GREEN SKILLS.pptx
- 1. GREEN SKILLS Vegetation is the basic instrument the creator uses to set all of nature in motion. Jitendra Kumar Yadav DAV Public School, Gumla
- 2. MEANING OF GREEN SKILLS The knowledge, abilities, values and attitudes needed to live in, develop and support a sustainable and resource-efficient society.
- 3. ENVIRONMENT 3 A sum total of all the living and non-living elements and their effects which influence human life.
- 4. ENVIRONMENT… 4 It is composed of living things and non living-things. Living things: Flora & Fauna Non-Living things: Lithosphere, Hydrosphere, Atmosphere & Biosphere
- 5. THE LITHOSPHERE Litho referring to rocks and minerals • It is believed the lithosphere evolved about 4.6 billion years ago. • It refers to the solid, rocky crust that covers the entire planet. • This solid, rocky crust is composed of- • Metamorphic rocks • Igneous rocks • Sedimentary rocks 5
- 6. THE HYDROSPHERE Hydro referring to water • It refers to the most important resource which is water. • It includes all forms of water in the Earth’s environment. • The forms of water include things such as the ocean, lakes, rivers, snow and glaciers, water underneath the earth’s surface and even the water vapour that is found in the atmosphere. 6
- 7. THE ATMOSPHERE Atmo referring to steam and vapor • It refers to the air that surrounds the earth. • It is always in motion and constantly changing. • It’s believed that there are about 14 different gases that make up the atmosphere. (78 percent nitrogen, 21 percent oxygen, 0.9 percent argon, and 0.1 percent other gases.) • The atmosphere is also responsible for the weather as the weather occurs within the lower atmosphere. 7
- 8. THE BIOSPHERE Bio referring to life • It is composed of all living organisms, including; plants and animals. • It is believed that all life exists in the biosphere. • Most of the living organisms are found from up to three meters below ground to thirty meters above it and also in the to 200 meters of the ocean and seas. • The biosphere could not survive if it wasn't for the other spheres as all organisms need water from the hydrosphere, minerals for the lithosphere and gases from the atmosphere. 8
- 9. 9
- 10. SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT Development that is conducted without depletion of natural resources. SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS: • 17 goals have been announced by the United Nations, termed as the Sustainable Development Goals(SDGs). • The aim is to achieve these goals by the end of 2030. • A pledge to do so has been taken by all the member nations of the UN. 10
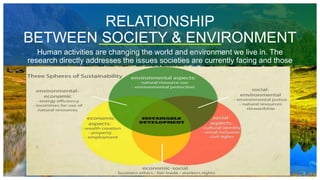
- 14. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN SOCIETY & ENVIRONMENT Human activities are changing the world and environment we live in. The research directly addresses the issues societies are currently facing and those they are likely to face in the future. 14
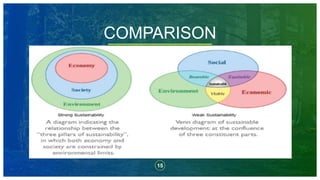
- 15. COMPARISON Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Maecenas porttitor congue massa Section 1 Title • Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Maecenas porttitor congue massa. Fusce posuere, magna sed pulvinar ultricies, purus lectus malesuada libero • Nunc viverra imperdiet enim. Fusce est. Vivamus a tellus. • Pellentesque habitant morbi tristique senectus et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas. Proin pharetra nonummy pede. Mauris et orci. Section 2 Title • Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Maecenas porttitor congue massa. Fusce posuere, magna sed pulvinar ultricies, purus lectus malesuada libero, sit amet commodo magna eros quis urna. • Nunc viverra imperdiet enim. Fusce est. Vivamus a tellus. • Pellentesque habitant morbi tristique senectus et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas. Proin pharetra nonummy pede 15
- 16. ECOLOGICAL IMBALANCE A situation when natural or man-made disturbances affect the natural balance of an ecosystem. 16 FACTORS: 1. Deforestation 2. Soil Erosion 3. Overexploitation of Resources 4. Environmental Pollution 5. Irregular Land Use 6. E-Waste
- 17. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Maecenas porttitor congue massa. Fusce posuere $0 $10,000 $20,000 $30,000 $40,000 $50,000 20XX 20XX 20XX 20XX 20XX ADD A FOOTER 17 Deforestation
- 18. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Maecenas porttitor congue massa. Fusce posuere $0 $10,000 $20,000 $30,000 $40,000 $50,000 20XX 20XX 20XX 20XX 20XX ADD A FOOTER 18 Soil Erosion
- 19. Category 1 Category 2 Category 3 Subject 1 50,000 400,000 1,600,000 Subject 2 500,000 4,000,000 16,000,000 Subject 3 75 80 90 Subject 4 5,625,000 48,000,000 216,000,000 Subject 5 0 0 0 Subject 6 5,625,000 48,000,000 216,000,000 Subject 7 1,687,500 9,600,000 21,600,000 Subject 8 562,500 2,400,000 10,800,000 Subject 9 281,250 2,400,000 4,320,000 Subject 10 7,593,750 52,800,000 187,920,000 TABLE SLIDE Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Maecenas porttitor congue massa ADD A FOOTER 19 Overexploitation of Resources
- 20. BIG IMAGE SLIDE Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit ADD A FOOTER 20
- 21. VIDEO SLIDE ADD A FOOTER 21 E-Waste
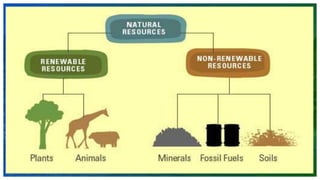
- 23. Conservation of Natural Resources “One person alone cannot save the planet’s biodiversity, but each individual’s effort to encourage nature’s wealth must not be underestimated.”- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
- 24. Air Conservation The conservation of air is the protection and cleaning of the earth's air supply. Air pollution can be caused by any number of sources, including transportation, power plants, and factories. This pollution can cause a number of health problems, so it is important to practice air conservation when possible.
- 25. Water Conservation Water conservation includes all the policies, strategies and activities to sustainably manage the natural resource of fresh water, to protect the hydrosphere, and to meet the current and future human demand (thus avoiding water scarcity). Population, household size and growth and affluence all affect how much water is used.
- 26. Energy Conservation Energy conservation is the effort to reduce wasteful energy consumption by using fewer energy services. This can be achieved by using energy more efficiently (using less energy for a constant service) or through behavioral changes that reduce the amount of service used (for example, by driving less). Energy efficiency is a means of achieving energy conservation; it provides different benefits, from minimizing the number of greenhouse gases, reducing the carbon footprint, and saving water,
- 27. The 4R Mindset
- 28. GREEN ECONOMY • Green Economy is defined as an economic system that is entirely focused on the concept of “green”. • A type of economy that advocates a macroeconomic approach, the investments and employment model, in this economy is based on green finance, green investments, and social equality.
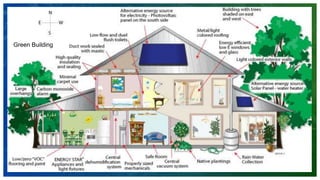
- 29. SECTORS OF GREEN ECONOMY 1. Green Buildings 2. Sustainable Agriculture & Forests 3. Renewable Energy 4. Green Transport Systems 5. Clean Technologies 6. Water Services 7. Waste Management
- 30. Customize this Template Template Editing Instructions and Feedback ADD A FOOTER 30 Green Building
- 31. THANK YOU!