Granulation
- 1. G RANULATION I RAHUL SINGOUR Formulation & Development
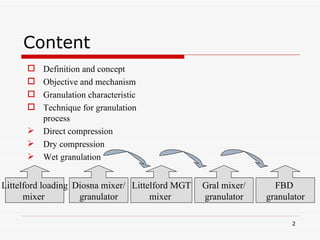
- 2. Content Definition and concept Objective and mechanism Granulation characteristic Technique for granulation process Direct compression Dry compression Wet granulation Littelford loading mixer Diosna mixer/ granulator Littelford MGT mixer Gral mixer/ granulator FBD granulator
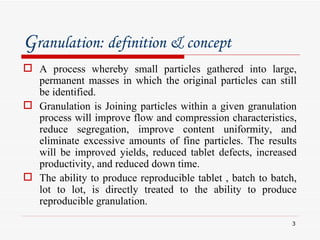
- 3. G ranulation: definition & concept A process whereby small particles gathered into large, permanent masses in which the original particles can still be identified. Granulation is Joining particles within a given granulation process will improve flow and compression characteristics, reduce segregation, improve content uniformity, and eliminate excessive amounts of fine particles. The results will be improved yields, reduced tablet defects, increased productivity, and reduced down time. The ability to produce reproducible tablet , batch to batch, lot to lot, is directly treated to the ability to produce reproducible granulation.
- 4. O bjective & mechanism The objective of the granulation process is to combine ingredients to produce a quality tablet. Granulation is process of collecting particles together by creating bonds between then and these bonds are formed by compression or by using a binding agent. Particles-particles bonding mechanisms involved in adhesion and cohesion of particles. Several forces that can be act : Valency, Van der waals forces and electrostatic forces. In wet granulation Liquid bridges developed between particles with tensile strength. Surface tension forces and capillary pressure are primarily responsible for initial granulation and strength.
- 5. mechanism Nucleation: Here, the particles adhere due to liquid bridges which are the initiation step of Granulation. These adhered particles play a role of nucleus for further enlargement of granules. Transition: Enlargement of nucleus takes place by two possible mechanisms. Individual particle adhere to the nucleus or two or more nuclei combine among themselves. Ball growth or enlargement of the granule
- 6. G ranules characteristic Particle size Av. Tablet weight Tablet weight variation Disintegration (DT) Granules friability Granules flow ability Dry rate kinetic of wet granules Surface area Dissolution rate Methods: Gas adsorption Air permeability Density Compressibility Tablet porosity Dissolution and other
- 7. G ranules characteristic Dense and hard granules decreasing DT and dissolution rate Higher compression load Less friability Bulk density largely depend on particle shape More spherical particle have higher density Increasing granules size then decreasing bulk density Smaller granules size are able to close packing
- 8. G ranules characteristicâĶâĶ.. Strength and friability Depend on- Granulating agent Granulator Effect on- Particle size Compressibility Flow properties Friction force Surface tension Mechanical force Electrostatic Cohesive force Method Response angle Hopper flow rate Larger granules possess more strength the smaller ones. Mixing time is increase, strength also increased.
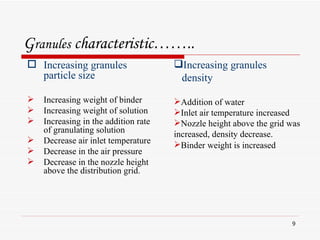
- 9. G ranules characteristicâĶâĶ.. Increasing granules particle size Increasing weight of binder Increasing weight of solution Increasing in the addition rate of granulating solution Decrease air inlet temperature Decrease in the air pressure Decrease in the nozzle height above the distribution grid. Increasing granules density Addition of water Inlet air temperature increased Nozzle height above the grid was increased, density decrease. Binder weight is increased
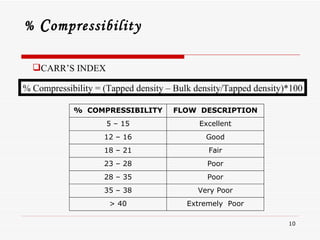
- 10. % C ompressibility CARRâS INDEX % Compressibility = (Tapped density â Bulk density/Tapped density)*100 % COMPRESSIBILITY FLOW DESCRIPTION 5 â 15 Excellent 12 â 16 Good 18 â 21 Fair 23 â 28 Poor 28 â 35 Poor 35 â 38 Very Poor > 40 Extremely Poor
- 11. F low Properties HAUSNER RATIO ANGLE OF REPOSE Hausner Ratio = Tapped Density / Bulk Density ÎĶ = tan-1 (h / r) HAUSNER RATIO TYPE OF FLOW Less than 1.25 Good Flow 1.25 â 1.5 Moderate More than 1.5 Poor Flow ANGLE OF REPOSE TYPE OF FLOW < 25 Excellent 25 â 30 Good 30 â 40 Passable > 40 Very Poor
- 12. T echniques for granulation process Three basic techniques are used to prepare powders for compression into a tablet: Direct compression Dry compression & Wet granulation
- 13. B asic processing step of granulation
- 14. D irect compression This method is used when a group of ingredient can be blended and placed in a tablet press to make a tablet without any of the ingredients having to be changed. Crystalline API Direct compressible diluent Limitation Low dose API, poor content uniformity High dose API which not easily compress, then it require usually restricted to about 30 % of direct compression formula hence tablet will costly and difficult to swallow. Direct compression diluent may interact with the API. Because of the dry nature of direct compression, static charge developed then cause uniform distribution.
- 15. C ompression granulation This process is used when the product needed to be granulated may be sensitive to moisture and heat. Dry granulation can be conducted on a pres using slugging tooling or on a roller compactor commonly referred to as a chilsonator. The initial bland of powders is forced into the die of a large-capacity tablet press and is compacted by means of flat-faced punches, the compacted mass called slugs and the process is referred to asâSluggingâ. Effective dose too high Moisture and heat sensitive material (API) e.g. Aspirin, Vitamins
- 17. r oller compactorâĶ. The compaction force of the roller compactor is controlled by three variable The hydraulic pressure exerted on the compaction roller, The rotational speed of the compaction rolls, The rotational speed of the feed screws. Advantages Increased production capacity Greater control of compaction pressure Dwell time and no need for excessive lubrication of the powder.
- 18. W et granulation Wet granulation form the granules by binding the powder together with an adhesive, instead of by compaction. Binder may have different form Solution Suspension Slurry Binder depends on Solubility (aqueous or non-aqueous solution) Component mixture When small quantity is permissible, then binder is blended in dry powder initially. In large quantity is refried, then binder is usually dissolved in liquid.
- 19. W et granulationâĶâĶâĶ. LIQUID PLAY A KEY ROLE Granules strength increased with addition of liquid. Granules formation and strength depend: Surface tension force Capillary pressure. Length of time depends on: Wetting properties of powder mix. Granulation fluid. Efficiency of granulator (RMG > PLM) End point determination Amount of water used to granulate is increase. Granules porosity decrease, and granules strength increased.
- 20. G ranulator for wet granulation These type of granulators are applicable: Littleford loading mixer Diosna (RMG type) Littleford MGT Gral mixer/granulator (modified industrial planetary mixer) Fluid bed granulator
- 21. L ittleford Loding mixer First high shear powder blender capable of rapidly pharmaceutical powder and wet massing The equipment may also capable of producing agglomerated granular particles that are ready for fluid bed or other drying methods. Time 30-60 sec. Temperature rise 10-15 0 C Plow-shaped mixing tools Chopper blades Spray nozzles Horizontal cylindrical shell
- 22. L ittleford
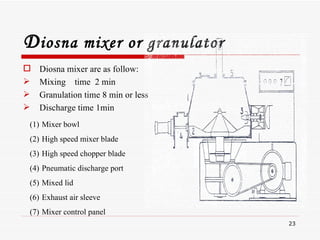
- 23. Diosna mixer are as follow: Mixing time 2 min Granulation time 8 min or less Discharge time 1min D iosna mixer or granulator Mixer bowl High speed mixer blade High speed chopper blade Pneumatic discharge port Mixed lid Exhaust air sleeve Mixer control panel
- 24. mixer blade chopper blade Mixer bowl Uniform distribution of all formulation ingredients. Short mixing and granulation time. Useful working capacity of upto 80% to 40% of bowl volume. Uniform granules by gentle processing. Wide range of applications. Easy scale up & Scale down between machine sizes. Bowl shape design to have no dead spaces. D iosna mixer or granulatorâĶâĶâĶ..
- 25. L ittleford MGT mixer-granulator Bowl Lid with counter weight Exhaust sleeve Discharge port Control panel
- 26. G ral mixer-granulator Mixing arm Bowl Chopper blade Bowl cover Hydraulic discharge port Mixer controller panel Bowl elevator cradle 1 2 Modification of industrial planetary mixer
- 28. D ifference between Gral and Planetary mixer Having two mixing device Provide large scale mixing motion on the powder Small chopper blade enter off center Advantage Hydraulic discharged part more effective Easily clear because mixing blade is not part of the bowl.
- 29. F luid Bed Granulation Homogeneous granules. Gentle product handling. Intensive mixing of the solid material. Uniform spraying of all particles in the fluid bed. Uniform, reproducible product quality.
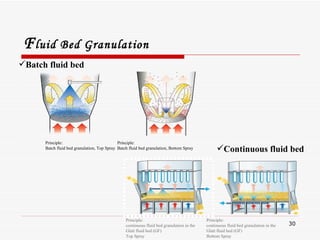
- 30. F luid Bed Granulation Principle: Batch fluid bed granulation, Top Spray Principle: Batch fluid bed granulation, Bottom Spray Batch fluid bed Continuous fluid bed Principle: continuous fluid bed granulation in the Glatt fluid bed (GF) Top Spray Principle: continuous fluid bed granulation in the Glatt fluid bed (GF) Bottom Spray
- 31. R eferences Lachman L., Lieberman H.A., and Kanig J.L. The theory and practice of industrial pahrmacy. Thired edition; Varghese publishing house , Bombay; 1991. Lieberman H.A. and Lachman L. Pharmaceutical dosage forms: tablet. Vol 1; Marcel Dekker , INC. New York; 1980. Lieberman H.A. and Lachman L. Pharmaceutical dosage forms: tablet. Vol 2; Marcel Dekker , INC. New York; 1980. Tousey M.D. The granulation process 101 âBasic technologies for tablet makingâ. Pharmaceutical technology tableting and granulation; 2002. http:// www.mcc-online.com/ granulation .htm http://www.pharmpedia.com/Tablet:Formulation_of_tablets/Binders
- 32. G ranulation I I Excipients of granulation and selection criteria Factor affecting granulation Selection criteria of granulation technique Example of different critical API granulation Granulation technique of Floating tablet and others. To be continuedâĶ!!
- 33. thanks
Editor's Notes
- ARISTO PHARMA PVT LTD
- ARISTO PHARMA PVT LTD