Global Economic Crisis
- 1. GLOBAL ECONOMIC CRISIS Course Instructor Sir Azeem Abbas
- 2. PRESENTED BY Afaq Muhammad Khan Zain Ali Khawaja Kapoor Junaid Iqbal Nazish Ashfaq Muhammad Hunain Ayaz
- 3. CONTENT What is Economic Crisis History of Economic Crisis Causes of World Economic Crisis Overall Effect of a Crisis Specific Countries Effected Conclusion
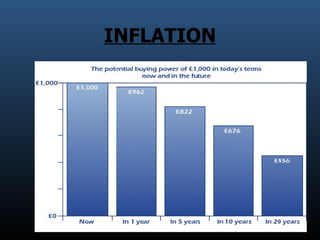
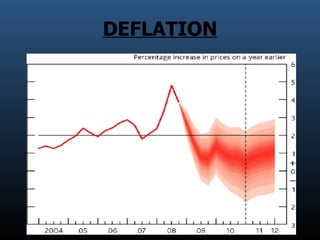
- 5. What is Economic Crisis A situation in which the economy of a country experiences a sudden downturn brought on by a financial crisis. An economy facing an economic crisis will most likely experience a falling GDP, rising/falling prices due to inflation/deflation. An economic crisis can take the form of a recession or a depression.
- 6. INFLATION
- 7. DEFLATION
- 8. Types of Crisis Food Crisis Financial Crisis Oil Crisis Industrial Crisis Export Crisis
- 9. History of World Economic Crisis The World Economic Crisis came after the world war 2 At The time of a great Depression. It was the largest and most important economic depression in modern history, and is used in the 21st century as a benchmark in how far the world's economy can fall. The Great Depression had shocking effect on every country, rich and poor. Personal income, tax revenue, profits and prices dropped, and international trade come by a half to two-thirds.
- 10. History of World Economic Crisis Unemployment in the United States rose to 25% and in some countries rose as high as 33%. Cities all around the world were hit hard, especially those dependent on heavy industry. The financial crisis of 2007ŌĆō2009 has been called the most serious financial crisis since the Great Depression by leading economists
- 11. Facts & Figures of Economic Crisis As a Result of Economic Crisis 13 Million of People became unemployed. Unemployment in the United States rise to 25% and in some countries rise as high as 33%. There is a sharp fall in export demand.
- 12. Facts & Figures of Economic Crisis Stock Market collapse. Industrial production fell by nearly 45% between 1929 and 1932. Home-building dropped by 80% between 1929 and 1932. From 1929 to 1932, about 5000 banks went out of business.
- 13. Overall Effects of the Economic Crisis
- 14. Overall Effects of Economic Crisis Higher bank capital requirements on the way Everyone should look for "exit strategiesŌĆØ BIS study confirms some perceptions of Basle accord Banks continue retreat from South Asia: Crisis causes massive unemployment Massive retreat by banks from emerging markets Putting Asia in its place Financial turmoil spreads across the world
- 15. Higher bank capital requirements Basle Committee issued a consultative document on 3 rd June under Banking Supervision. The Committee comments from all interested parties by 31 March 2000. the standards being applied in over 100 countries. B.I.S suggested resistance from private sector.
- 16. Everyone should look for "exit strategies" The dramatic events in many parts of the emerging world have major effects on macroeconomic variables. The current difficulties remain deeply rooted in excessive capital. Recent experiences show there can be "a darker side to the operation of a market economy. There is no single or simple answer to current economic problems. Lack of stability in one area often contributes to instability in the other.
- 17. BIS study confirms some perceptions of Basle accord The pressures on banks to increase their capital to meet the minimum capital resulted in banks cutting their bank lending. The 1988 Basle Accord for common capital requirements has been adopted by the G-10 countries the adoption and implementation of the Basle accord by developing countries is being promoted The working group considered two major questions: Adoption of fixed minimum capital requirements led some banks to maintain higher capital ratios the fixed capital requirements have in fact been successful in limiting risk-taking. The framework established a structure that was intended to make regulatory capital more sensitive to differences in risk profiles.
- 18. Banks continue retreat from South International Banks continued to withdraw from the developing world throughout 1998. The withdrawal from Asia amounted to $28 billion. The retrenchment in Asia was half that in the first half of 1998. There was a pull-back of $12 billion from Brazil. The retreat from eastern Europe was essentially attributable to the Russian developments. the claims of the BIS reporting area banks on the developing world stood at $705.9 billion at end 1998 some 52.8% was short-term for a period up to and including one year.
- 19. Crisis causes massive unemployment The fallout from the financial crisis in Asia - which began in mid-1997 - has caused massive unemployment. The economic turmoil in South-east and East Asia. The 24-page study, released to coincide with a review here of the 1995 UN Social Summit in Copenhagen.
- 20. Massive retreat by banks from emerging markets Banks "retreated massively" from emerging market economies. Basle-based Bank for International Settlements reported in its quarterly review of international banking. The available data provide evidence of an international credit squeeze. The cutback on lending to non-bank customers inside the BIS area is probably indicative leveraged positions. Net repayments by non-banks in the Caribbean and other offshore centres. Borrowers appear to be reducing their gearing since 1997.
- 21. Financial turmoil spreads across the world THE wild fluctuations in stock markets around the world in late October 1997. The turmoil that started in South-East Asia. It has also badly rocked many South American countries On 30 October 1997, Brazil's stock market index plunged 9.8%.
- 23. Effected Countries By World Economic Crisis The Most Effected Countries By World Economic Crisis are Argentina Thailand Australia Russia Malaysia Mexico
- 24. Effected Countries By World Economic Crisis Argentina Countering claims that the Argentine economic crisis was caused by extravagant government spending, a US think-tank has traced the roots of the Latin American countryŌĆÖs troubles to external shocks and wrong-headed policies backed by the international financial institutions.
- 25. Effected Countries By World Economic Crisis Australia Australia's extreme dependence on agricultural and industrial exports meant it was one of the hardest-hit countries in the Western world, amongst the likes of Canada and Germany. Falling export demand and commodity prices placed massive downward pressures on wages. Further, unemployment reached a record high of 29% in 1932, with incidents of civil unrest becoming common. After 1932, an increase in wool and meat prices led to a gradual recovery .
- 26. Effected Countries By World Economic Crisis Thailand Two years after the start of the Asian economic crisis, the writer says, there has been no fundamental rethinking of the direction of Thailand's economic policies and despite some minor measures the country remains vulnerable to the speculative flows of global capital that brought it down two years ago.
- 27. CONCLUSION
- 28. Building a World Economic Structure where People Matter Alternative Global Monetary System 'Money is the blood of our community, and now that blood is poisoned!ŌĆś He discussed - the Tlaloc - a community currency system Encourage audience members to fundamentally re-think their understanding of money
- 29. 'It is like the Titanic. If we do not want to drown, we must learn how to swim.ŌĆś Communities can create their own money Such systems represent an interim step in the transition from a 'profit economy' to a 'gift economy The Mexican system had encountered any problems with counterfeiting or theft ? NO
- 30. Finger Pointing or focusing the Systemic Reforms Argentina is focusing attention once again on the urgent need for reforming the global financial system Argentina requires a haircut not only for foreign bondholders but also for the IMF itself UN Conference provides motion to the financial reforms but US is set to go against any step towards reforming Bretton Woods
- 31. Govt., Political Class must take responsibilities IMF must also be accounted for crisis Experts suggest that if reforms arenŌĆÖt made then the world will suffer more crisis The crisis was long foreseen due to countryŌĆÖs currency board system and Peso-Dollar Link IMF Encouraged Argentina Markets can never be substitute for the states
- 32. A well governed state can provide anti-dote for the ills of the market Nominal exchange rate as an anchor for inflationary expectations, pricing decisions and wage setting The inflow of foreign funds providing a cushion of sorts Non-availability of credit to small and medium Argentine enterprises
- 33. Foreign-owned enterprises used the peso-dollar link Argentina has been forced to cut the peso-dollar link and has imposed controls and find ways to rescue the corporations In a world of volatile exchange rates Pegging is a highly risky strategy For growth financial institutions are required Remind us need to reform the global financial system
- 34. Reform the IMF Quota and Decision Making System Quota system in the IMF and World Bank should be reformed Distribution of voting rights among member states A few major developed countries hold a majority of the shares allocated Few countries influence Executive Board and Staff
- 35. Asian Participation in the Reform Process The full participation of developing countries is demanded The IFIs operate according to the changing economic climate Quota system should be adjusted to reflect the demands of member countries JapanŌĆÖs Quota as an Example Decision-making of the Bretton Woods institutions need to be fully respected once it is agreed
- 36. Reforms are therefore needed to the decision-making structures of IFIs This would account different interests and circumstances of individual countries that are at different stages of development Participation of developing countries is important so it is geared to financing development Voice of developing countries is muted Transparent and Democratic Forums are required
- 37. Better Institutions and Instruments for Capital Flows Setting up better institutions and instruments to handle problems of international capital flows Certain degree of humility and a healthy dose of pragmatism More crisis unless the quality of the coordination of macro-economic, financial and monetary policies was improved EAST ASIAN CRISIS
- 38. Most Serious since the breakdown of Bretton Woods Duration and severity a major influence on the economic performance of most countries in both the developed and developing worlds Since 1990 East Asian countries have provided the strongest stimulus for growth in the world economy Global consequences of the crisis will depend on how fast the East Asian countries Priority should be to restore confidence and stability in currency and financial markets, while avoiding a deep and prolonged recession.
- 39. Loans should be rolled over and rescheduled Credit crunch seems deep Access to trade credit has been curtailed Import cuts rather than to export expansion Idea of the G7 ŌĆ£is not workingŌĆØ and that a ŌĆ£steering groupŌĆØ of more nations would be better
- 40. Improvement at the national level with effective supervision of the banking system Lessons from the Latin American crises of the eighties were not sufficient to prevent the Mexican crisis of 1995 Avoid ready-made and simplistic remedies and concentrate on setting up better institutions and instruments
- 41. THANK YOU