Graphs Changes States in States Secundary School
- 1. Changes of State Do now activity: 1. What are three states of matter? 2. What is the law of the conservation of mass? 3. Explain what happens to the particles found within an ice cube when the ice cube is placed in a mug of warm water.
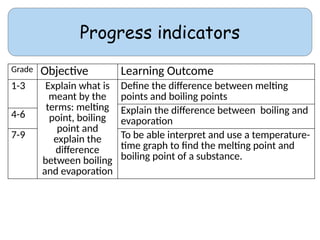
- 2. Progress indicators Grade Objective Learning Outcome 1-3 Explain what is meant by the terms: melting point, boiling point and explain the difference between boiling and evaporation Define the difference between melting points and boiling points Explain the difference between boiling and evaporation 4-6 7-9 To be able interpret and use a temperature- time graph to find the melting point and boiling point of a substance.
- 3. For any substance undergoing a change of state, it¡¯s temperature stays the same whilst the change of state is taking place. ? The temperature at which a solid changes to a liquid is called the ¡.. ? The temperature at which a liquid turns to a gas is called the ¡ ? The temperature at which a liquid changes to a solid is called its ¡ Melting point Boiling point Freezing point Which two temperatures will always be the same?
- 4. Why do you think salt is added to a pan of water you want to boil? Or salt is added to roads or paths to stop them from freezing over? Impurities in a substance can affect the melting point and boiling point of that substance, for example the melting point of water is lowered if you add salt to the water.
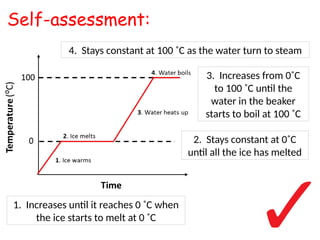
- 5. ? Stays constant at 0?C until all the ice has melted ? Increases from 0?C to 100 ?C until the water in the beaker starts to boil at 100 ?C ? Increases until it reaches 0 ?C when the ice starts to melt at 0 ?C ? Stays constant at 100 ?C as the water turn to steam Task: There are four points labelled on the graph opposite, sketch the graph in your books and order the statements above to match the numbers. Temperature (?C) Time 100 0 1. Ice warms 2. Ice melts 3. Water heats up 4. Water boils
- 6. 1. Increases until it reaches 0 ?C when the ice starts to melt at 0 ?C 2. Stays constant at 0?C until all the ice has melted 3. Increases from 0?C to 100 ?C until the water in the beaker starts to boil at 100 ?C 4. Stays constant at 100 ?C as the water turn to steam Self-assessment:
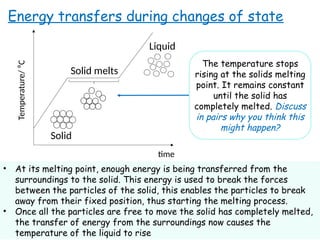
- 7. time Temperature/ ?C Solid Energy transfers during changes of state Solid melts Liquid The temperature stops rising at the solids melting point. It remains constant until the solid has completely melted. Discuss in pairs why you think this might happen? ? At its melting point, enough energy is being transferred from the surroundings to the solid. This energy is used to break the forces between the particles of the solid, this enables the particles to break away from their fixed position, thus starting the melting process. ? Once all the particles are free to move the solid has completely melted, the transfer of energy from the surroundings now causes the temperature of the liquid to rise
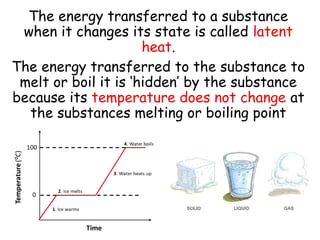
- 8. The energy transferred to a substance when it changes its state is called latent heat. The energy transferred to the substance to melt or boil it is ¡®hidden¡¯ by the substance because its temperature does not change at the substances melting or boiling point
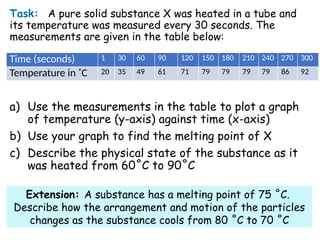
- 9. Task: A pure solid substance X was heated in a tube and its temperature was measured every 30 seconds. The measurements are given in the table below: a) Use the measurements in the table to plot a graph of temperature (y-axis) against time (x-axis) b) Use your graph to find the melting point of X c) Describe the physical state of the substance as it was heated from 60?C to 90?C Time (seconds) 1 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 Temperature in ?C 20 35 49 61 71 79 79 79 79 86 92 Extension: A substance has a melting point of 75 ?C. Describe how the arrangement and motion of the particles changes as the substance cools from 80 ?C to 70 ?C
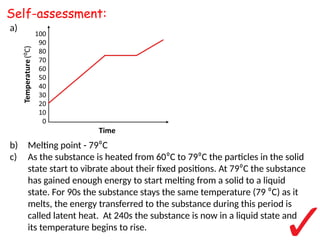
- 10. a) b) Melting point - 79?C c) As the substance is heated from 60?C to 79?C the particles in the solid state start to vibrate about their fixed positions. At 79?C the substance has gained enough energy to start melting from a solid to a liquid state. For 90s the substance stays the same temperature (79 ?C) as it melts, the energy transferred to the substance during this period is called latent heat. At 240s the substance is now in a liquid state and its temperature begins to rise. Self-assessment:
- 11. Exam-style Question Task: Use your knowledge of what you have learned this lesson to complete the exam-style question.
- 12. Mark Scheme: AB ? Changing state from a solid to a liquid / melting 1 ? At a steady temperature 1 BC ? Temperature of liquid rises 1 ? Until it reaches boiling point 1
- 13. Plenary ~ Pick a task: Summarise what you have learnt today in 3 sentences Write a definition for the following key words: a) Vaporisation b) Density c) Freezing d) Latent heat e) Melting point