Ggfcfdcd gdffdc Das System von Services bei asam.pdf
- 1. Dresden 17.05.2022 SOVD ŌĆō Service Oriented Vehicle Diagnostics Bernd Wenzel ASAM e.V. Tobias Weidmann Vector Informatik GmbH
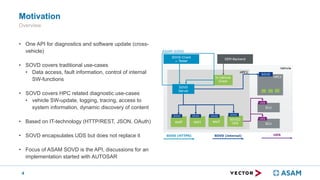
- 3. Motivation 3 Challenge ŌĆó New architectures based on HPCs, multiple OS, the different applications and their dependencies put a major challenge also to diagnostics. ŌĆó Focus extends from identifying hardware errors to analyzing software issues. ŌĆó SW-analysis requires different type of data ŌĆó Logs, traces, process information, stack traces ŌĆó Diagnostic content in the vehicles will change dynamically, this contrasts with the static approach of UDS. ŌĆó SW-update will change from transferring individual bits and bytes to controlling a complex update procedure in the vehicle.
- 4. Motivation 4 Overview ŌĆó One API for diagnostics and software update (cross- vehicle) ŌĆó SOVD covers traditional use-cases ŌĆó Data access, fault information, control of internal SW-functions ŌĆó SOVD covers HPC related diagnostic use-cases ŌĆó vehicle SW-update, logging, tracing, access to system information, dynamic discovery of content ŌĆó Based on IT-technology (HTTP/REST, JSON, OAuth) ŌĆó SOVD encapsulates UDS but does not replace it ŌĆó Focus of ASAM SOVD is the API, discussions for an implementation started with AUTOSAR
- 5. Concepts ŌĆó REST is based on HTTP, basically a web browser is sufficient to execute ŌĆó Resources are the core element ŌĆó HTTP verbs on the resources represent the different operations ŌĆó Knowledge of the initial URL is sufficient, further links are provided to discover the API ŌĆó REST is stateless, i.e. every request contains all the relevant information that the server can process it 5 No automotive specific stack needed on client side HTTP/REST in a nutshell
- 8. Discovering of entities and resources ŌĆó Discovery of contained entities ŌĆó Query sub-entities of an entity ŌĆó Query related entities of an entity ŌĆó Query entity capabilities ŌĆó Areas represent a topological view on the entities Access to capability description content ŌĆó Query an online capability description ŌĆó Query schema information for content processing 8 Method for capability discovery Identical format for offline and online capability description used, based on OpenAPI an JSON Schema Root: SOVDServer Driving: Area Perception: Area Controlling: Area DrivingComputer: Component PowerSteering: Component Navi: App WindowControl: App Linux: Component VehicleHealth: Function
- 9. 9 Method for data resource read / write access Methods ŌĆó Retrieve the list of data available for an entity ŌĆó Data is categorized according to its semantic ŌĆó E.g. currentData, identData, storedData, sysInfo ŌĆó Read/write access to data ŌĆó Possibilities to group data ŌĆó Possibilities to create aggregated data sets on entity level ŌĆó Periodic / Trigger Based data access is planned for v1.1 WindowControl: App data: RessourceCollection data-lists: RessourceCollection <currentData> DriverWindow: data <currentData> PassengerWindow: data <identData> AppInfo: data
- 10. Methods ŌĆó Read faults from an entity ŌĆó Read details for a fault ŌĆó Delete all faults of an entity ŌĆó Delete single fault of an entity Query parameters ŌĆó Status, based on key value pair ŌĆó Severity Access to environment data for a single fault code ŌĆó OEM specific key value pairs 10 Method for fault handling Camera: Component faults: RessourceCollection Battery Voltage Low: Fault No Sensor Signal: Fault Not Calibrated: Fault
- 11. 11 Method for control of operations Operations (SW-internal functions, actuators) ŌĆó List available operations ŌĆó Initiate the execution (potentially multiple) ŌĆó Monitor the status, adjust the execution ŌĆó Terminate the execution Target modes ŌĆó Retrieve list of all supported modes of an entity ŌĆó Explicit control of entity states via their defined modes Locking ŌĆó Goal: avoid parallel usage of entities in certain sequences ŌĆó Acquire a lock on an entity ŌĆó Release an acquired lock on an entity Powersteering: Component SteeringAngleControl: Operation Angle:float ŌĆ£id-xx-yy-zzŌĆØ: Execution Angle: 45.0┬░ right Diagnostic- session: mode <requires> ŌĆ£id-uu-vv-wwŌĆØ: lock <requires>
- 12. Method for software update 12 Basics ŌĆó It is assumed that there is a central component in the vehicle which performs the software update ŌĆó ASAM SOVD provides an API to trigger this central software update component ŌĆó Update procedure itself is not subject to ASAM SOVD Methods ŌĆó Retrieve list of all updates provided by the entity ŌĆó Get details of update ŌĆó Automated installation of an update ŌĆó Prepare installation of an update ŌĆó Execute installation of an update ŌĆó Get status of an update ŌĆó Delete update package from a SOVD server ŌĆó Register an update at the SOVD server /updates Root: SOVDServer /autonomous /update-1 /update-4 /prepare /execute /automated
- 13. Basics ŌĆó Access to aggregated log information ŌĆó Evaluation by software experts ŌĆó Transport as bulk-data possible Methods ŌĆó Retrieve list of all log information ŌĆó Configure SOVD logging ŌĆó Retrieve the current SOVD logging configuration ŌĆó Reset SOVD Logging configuration to default Supported Context Types ŌĆó RFC 5424 (syslog protocol) ŌĆó AUTOSAR diagnostic log and trace 13 Method for logging Request: HTTP GET {base_uri}/components/DrivingComputer/logs/entries Response: HTTP 200 OK { "items": [ { "timestamp": "2021-07-20T00:00:04.387819Z", "context": { "type": "RFC5424", "host": "Linux", "process": "systemd", "pid": 1 }, "severity": "info", "msg": "Closed D-Bus User Message Bus Socket", }, { ŌĆ” }
- 14. Agenda 14 Motivation Concepts Methods Overview 1 2 3 Standardization activities based on SOVD 4
- 15. Standardization activities based on SOVD 15 Overview ASAM SOVD 1.0 ŌĆó Released on TSC meeting in July AUTOSAR Alignment ŌĆó Involved in internal review ŌĆó Handled in concept group 704 ŌĆó ara::diag extension ISO Standardization ŌĆó Joint NWIP in preparation with other SC31 groups ASAM Follow Up project ŌĆó Started 09/2022, release planned for 12/2024 ŌĆó Compatible minor version ŌĆó Integration of ISO feedback ŌĆó Event based communication
- 16. Standardization activities based on SOVD 16 AUTOSAR concept source: AUTOSAR SOVD concept group
- 17. Standardization activities based on SOVD 17 SOVD v1.1 Enhancements to Data Access ŌĆó Cyclic reception of sensor data or variables values ŌĆó SOVD will support Cyclic access to data resources ŌĆó Reduce communication overhead for data access at a high frequency ŌĆó Trigger based data access ŌĆó Especially for sensor data, DTCs and environment data, HPC system information SOVD for legally required diagnostics ŌĆó The project group will discuss and analyze how SOVD could be used to fulfill legally required diagnostics
- 18. Standardization activities based on SOVD 18 SOVD v1.1 Enhanced Diagnostic Use Cases ŌĆó In-vehicle data communication logging ŌĆó SOVD will provide a possibility to control an in-vehicle data logger. The use-case is to provide snapshots of the in-vehicle communication for complex failure scenarios ŌĆó Execution of diagnostic command sequences or customs scripts ŌĆó SOVD will provide the possibility to control the execution of an in-vehicle diagnostic script. ŌĆó The scripting language will not be standardized. Enhancements to existing Services ŌĆó Extend Logging API to support also continuous transport of log-information ŌĆó File Handling via Third Party Providers ŌĆó Enhancements to Multi client access to the vehicle ŌĆó Reset to Default Setting and/or Restart
- 19. Thank you for your attention! Bernd Wenzel Senior Technical Consultant ASAM e.V. Phone: +49 371 5607 742 Email: bernd.wenzel@asam.net 19 Tobias Weidmann Manager Customer Services Vector Informatik GmbH Phone: +49 711 80670 2549 Email: tobias.weidmann@vector.com