google adword controversy
- 1. GOOGLE ADWORDS & CONSIM CONTROVERSY SUBMITTED BY: RAHUL SONI LL.M. (BUSINESS LAW) ID NO. 530
- 2. STEPS OF RESEARCH Observation Formulation of ‘Idea’ Introduction Consim controversy Conclusions
- 3. OBSERVATION: This paper shall state that the trademark law concerning the internet is unsettled, which increasing trademark infringement and leading to a number of lawsuits. The paper explores such aspects like domain name and adwords in relation to trademark infringement under consim controversy.
- 4. IDEA The internet offers tremendous opportunities to creative businesses to expand their traditional views of marketing. However, due to essential nature of the internet system, which works both on a software system where both temporary copying and storing is a common place, and a domain name based system that is overcrowded, companies must tread carefully when developing marketing strategies for the internet and demonstrate that trademark law concerning the internet is unsettled, and will remain the same for sometime, leading to a number of lawsuits.
- 5. INTRODUCTION: A). GENERAL •Trademarks tie a face to the product. The face is often a name or a symbol, but it can also be a sound or smell or even a ‘look’. • At common law, trademark consisted of a word, phrase, logo, pattern, colour design or other indicator of the source of the product under Section 2(1) (zb). •The purpose of a trademark, traditionally, has been to protect against the confusions to the consumers when selecting the products or services. •Trademarks perform a filtering function for the consumers, wherein they are able to lower the time and cost expended for the search of a product based on the trustworthiness of a producer’s mark.
- 6. B). TRADEMARK INFRINGEMENT & INTERNET Dilution is lessening the capacity of a famous mark to identify and distinguish goods or services. For dilution, following things should be considered by the court: (1)the famousness of a mark, (2) the commercial use of the trademark in the commerce, (3) whether the use began after the mark became famous, (4) whether the use has caused dilution of the distinctive quality of the mark. • David v. Goliath was the first issue before the courts while dealing with the issues of ‘cyber squatting’.
- 7. CONSIM CONTROVRSY: ÔÉòConsim Info, which owns matrimony portal BharatMatrimony.com, filed a trademark infringement case against the internet search company Google and three other matrimony portals Jeevansathi.com, Shaadi.com and SimplyMarry.com in the Madras High Court. WHY? ÔÉòAN INDIAN company has sued Google over what it claims is trademark infringement as it accused the search engine giant of using it's trademark to divert business to the competitors. ÔÉòConsim Info, which runs a number a portal including the popular BharatMatrimony.com has stated that when a user searched for Bharatmatrimony on Google, the search engine dishes up advertisements of the competitors.
- 8. It also said that trademarks are also shown by Google in links from competitors and as such demanded that advertisements of competitors are not shown when words similar to its trademarks are searched. While not denying that Bharatmatrimony might also be benefiting, when users searched for the competitors, Consim said it wants this practice to be stopped. Apart from Google India, Consim Info has also asked People Interactive Pvt Ltd, Jeevansathi Internet Services Pvt Ltd and Times Business Solutions Ltd, to surrender all compact discs, master copies, advertising materials, pamphlets, brochures, etc, which bear Consim’s trademarks and/or any other variants to the company. While the compensation demanded by Consim Info is only Rs. 10.05 lakh, this case might force Google India to change it’s trademark policy.
- 9. GOOGLE: THE LOST FAITH Google relied on the fact that its policy protects the domain name if and only if, the domain name has been registered as a trademark in the respective domestic law of trademarks and a copy of the same has been filed with Google.  But, at the time infringement was alleged, there were no competitive ads for Jet Airways, Microsoft, IBM and many others…  However, the question of domain name being capable of registration as a trademark has been discussed by the Indian courts in several cases before the SC  Hence the issue was of „clear infringement of competitive policy on the internet and protection of goodwill‟. 
- 10. THE GLOBAL PERCEPTIONS USA: Google merely provides neutral tools. Jurin V. Google, 2010. But in Rescuecom Corp. v. Google Inc. , held liable the use of the trademarked word Europe: not infringement, alternative to goods & services. (Article 5 (1)(a) of directive 89/104). Israel: Sponsored linksno illicit advantage that would amount to trademark infringement. Australia: Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC): not trademark infringement. India: restrain from displaying their names in the website in the “Adwords” programme
- 11. Arguments in Favour 1. Prevention of competitive advertising on E-commerce platform like Google. 2. Users did not get distracted or misguide, It save time & money. 3. Trademark is protected even over internet on intangible manner. 4. Internet offers tremendous opportunities to creative businesses to expand their traditional views of marketing like online shopping, payments etc. 5. Trademark act as filtering method which limit the searching capabilities of search engine. 6. Users get limited information, based on the trademark over internet. 7. Territorial effect of Trademark in Search Engine Capabilities.
- 12. Arguments in Against 1. Search engine is like a dictionary, the reference to a certain words in a dictionary, cannot be termed as infringement but in Yahoo!.Inc V. Akash Arora and Anr. 2. Adwords software are available on internet which can prohibit such ads, so it does not limit the search capabilities of search engine. 3. Consim had only obtained registration of a ‚combination‛ of words and accordingly, they cannot claim monopoly over each of the constituent words of the trademark such as ‚tamil‛, ‚telugu‛ and ‚matrimony‛, as these are generic terms and part of the public domain. 4. The competitive bidding over the search results of the search engines involves the democratic enlightenment of the companies. . 5. There is nothing in the Google’s Policy which is against the interest of any company.
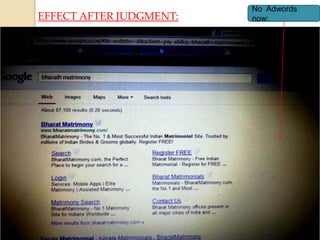
- 13. EFFECT AFTER JUDGMENT: No Adwords now:
- 14. CONCLUSIONS: 1. The trademark law for the e-commerce has not gained maturity and a lot is required to be done in this field in order to combat with the latest upcoming issues. 2. The companies entering the e-commerce should be well prepared and should have necessary information regarding the trends and practices of the same. 3. The Indian community should resort to the issues running in a careful manner in order to protect the trade rights and trade related rights of the corporate houses in order to maintain the democracy in the commerce world and internet arena. 4. The govt may introduce some of the guidelines for the search engines to be adopted while developing national databases so that the display pages do not contravene the economic interests of the companies.