Get Comfortable with Visual Aids
- 1. GET COMFORTABLE WITH VISUAL AIDS BY: CLAIRE SHERRINGTON
- 2. Get Comfortable with Visual Aids WHAT ARE WE TALKING ABOUT TODAY ..... ’éó Why ? ’éó What are visual aids ? ’éó What makes a good one ? ’éó Delivery ’éó ..... Those powerpoints 2
- 3. Get Comfortable with Visual Aids WHY USE VISUAL AIDS ? ’éó Increase understanding ’éó Save time ’éó Enhance retention ’éó Promote attentiveness ’éó Control nervousness 3
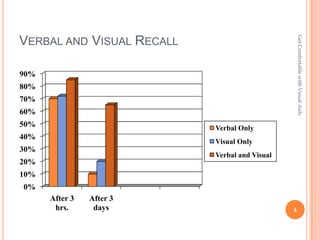
- 4. Get Comfortable with Visual Aids VERBAL AND VISUAL RECALL 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% Verbal Only 40% Visual Only 30% Verbal and Visual 20% 10% 0% After 3 After 3 hrs. days 4
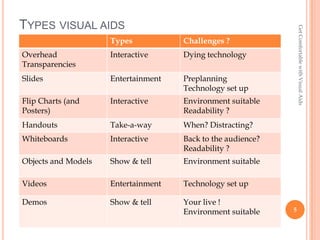
- 5. TYPES VISUAL AIDS Get Comfortable with Visual Aids Types Challenges ? Overhead Interactive Dying technology Transparencies ║▌║▌▀Żs Entertainment Preplanning Technology set up Flip Charts (and Interactive Environment suitable Posters) Readability ? Handouts Take-a-way When? Distracting? Whiteboards Interactive Back to the audience? Readability ? Objects and Models Show & tell Environment suitable Videos Entertainment Technology set up Demos Show & tell Your live ! Environment suitable 5
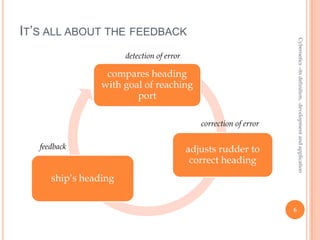
- 6. ITŌĆÖS ALL ABOUT THE FEEDBACK Cybernetics ŌĆōits definition, development and application detection of error compares heading with goal of reaching port correction of error feedback adjusts rudder to correct heading shipŌĆÖs heading 6
- 7. Cybernetics ŌĆōits definition, development and application 7 OBJECT
- 8. Get Comfortable with Visual Aids WHAT MAKES A GOOD VISUAL AID ? ’éó Visible ’éó Simple ’éó Colorful, but don't let them upstage you ’éó Justified by the content 8
- 9. Get Comfortable with Visual Aids DELIVERY ’éó Preparation - practice ! ’éó DonŌĆÖt let them distract you ’éó Know how to use them ’éó Have a back up plan ’éó Speak to the audience With technology .... ’éó Turn off the technology to reinforce the message ’éó Use a pointer 9
- 10. Get Comfortable with Visual Aids LETS TAKE A MOMENT ON POWERPOINTS ’éó Don't read the slides to your audience! ’éó 20 point font 32 point font 48 point font 60 point font 72 point ’éó Choose colors for easy reading ’éó Use bullet points instead of full sentences. ’éó Avoid charts and diagrams that are hard to see. ’éó Don't let the text or graphics fly around too much. 10
- 11. Get Comfortable with Visual Aids IN CONCLUSION ’éó Practice ! ’éó Be Prepared ’éó Try variety ’éó Visual aids can add interest and fun to the presentation ’éó Use them; but use them well 11
- 12. Get Comfortable with Visual Aids WHAT TO KNOW MORE ? ’éó Your folder ’éó http://toastmasters.wikia.com/wiki/Visual_Aid ’éó http://www.toastmasters.org/MainMenuCategories /FreeResources/NeedHelpGivingaSpeech/TipsTech niques/VisualAidsPowerPoint.aspx ’éó Using powerpoint: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3QwC1cl0Wa4 &feature=related 12
Editor's Notes
- #3: ║▌║▌▀Ż two- Today, I am going to tell you what visual aids ....
- #4: Increase understanding ŌĆō 40% of us learn best visually. They allow for different learning stylesSave time ŌĆō A picture paints 1000 words.Enhance retention ŌĆō People remember 10% of what they hear a week after they hear it. They remember up to 66% of what they see and hear.Promote attentiveness ŌĆō visual aids give your audience something on which to focus attention.Control nervousness ŌĆō displaying visual aids gives the speaker something purposeful to do, helping to dissipate nervous energy.
- #6: What can go wrong?Computer-based┬ĀBest known is PowerPoint.Can use both words and pictures.Keep information on slides to a few key points.Limit animations to those that are necessary so the audience isnŌĆÖt distracted from your presentation.Use a remote wherever possible so you are not tethered to the computer.┬ĀProps┬ĀThese areobjects that can be demonstrated to, or handled by, the audience. They can also be costumes or rewards, e.g. chocolate.Pick them up only when you describing the point to which they relate, then put them down. This reduces your chances of fidgeting with the prop.If you are going to hand the prop out to the audience, time it to avoid the audience becoming absorbed in the prop and ignoring your presentation.┬ĀWhiteboards / Flipcharts┬ĀGood for recording information/feedback from an audience or to display information youŌĆÖve pre-written.If you pre-write information, keep it covered until it is needed.Try to keep to 2-3 main points on the whiteboard/flipchart page.Consider asking someone else (with good handwriting!) to record feedback so you can remain connected to your audience.Make sure the whiteboard is properly cleaned before you start so the writing is clear.┬ĀVideos┬ĀTry to keep them short, and only use content that emphasises your points.Have them ready to go and paused before your presentation.┬Ā┬ĀHandouts┬ĀThis is an opportunity to expand on the points given in your presentation but remember to keep the information relevant.Consider when youŌĆÖll hand them out:At the beginning means the audience knows what notes they need to take to supplement yours.At the end means your audience is less likely to be distracted during your presentation.┬Ā
- #7: ║▌║▌▀Ż four In order to steer, you have to see where youŌĆÖre going; see whether thatŌĆÖs towards the goal or off-course from the goal; then change your actions to head back toward the goal. I act. I see the consequences. I say, ŌĆ£No, not quite what I meant.ŌĆØ And so I correct by acting again. ThatŌĆÖs the cybernetic loop.Becker, Slabosky and Umpleby(2006) defined ŌĆ£feedback as the information about the results of a process which is used to change the process" . This is a cybernetic loop. Feedback can be either negative or positive in nature depending on how the system reacts. Negative feedback creates a ŌĆ£deviationŌĆØ, where a system will respond to negativity by reducing or neutralizing the feedback, called a ŌĆśsteady stateŌĆÖ. Positive feedback or ŌĆ£deviationŌĆØ can maintain or can intensify a systemŌĆÖs expansion called a ŌĆśgrowth stateŌĆÖ.. Delobelle also by suggests that feedback as an optimum course called the norm and this norm can be affected by realisations that can deviate from the norm. The amount of feedback in a loop can be affected by a systems behaviour this related to the feedback is either active or passive, it can also be purpose or non-purposeful.
- #9: VisibleSimpleColorful, but don't let them upstage youJustified by the content -- not too many or too few slidesPreparation - know how to use them, have a back up plan
- #12: ║▌║▌▀Ż twelve
- #13: ║▌║▌▀Ż eleven