Git For Beginer
- 1. knowledge sharing Prepared by Hieu Tran Pho team/DEK-VN
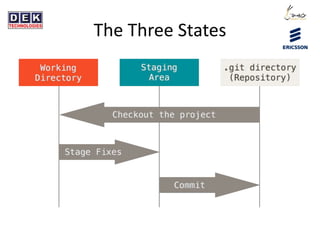
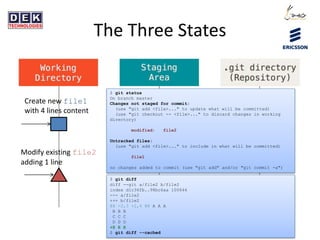
- 3. The Three States $ git status On branch master Changes not staged for commit: (use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed) (use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in working directory) modified: file2 Untracked files: (use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed) file1 no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a") $ git diff diff --git a/file2 b/file2 index d1c36fb..98bc6aa 100644 --- a/file2 +++ b/file2 @@ -2,3 +2,4 @@ A A A B B B C C C D D D +E E E $ git diff --cached Create new file1 with 4 lines content Modify existing file2 adding 1 line
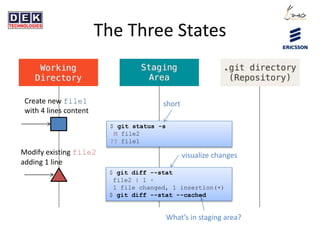
- 4. The Three States Create new file1 with 4 lines content Modify existing file2 adding 1 line $ git status -s M file2 ?? file1 $ git diff --stat file2 | 1 + 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+) $ git diff --stat --cached short visualize changes Whatâs in staging area?
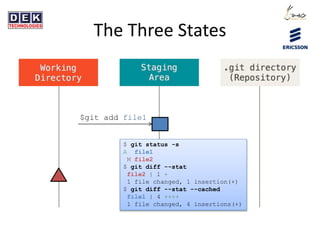
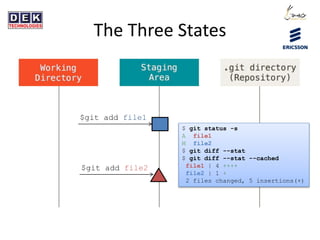
- 5. The Three States $git add file1 $ git status -s A file1 M file2 $ git diff --stat file2 | 1 + 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+) $ git diff --stat --cached file1 | 4 ++++ 1 file changed, 4 insertions(+)
- 6. The Three States $git add file1 $ git status -s A file1 M file2 $ git diff --stat $ git diff --stat --cached file1 | 4 ++++ file2 | 1 + 2 files changed, 5 insertions(+) $git add file2
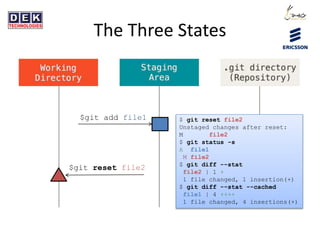
- 7. The Three States $git add file1 $ git reset file2 Unstaged changes after reset: M file2 $ git status -s A file1 M file2 $ git diff --stat file2 | 1 + 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+) $ git diff --stat --cached file1 | 4 ++++ 1 file changed, 4 insertions(+) $git reset file2
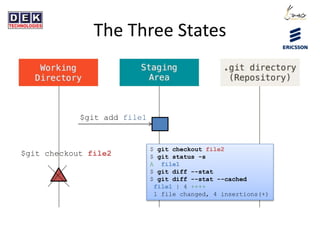
- 8. The Three States $git add file1 $ git checkout file2 $ git status -s A file1 $ git diff --stat $ git diff --stat --cached file1 | 4 ++++ 1 file changed, 4 insertions(+) $git checkout file2
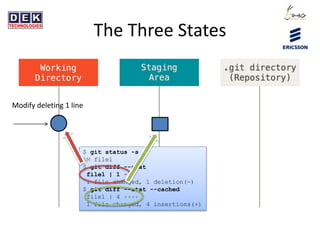
- 9. The Three States $ git status -s AM file1 $ git diff --stat file1 | 1 - 1 file changed, 1 deletion(-) $ git diff --stat --cached file1 | 4 ++++ 1 file changed, 4 insertions(+) Modify deleting 1 line
- 10. The Three States Modify deleting 1 line $git commit -m âMy messageâ $ git commit -m"My message" [master 11e6b70] My message 1 file changed, 4 insertions(+) create mode 100644 file1 $ git status -s M file1 $ git diff --stat file1 | 1 - 1 file changed, 1 deletion(-) $ git diff --stat --cached
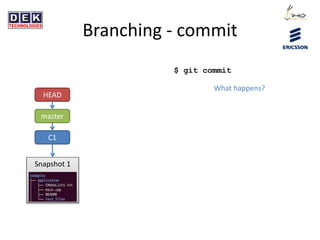
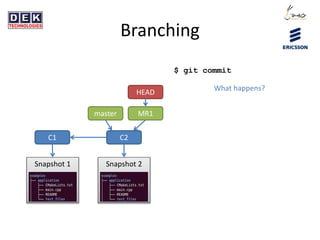
- 11. Branching - commit C1 Snapshot 1 master HEAD What happens? $ git commit
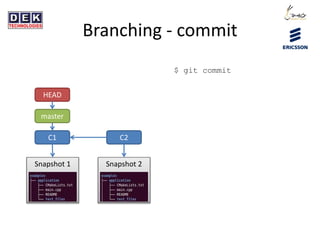
- 12. Branching - commit C1 C2 Snapshot 1 Snapshot 2 master HEAD $ git commit
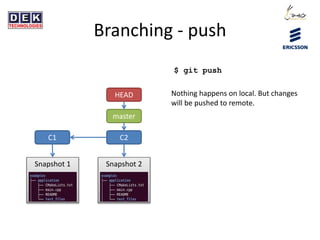
- 13. Branching - push C1 C2 Snapshot 1 Snapshot 2 master HEAD $ git push Nothing happens on local. But changes will be pushed to remote.
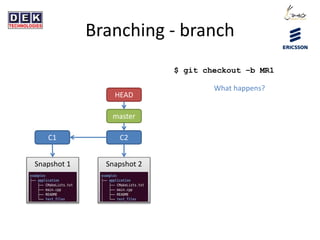
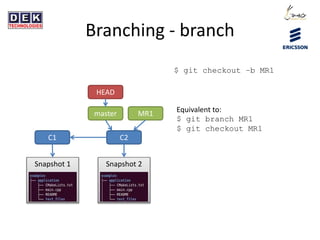
- 14. Branching - branch C1 C2 Snapshot 1 Snapshot 2 master HEAD $ git checkout âb MR1 What happens?
- 15. Branching - branch C1 C2 Snapshot 1 Snapshot 2 master HEAD $ git checkout âb MR1 MR1 Equivalent to: $ git branch MR1 $ git checkout MR1
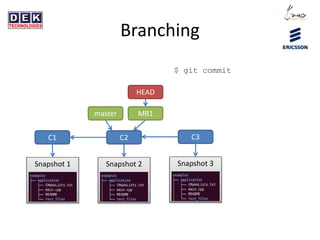
- 16. Branching C1 C2 Snapshot 1 Snapshot 2 master HEAD $ git commit MR1 What happens?
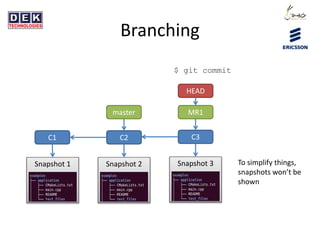
- 17. Branching C1 C2 Snapshot 1 Snapshot 2 master $ git commit HEAD MR1 C3 Snapshot 3
- 18. Branching C1 C2 Snapshot 1 Snapshot 2 master $ git commit HEAD MR1 C3 Snapshot 3 To simplify things, snapshots wonât be shown
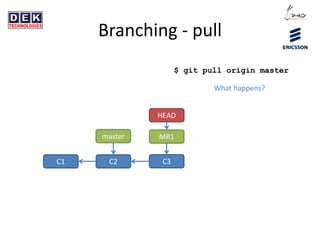
- 19. Branching - pull C1 C2 master $ git pull origin master HEAD MR1 C3 What happens?
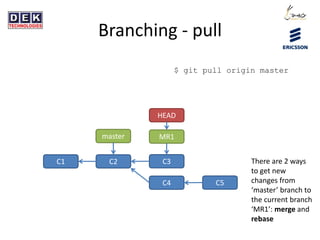
- 20. Branching - pull $ git pull origin master C1 C2 master HEAD MR1 C3 C4 C5 There are 2 ways to get new changes from âmasterâ branch to the current branch âMR1â: merge and rebase
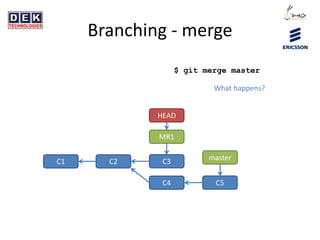
- 21. Branching - merge $ git merge master C1 C2 master HEAD MR1 C3 C4 C5 What happens?
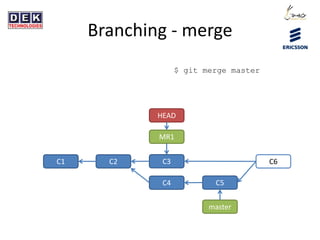
- 22. Branching - merge $ git merge master C1 C2 master HEAD MR1 C3 C4 C5 C6
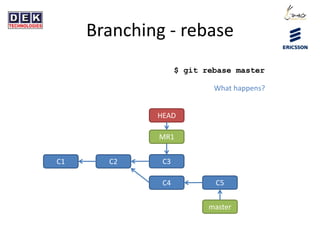
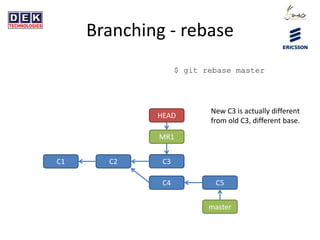
- 23. Branching - rebase $ git rebase master C1 C2 master HEAD MR1 C3 C4 C5 What happens?
- 24. Branching - rebase $ git rebase master C1 C2 master HEAD MR1 C3 C4 C5 New C3 is actually different from old C3, different base.
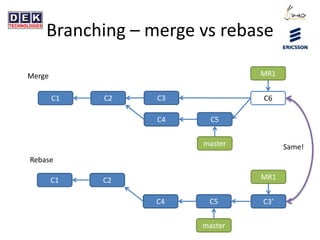
- 25. Branching â merge vs rebase C1 C2 master MR1 C3âC4 C5 C1 C2 master MR1 C3 C4 C5 C6 Merge Rebase Same!
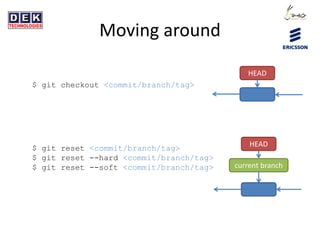
- 26. Moving around $ git checkout <commit/branch/tag> $ git reset <commit/branch/tag> $ git reset --hard <commit/branch/tag> $ git reset --soft <commit/branch/tag> HEAD current branch HEAD
- 27. Rewrite history âĒ N.B. you can only rewrite history on local. You should not rewrite history of commits that you have pushed. âĒ Using rebase interactive âĒ $ git rebase -i âĒ You can: â Squash commits into one â Amend a commit â Re-order commits â Edit a commit message â Drop a commit â Etc.
- 28. Rewrite history - example $ git log --oneline c0ec642 aaaa 4d320e5 ccc a6fb541 bbb 11e6b70 My message 0ef9202 First commit $ git rebase -i 0ef9202 # or git rebase HEAD~4 pick 11e6b70 My message pick a6fb541 bbb pick 4d320e5 ccc pick c0ec642 aaaa # Rebase 0ef9202..c0ec642 onto 0ef9202 # âĶ HEAD~4
- 29. Rewrite history - example Suppose we want to re-order the commits, and also meld the commit âaaaaâ and commit âMy messageâ into one. pick 11e6b70 My message squash c0ec642 aaaa pick a6fb541 bbb pick 4d320e5 ccc # Edit new message for the combined commit [detached HEAD ae5869b] My message + aaaa 1 file changed, 6 insertions(+) create mode 100644 file1 Successfully rebased and updated refs/heads/MR1. $ git log --oneline 8abba8a ccc cb566cd bbb ae5869b My message + aaaa 0ef9202 First commit
- 30. Some handy git commands git branch -a list all branches git pull --ff-only pull but fast-forward merge only git pull --rebase pull but instead of merging, rebase git checkout list all modified files git checkout . discard all modifications in current and sub- directories git clean -xdf clean ALL untracked files git apply some.patch apply a patch git fetch --tags fetch new tags from remote git describe develop whatâs the newest release git checkout <commit> -- needed_file checkout file from a commit or branch, checked out will be put in staged area git grep âneedleâ self-explaintory
- 31. Q&A
- 32. Thank you âĒ Thank you for listening


![The Three States
Modify deleting 1 line
$git commit -m
âMy messageâ
$ git commit -m"My message"
[master 11e6b70] My message
1 file changed, 4 insertions(+)
create mode 100644 file1
$ git status -s
M file1
$ git diff --stat
file1 | 1 -
1 file changed, 1 deletion(-)
$ git diff --stat --cached](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gitsharing-150323211758-conversion-gate01/85/Git-For-Beginer-10-320.jpg)


![Rewrite history - example
Suppose we want to re-order the commits, and also meld the commit âaaaaâ
and commit âMy messageâ into one.
pick 11e6b70 My message
squash c0ec642 aaaa
pick a6fb541 bbb
pick 4d320e5 ccc
# Edit new message for the combined commit
[detached HEAD ae5869b] My message + aaaa
1 file changed, 6 insertions(+)
create mode 100644 file1
Successfully rebased and updated refs/heads/MR1.
$ git log --oneline
8abba8a ccc
cb566cd bbb
ae5869b My message + aaaa
0ef9202 First commit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gitsharing-150323211758-conversion-gate01/85/Git-For-Beginer-29-320.jpg)


