odoo 18 SalesCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to configure proforma invoice in Odoo 18 Sales module. A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice that serves as a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer.How to Configure Deliver Content by Email in Odoo 18 Sales



How to Configure Deliver Content by Email in Odoo 18 SalesCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to configure proforma invoice in Odoo 18 Sales module. A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice that serves as a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer.Odoo 18 Accounting Access Rights - Odoo 18 ║▌║▌▀Żs



Odoo 18 Accounting Access Rights - Odoo 18 ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on accounting access rights in odoo 18. To ensure data security and maintain confidentiality, Odoo provides a robust access rights system that allows administrators to control who can access and modify accounting data. Effective Product Variant Management in Odoo 18



Effective Product Variant Management in Odoo 18Celine George
╠²
In this slide weŌĆÖll discuss on the effective product variant management in Odoo 18. Odoo concentrates on managing product variations and offers a distinct area for doing so. Product variants provide unique characteristics like size and color to single products, which can be managed at the product template level for all attributes and variants or at the variant level for individual variants.How to Configure Recurring Revenue in Odoo 17 CRM



How to Configure Recurring Revenue in Odoo 17 CRMCeline George
╠²
This slide will represent how to configure Recurring revenue. Recurring revenue are the income generated at a particular interval. Typically, the interval can be monthly, yearly, or we can customize the intervals for a product or service based on its subscription or contract. Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptx



Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxmansk2
╠²
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxAdministrative bodies( D and C Act, 1940



Administrative bodies( D and C Act, 1940P.N.DESHMUKH
╠²
These presentation include information about administrative bodies such as D.T.A.B
CDL AND DCC, etc.One Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



One Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss the one click RFQ Cancellation in odoo 18. One-Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 is a feature that allows users to quickly and easily cancel Request for Quotations (RFQs) with a single click.Bß╗ś TEST KIß╗éM TRA GIß╗«A K├ī 2 - TIß║ŠNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUß║©N FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...



Bß╗ś TEST KIß╗éM TRA GIß╗«A K├ī 2 - TIß║ŠNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUß║©N FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
╠²
https://app.box.com/s/ij1ty3vm7el9i4qfrr41o756xycbahmgAI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...



AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria
╠²
Bß╗ś TEST KIß╗éM TRA GIß╗«A K├ī 2 - TIß║ŠNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUß║©N FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...



Bß╗ś TEST KIß╗éM TRA GIß╗«A K├ī 2 - TIß║ŠNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUß║©N FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
╠²
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS (REFRACTION) physical sciences G11
- 1. PHYSICAL SCIENCES GEOMETRICAL OPTICS (REFRACTION) Grade 11 Presented by NM MAPHOTO
- 2. OBJECTIVE ’üĄ Define refraction ’üĄ Definition of refractive Index ’üĄ Defining SnellŌĆÖs Law ’üĄ Understand refractive index ’üĄ Recognizing situations where refraction will occur. ’üĄ Identify which direction light will bent when it passes from one medium to another. ’üĄ Calculating refracted ray, incident ray, angle of incident or angle of refraction
- 3. CONTENT Introduction Definition of refraction Demonstration of refraction Refraction index Table of refraction index Ray diagrams SnellŌĆÖs law Ray reflecting on two medium Assessment References
- 4. INTRODUCTION Everyday life situation that involve refraction of light. What happens when light passes from one medium to another. How the direction of light as it passes from one medium to another is associated with a change in velocity and wavelength and frequency.
- 5. REFRACTION Refraction occurs at the boundary of two media when light travels from one medium into the other and its speed changes, but its frequency remains the same. If the light ray hits the boundary at an angle which is not perpendicular to or parallel to the surface, then it will change direction and appear to ŌĆśbendŌĆÖ.
- 6. DEMONSTATION OF REFRACTION ’üĄ The picture shows two mediums which is water and air. ’üĄ When the person looks in the water, she see the image of chest not the actual chest. ’üĄ It appears to bend due to refraction.
- 7. REFRACTIVE INDEX The refractive index (symbol n) of a material is the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to its speed in the material and gives an indication of how difficult it is for light to get through the material. where n = c/v n = refractive index (no unit) c = speed of light in a vacuum (3,00 ├Ś 108 m┬ĘsŌłÆ1) v = speed of light in a given medium (m┬ĘsŌłÆ1)
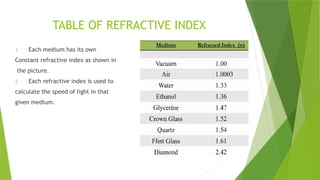
- 8. TABLE OF REFRACTIVE INDEX 1. Each medium has its own Constant refractive index as shown in the picture. 2. Each refractive index is used to calculate the speed of light in that given medium.
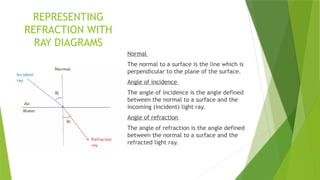
- 9. REPRESENTING REFRACTION WITH RAY DIAGRAMS Normal The normal to a surface is the line which is perpendicular to the plane of the surface. Angle of incidence The angle of incidence is the angle defined between the normal to a surface and the incoming (incident) light ray. Angle of refraction The angle of refraction is the angle defined between the normal to a surface and the refracted light ray.
- 10. SNELLŌĆÖS LAW ’üĄ There is a relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction of the indexes of refraction of 2 medium (n). ’üĄ SnellŌĆÖs law applies to refraction of light in any situation regardless of the media. n1= refractive index of medium 1 n2= refractive index of medium 2
- 11. Ray reflecting between two medium 1. A ray entering a material of larger index bends towards the normal. 2. A ray entering a material of smaller index bends away from the normal. 3. A ray oriented perpendicular to a surface does not bends, regardless of the materials.
- 13. Summery of refraction ’üĄ Video summery of refraction https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zarxpu43-ls
- 14. REFERENCES ’üĄ Nagar, V. (2023). Geometric Optics.PDF. Geometrical Optics.PDF (slideshare.net) (Accessed 17 August 2024). ’üĄ Oh, M. (2011). Refraction. Available from slideshare at Refraction | PPT (slideshare.net) (Accessed 16 August 2024). ’üĄ Siyavula (2013). Geometrical optics. Available from slideshare at Geometrical optics | PPT (slideshare.net) (Accessed 18 August 2024) ’üĄ Swetha, R. (2017). Refraction. Available from slideshare at Refraction | PPT (slideshare.net) (Accessed 17 August 2024). ’üĄ Tatualia, E. (2015). Refraction of light. Available from slideshare at Refraction of Light | PPT (slideshare.net) (Accessed 17 August 2024). ’üĄ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zarxpu43-ls
- 15. THANK YOU





