GLUCOSE TOLERANCE TEST.pptx for Nursing Students
- 1. GLUCOSE TOLERANCE TEST MRS. SUDHA GAUTAM ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR
- 2. INTRODUCTION ŌĆó The ability to utilize carbohydrates can be determined by Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT) ŌĆó At first, fasting blood glucose is estimated. ŌĆó Then loading dose of glucose is given. ŌĆó The blood glucose levels are estimated at regular intervals after giving the glucose load to the client. ŌĆó In cases of Insulin Deficiency, blood glucose levels get elevated due to impaired glucose utilization.
- 3. A) DECREASED GLUCOSE TOLERANCE ŌĆó Non- utilization of carbohydrate load is observed in conditions causing hyper-glycemia such as ŌĆō ’ā╝Diabetes Mellitus ’ā╝Hyperactivity of anterior pituitary and adrenal cortex ’ā╝Hyperthyroidism ’ā╝Stress
- 4. B) INCREASED GLUCOSE TOLERANCE ŌĆó Increased carbohydrate tolerance is observed in conditions that lead to hypo-glycemia such as ŌĆō ’ā╝Hypopituitarism ’ā╝Hyperinsulinism ’ā╝Hypothyroidism ’ā╝Adrenal Cortical Hypofunction ’ā╝Decreased gastro intestinal absorption like celiac disease.
- 5. INDICATIONS FOR GTT ŌĆó In asymptomatic persons with sustained or transient glycosuria. ŌĆó In clients with symptoms of Diabetes but glycosuria or hyperglycemia is absent. ŌĆó Clients with family history but no symptoms or positive blood findings. ŌĆó In persons with or without symptoms of Diabetes Mellitus showing one abnormal blood finding. ŌĆó In patients with neuropathies or retinopathies of unknown origin. ŌĆó In women with H/O having delivered large babies.
- 6. CONTRAINDICATIONS OF ORAL GTT ŌĆó In proven cases of diabetes mellitus the test is not required ŌĆó GTT is required in doubtful cases and is not recommended for follow up of patients. ŌĆó The test should not be carried out in acutely ill patients.
- 7. PRECAUTIONS FOR GTT ŌĆó The patient is instructed to have a good carbohydrate diet for 2 ŌĆō 3 days prior to the test. ŌĆó Further more a diet containing about 50 - 75 grams of carbohydrate should be taken on the evening prior to the test. ŌĆó Patient is advised not to take drugs that may influence the blood glucose levels for at least 2 days prior to the test. ŌĆó Patient should abstain from smoking during the test as it may negatively impact the blood glucose levels. ŌĆó Strenuous exercises on the previous day is to be avoided and till the day testing is done.
- 8. TYPES OF GLUCOSE TOLERANCE TEST ŌĆó Standard Oral Glucose Tolerance Test ŌĆó I/V Glucose Tolerance Test ŌĆó Mini Glucose Tolerance Test
- 9. A. PROCEDURE FOR ORAL GTT ŌĆó The diagnosis of diabetes can be made on the basis of individuals response to the oral glucose load, commonly referred to as Oral Glucose Tolerance Test. ŌĆó The test is conducted preferably in the morning (ideal 09:00 AM to 11:00 AM) ŌĆó A fasting blood sample is drawn and urine is collected. ŌĆó The patient is given 75 grams of glucose orally dissolved in about 300 ml of water and it is to be drunk in about 5 minutes. ŌĆó Blood and urine samples are collected at 30 minutes interval for at least 2 hours. ŌĆó All blood samples are subjected to glucose estimation while urine samples are qualitatively tested for glucose.
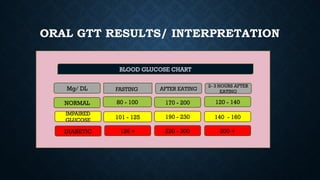
- 10. ORAL GTT RESULT/ INTERPRETATION
- 11. ORAL GTT RESULTS/ INTERPRETATION Mg/ DL AFTER EATING 2- 3 HOURS AFTER EATING BLOOD GLUCOSE CHART NORMAL FASTING 80 - 100 170 - 200 120 - 140 IMPAIRED GLUCOSE 101 - 125 190 - 230 140 - 160 DIABETIC 126 + 220 - 300 200 +
- 13. B. I/V GLUCOSE TOLERANCE TEST ŌĆó This test is undertaken for patients with malabsorption disorders (Celiac Disease or Enteropathies) ŌĆó In such cases glucose cannot be well absorbed ŌĆó The result of GTT becomes inconclusive. ŌĆó It is carried by giving 25 gm of glucose dissolved in 100 ml distilled water as i/v injection within 5 minutes. ŌĆó Completion of infusion takes 0 time. ŌĆó Blood samples are taken at 10 minutes interval for the next hour. ŌĆó The peak value is reached within a few minutes and the value returns to normal in 45- 60 minutes.
- 14. I/V GTT INTERPRETATION ŌĆó In normal individuals blood glucose level returns to normal within 60 minutes. ŌĆó In diabetes mellitus, decline is slow. ŌĆó The initial values are attained in 120 minutes
- 15. FACTORS AFFECTING GTT a) Acute Infections b) Liver Diseases c) Hyperthyroidism ŌĆō There is steep rise in the curve. d) Hypothyroidism ŌĆō A flat curve is obtained in hypothyroidism. THYROID HORMONE increases the absorption of glucose from the gut. e) Starvation
- 16. MINI OR MODERN GTT ŌĆó As per WHO recommendations in Mini GTT minimum 2 samples are collected- a. Fasting (Zero Hour) b. 2 Hour Post glucose load ŌĆó Urine samples are also collected during the same time ŌĆó The diagnosis is made from the difference observed in the two results
- 17. MINI GTT TEST RESULT INTERPRETATION TIME OF SAMPLE COLLECTION NORMAL PERSON CRITERIA FOR DIAGNOSING DIABETES MELLITUS CRITERIA FOR DIAGNOSING IGT FASTING <110 mg/dl <(6.1 mmol/L) >126 mg/dl >(7.0 mmol/L) 110 ŌĆō 126 mg/dl 2 hours after glucose load <140 mg/dl <(7.8 mmol/L) > 200 mg/dl 140 ŌĆō 199 mg/dl
- 18. PRECAUTIONS BEFORE GTT ŌĆó For proper evaluation of the test, the subjects should be normally active and free from acute illness. ŌĆó Medications that may impair glucose tolerance include diuretics, contraceptives drugs, glucocorticoids, niacin and phenytoin should be avoided on that day. CRITERIA FOR DIAGNOSIS OF DIABETES MELLITUS A random plasma glucose concentration ( > 200 mg/dl ) accompanied by classic symptoms of DM ( polyuria, polydipsia, weight loss) is sufficient for the diagnosis of DM.
- 19. THANK YOU