Google search techniques
- 2. Google Search Techniques 1. What is Google? 2. Google Web Search Basics 3. Full-Word Wildcards 4. Special Syntax 5. Special Search
- 3. 1. What is Google? ’é¦ Google is a full-text search engine, which uses computerized "spiders" to index millions, sometimes billions, of pages, allowing for much narrower searches than searchable subject index, which searches only the titles and descriptions of sites, and doesn't search individual pages ’é¦ Google is case-insensitive. If you search for seven, SEVEN, sEvEn, or even 7, you get the same results. ’é¦ Singular is different from plural. Searches for apple and apples turn up different pages ’é¦ The order of words matters. Google considers the first word most important, the second word next, and so on ’é¦ Google ignores most little words, including include "I," "where," "how," "the," "of," "an," "for," "from," "how," 'it," "in," and "is,ŌĆ£. ’é¦ Google search word limit is 32
- 4. ’é¦ Google Alerts - http://www.google.com/alerts - Google Alerts are email updates of the latest relevant Google results (web, news, etc.) based on your choice of query or topic ’é¦ Google News Search ŌĆō http://news.google.com/ ’é¦ Google Blog Search - http://blogsearch.google.com/ ’é¦ Google Book Search - http://books.google.com/ ’é¦ Google Image Search - http://images.google.com/ ’é¦ Google Maps Search - http://maps.google.com/ ’é¦ Google Product Search - http://www.google.com/products ’é¦ Google Scholar Search - http://scholar.google.com ’é¦ Google Group Search - http://groups.google.com ’é¦ Google Video Search - http://video.google.com/
- 5. ’é¦ Google Mobile - http://www.google.com/mobile/ ’é¦ Google Earth - http://earth.google.com/ ’é¦ Google Finance - http://finance.google.com/ ’é¦ Google Blog - http://www.blogger.com ’é¦ Google Photo - http://picasaweb.google.com ’é¦ Google Language Tools - http://www.google.com/language_tools ’é¦ Google Pack - http://pack.google.com ’é¦ Google Gmail - http://gmail.google.com ’é¦ And more on Google Labs - http://labs.google.com/
- 6. 2. Google Web Search Basics 1. Phrase Searches ’é¦ Enter key words search techniques. Google will find matches where the keywords appear anywhere on the page ’é¦ If you want Google to find you matches where the keywords appear together as a phrase, surround them with quotes, like this ŌĆ£search techniquesŌĆØ 2. Basic Boolean ’é¦ Google's Boolean default is AND, which means that if you enter query words without modifiers, Google will search for all your query words ’é¦ If you prefer to specify that any one word or phrase is acceptable, put an OR (in capital letter), lower case or wonŌĆÖt work correctly. For example: enter Yahoo OR Google. ’é¦ A computer programming character | can work like OR (e.g. Yahoo | Google) ’é¦ If you want to search for a particular term along with two or more other terms, group the other terms within parentheses, like so ŌĆ£search techniquesŌĆØ (Yahoo OR Google)
- 7. 3. Negation ’é¦ If you want to specify that a query item must not appear in your results, prepend a (minus sign or dash): ŌĆ£search techniquesŌĆØ ŌĆōGoogle. This will search the pages that contain ŌĆ£search techniquesŌĆØ, but not the word Google ’é¦ Note that the symbol must appear directly before the word or phrase that you don't want. If there's space between, as in the following query, it won't work as expected ŌĆ£search techniquesŌĆØ ŌĆō Google 4. Explicit Inclusion ’é¦ Google will search for all the keywords and phrases that you specify, however, there are certain words that Google will ignore because they are considered too common to be of any use in the search (e.g. ŌĆ£aŌĆØ, ŌĆ£theŌĆØ, ŌĆ£ofŌĆØ, etc.) ’é¦ You can force Google to take a stop word into account by prepending a + (plus) character, as in +the ŌĆ£search techniquesŌĆØ.
- 8. 5. Synonyms ’é¦ The Google synonym operator, the ~ (tilde) character, prepended to any number of keywords in your query, asks Google to include not only exact matches, but also what it thinks are synonyms for each of the keywords. Searching for: ~ape turns up results for monkey, gorilla, chimpanzee, and others (both singular and plural forms) of the ape or related family, as if you'd searched for: monkey gorilla chimpanzee (Synonyms are bolded along with exact keyword matches on the results page, so they're easy to spot) 6. Number Range ’é¦ The number range operator, .. (two periods), looks for results that fall inside your specified numeric range (e.g. digital camera 3..5 megapixel $800..$1000) ’é¦ You can also use the number range syntax with just one number, making it the minimum or maximum of your query (e.g. digital camera ..5 megapixel $800..)
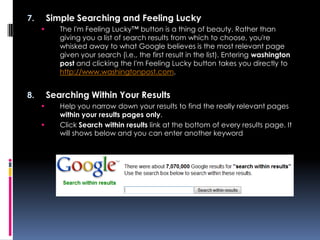
- 9. 7. Simple Searching and Feeling Lucky ’é¦ The I'm Feeling LuckyŌäó button is a thing of beauty. Rather than giving you a list of search results from which to choose, you're whisked away to what Google believes is the most relevant page given your search (i.e., the first result in the list). Entering washington post and clicking the I'm Feeling Lucky button takes you directly to http://www.washingtonpost.com. 8. Searching Within Your Results ’é¦ Help you narrow down your results to find the really relevant pages within your results pages only. ’é¦ Click Search within results link at the bottom of every results page. It will shows below and you can enter another keyword
- 10. 3. Full-Word Wildcards ’é¦ the wildcard will act as a substitute for one full word. Searching for sevEN* mice, therefore, finds three blind mice, 7 blue mice, sevengreen mice, etc. ’é¦ * is a stand-in for one word; ** signifies two words, and so on
- 11. 4. Special Syntax ’é¦ site: allows you to narrow your search by a site or by a top-level domain ’é¦ site:org ’é¦ inurl: restricts your search to the URLs of web pages. This syntax usually works well for finding search and help pages because they tend to be regular in composition. An allinurl: variation finds all the words listed in a URL ’é¦ inurl:virus ’é¦ link: returns a list of pages that link to the specified URL. Enter link:www.google.com and you'll get a list of pages that link to the Google home page, http://www.google.com (not anywhere in the google.com domain) ’é¦ cache: finds a copy of the page that Google indexed even if that page is no longer available at its original URL or has since changed its content completely
- 12. ’é¦ filetype: searches the suffixes or filename extensions ’é¦ "leading economic indicators" filetype:doc , filetype:ppt ’é¦ related: , as you might expect, finds pages that are related to the specified page. This is a good way to find categories of pages; a search for related:google.com returns a variety of search engines, including Lycos, Yahoo!, and Northern Light ’é¦ info:www.nytimes.com/technology ’é¦ phonebook: , as you might expect, looks up phone numbers ’é¦ phonebook:(510) 555-1212 or phonebook: <name> ’é¦ define: gives you a page full of definitions of a word from around the Web ’é¦ movie: syntax to find reviews of movies on the Web ’é¦ music: explicitly searches for music-related information
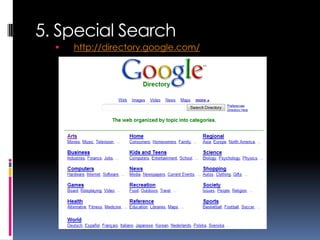
- 13. 5. Special Search ’é¦ http://directory.google.com/
- 14. Thanks Nirav