GLP (Good Laboratory Practices)
- 1. TOPIC:-GOOD LABORATORY PRACTICE Prepared by :- Vijay Banwala
- 3. ? In the early 70¡¯s FDA became aware of cases of poor laboratory practice all over the US. ? They discovered many fraudulent activities and a lot of poor lab practices. ? Examples of some poor lab practices are : 1.Equipment do not calibrated to standard form,therefore giving wrong measurement. GLP was first introduced in New Zealand and Denmark in 1972, and then in US in 1978 in response to Industrial Bio Test Labs scandal.
- 4. Therapeutic concept Target validation Lead finding Target selection Lead optimization Preclinical development Clinical development Regulatory approval Product Discovery Development Drug Discovery and Development Process
- 5. Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) ? GLP is a regulation created by USFDA and these regulations was proposed on November 19,1976 and designated as a new part of Chapter 21 of the Code of Federal Regulations(CFR) as 21 CFR Part 58 in 1979. ? GLP in OECD principles is defined as ¡°a quality system concerned with the organizational process and the conditions in which non-clinical health and environmental safety studies was planned, performed, monitored, recorded, archived and reported¡±.
- 6. GLP :- 1) GLPs was initially invoked in a reaction to malpractices in the laboratories conducting safety experiments of medicines. 2) In the early 1970s,research laboratories in the USA found doing work in unethical ways:- Data generation without conduct of the study. Replacement of dead animal and fabrication of test result.
- 7. Advantages of GLP :- Assures that the data in true reflection of result obtained from studies. :-Preclinical safety and residue safety. :-Generation of high quality test data. :-Mutual acceptance of data :-Increases public confidence. :-Shortens the time-to-market for new products. Disadvantages of GLP :-More man power is required. :-Expensive process.
- 8. Objectives of GLP 1.)GLP makes sure that the data submitted was true reflection of the results obtained from the study. 2.)GLP make sure that the data is traceable. 3.)Promotes international acceptance of test.
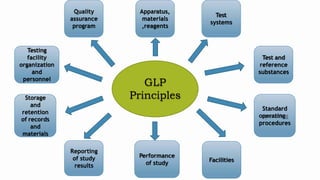
- 9. GLP Principles Testing facility organization and personnel Storage and retention of records and materials Reporting of study results Quality assurance program Facilities Apparatus, materials ,reagents Test systems Test and reference substances Standard operating procedures Performance of study
- 10. How to practice GLP? A. General provisions B. Organization and Personnel C. Facilities D. Equipment E. Testing facilities operation F. Test and control articles G. Protocol for and the conduct of the study H. Records and Reports
- 11. A. General provisions 1) It prescribes GLP for conducting non-clinical laboratory studies that support research and marketing permits of products regulated by FDA. 2) Applicability to studies performed under grants and contracts. 3) Inspection of the testing facility.
- 12. B. Organization and Personnel 1) Organization 2) Personnel 3) Testing facility management 4) Study director 5) Quality assurance unit
- 13. C. Facilities 1) General facilities: a) Testing system facilities b) Archive facilities c) Waste disposal 2) Animal care facilities
- 14. D. Equipment 1.)Appropriate design and adequate capacity. 2.)Equipment used for generation, measurement or assessment of data shall be adequately tested, calibrated and standardized. 3.)Log books for each equipment should be there.
- 15. E. Testing Facilities Operation 1) Standard operating procedures(SOPs) 2) Reagents and solutions 3) Animal care
- 16. F.Test and Control Articles 1) Test and control article characterization 2) Test and control article handling 3) Mixture of articles with carriers
- 17. G. Protocol for and conduct of a nonclinical laboratory study 1) Protocol 2) Conduct of a nonclinical study
- 18. Storage, retrieval and retention of records and data:- 1) Archives should be there for orderly storage and expedient of all raw data, documentation, protocols, specimens and final reports. 2) Index of material retained. 3) Master schedule sheet, copies of protocols and records of Quality Assurance inspections shall be maintained by QAU. 4) Wet specimens and samples of test and control articles shall be retained until the quality of preparation affords evaluation.